mirror of
https://gitee.com/mirrors/Spring-Cloud-Alibaba.git
synced 2021-06-26 13:25:11 +08:00
Merge branch '1.x' of https://github.com/spring-cloud-incubator/spring-cloud-alibabacloud into 1.x
This commit is contained in:
@@ -0,0 +1,53 @@
|
||||
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
|
||||
<project xmlns="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
|
||||
xsi:schemaLocation="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0 http://maven.apache.org/xsd/maven-4.0.0.xsd">
|
||||
|
||||
<parent>
|
||||
<groupId>org.springframework.cloud</groupId>
|
||||
<artifactId>spring-cloud-alibaba-examples</artifactId>
|
||||
<version>0.1.0.BUILD-SNAPSHOT</version>
|
||||
<relativePath>../../pom.xml</relativePath>
|
||||
</parent>
|
||||
<modelVersion>4.0.0</modelVersion>
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
<artifactId>nacos-config-example</artifactId>
|
||||
<packaging>jar</packaging>
|
||||
<description>Example demonstrating how to use nacos config</description>
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
<dependencies>
|
||||
<dependency>
|
||||
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
|
||||
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-web</artifactId>
|
||||
</dependency>
|
||||
<dependency>
|
||||
<groupId>org.springframework.cloud</groupId>
|
||||
<artifactId>spring-cloud-starter-alibaba-nacos-config</artifactId>
|
||||
</dependency>
|
||||
|
||||
<dependency>
|
||||
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
|
||||
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-actuator</artifactId>
|
||||
</dependency>
|
||||
|
||||
</dependencies>
|
||||
|
||||
<build>
|
||||
<plugins>
|
||||
<plugin>
|
||||
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
|
||||
<artifactId>spring-boot-maven-plugin</artifactId>
|
||||
</plugin>
|
||||
<plugin>
|
||||
<groupId>org.apache.maven.plugins</groupId>
|
||||
<artifactId>maven-deploy-plugin</artifactId>
|
||||
<version>${maven-deploy-plugin.version}</version>
|
||||
<configuration>
|
||||
<skip>true</skip>
|
||||
</configuration>
|
||||
</plugin>
|
||||
</plugins>
|
||||
</build>
|
||||
|
||||
</project>
|
||||
@@ -0,0 +1,187 @@
|
||||
# Nacos Config Example
|
||||
|
||||
## 项目说明
|
||||
|
||||
本项目演示如何使用 Nacos Config Starter 完成 Spring Cloud 应用的配置管理。
|
||||
|
||||
[Nacos](https://github.com/alibaba/Nacos) 是阿里巴巴开源的一个更易于构建云原生应用的动态服务发现、配置管理和服务管理平台。
|
||||
|
||||
## 示例
|
||||
|
||||
### 如何接入
|
||||
在启动示例进行演示之前,我们先了解一下 Spring Cloud 应用如何接入 Nacos Config。
|
||||
**注意 本章节只是为了便于您理解接入方式,本示例代码中已经完成接入工作,您无需再进行修改。**
|
||||
|
||||
1. 首先,修改 pom.xml 文件,引入 Nacos Config Starter。
|
||||
|
||||
<dependency>
|
||||
<groupId>org.springframework.cloud</groupId>
|
||||
<artifactId>spring-cloud-starter-alibaba-nacos-config</artifactId>
|
||||
</dependency>
|
||||
|
||||
2. 在应用的 /src/main/resources/bootstrap.properties 配置文件中配置 Nacos Config 地址
|
||||
|
||||
spring.cloud.nacos.config.server-addr=127.0.0.1:8080
|
||||
|
||||
3. 完成上述两步后,应用会从 Nacos Config 中获取相应的配置,并添加在 Spring Environment 的 PropertySources 中。这里我们使用 @Value 注解来将对应的配置注入到 SampleController 的 userName 和 age 字段,并添加 @RefreshScope 打开动态刷新功能
|
||||
|
||||
@RefreshScope
|
||||
class SampleController {
|
||||
|
||||
@Value("${user.name}")
|
||||
String userName;
|
||||
|
||||
@Value("${user.age}")
|
||||
int age;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
### 启动 Nacos Server 并添加配置
|
||||
|
||||
1. 首先需要获取 Nacos Server,支持直接下载和源码构建两种方式。**推荐使用最新版本 Nacos Server**
|
||||
|
||||
1. 直接下载:[Nacos Server 下载页](https://github.com/alibaba/nacos/releases)
|
||||
2. 源码构建:进入 Nacos [Github 项目页面](https://github.com/alibaba/nacos),将代码 git clone 到本地自行编译打包,[参考此文档](https://nacos.io/zh-cn/docs/quick-start.html)。
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
2. 启动 Server,进入下载到本地并解压完成后的文件夹(使用源码构建的方式则进入编译打包好的文件夹),再进去其相对文件夹 nacos/bin,并对照操作系统实际情况执行如下命令。[详情参考此文档](https://nacos.io/zh-cn/docs/quick-start.html)。
|
||||
|
||||
1. Linux/Unix/Mac 操作系统,执行命令 `sh startup.sh -m standalone`
|
||||
1. Windows 操作系统,执行命令 `cmd startup.cmd`
|
||||
|
||||
3. 在命令行执行如下命令,向 Nacos Server 中添加一条配置。
|
||||
|
||||
curl -X POST "http://127.0.0.1:8080/nacos/v1/cs/configs?dataId=nacos-config-example.properties&group=DEFAULT_GROUP&content=user.id=1%0Auser.name=james%0Auser.age=17"
|
||||
|
||||
**注:你也可以使用其他方式添加,遵循 HTTP API 规范即可,若您使用的 Nacos 版本自带控制台,建议直接使用控制台进行配置**
|
||||
|
||||
添加的配置的详情如下
|
||||
|
||||
dataId 为 nacos-config-example.properties
|
||||
group 为 DEFAULT_GROUP
|
||||
|
||||
内容如下
|
||||
|
||||
user.id=1
|
||||
user.name=james
|
||||
user.age=17
|
||||
|
||||
### 应用启动
|
||||
|
||||
1. 增加配置,在应用的 /src/main/resources/application.properties 中添加基本配置信息
|
||||
|
||||
spring.application.name=nacos-config-example
|
||||
server.port=18084
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
2. 启动应用,支持 IDE 直接启动和编译打包后启动。
|
||||
|
||||
1. IDE直接启动:找到主类 `Application`,执行 main 方法启动应用。
|
||||
2. 打包编译后启动:首先执行 `mvn clean package` 将工程编译打包,然后执行 `java -jar nacos-config-example.jar`启动应用。
|
||||
|
||||
### 验证
|
||||
|
||||
#### 验证自动注入
|
||||
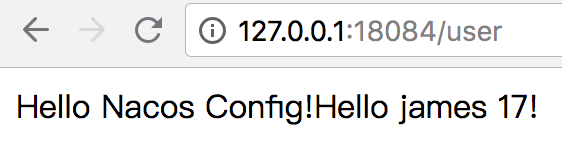
在浏览器地址栏输入 `http://127.0.0.1:18084/user`,并点击调转,可以看到成功从 Nacos Config Server 中获取了数据。
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
#### 验证动态刷新
|
||||
1. 执行如下命令,修改 Nacos Server 端的配置数据
|
||||
|
||||
curl -X POST "http://127.0.0.1:8080/nacos/v1/cs/configs?dataId=nacos-config-example.properties&group=DEFAULT_GROUP&content=user.id=1%0Auser.name=james%0Auser.age=18"
|
||||
|
||||
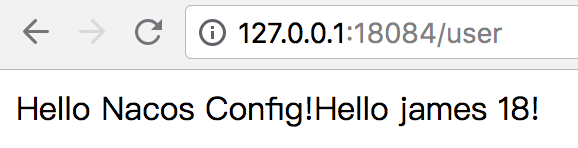
2. 在浏览器地址栏输入 `http://127.0.0.1:18084/user`,并点击调转,可以看到应用从 Nacos Server 中获取了最新的数据,age 变成了 18。
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
## 原理
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
### Nacos Config 数据结构
|
||||
|
||||
Nacos Config 主要通过 dataId 和 group 来唯一确定一条配置,我们假定你已经了解此背景。如果不了解,请参考 [Nacos 文档](https://nacos.io/zh-cn/docs/concepts.html)。
|
||||
|
||||
Nacos Client 从 Nacos Server 端获取数据时,调用的是此接口 `ConfigService.getConfig(String dataId, String group, long timeoutMs)`。
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
### Spring Cloud 应用获取数据
|
||||
|
||||
#### dataID
|
||||
|
||||
在 Nacos Config Starter 中,dataId 的拼接格式如下
|
||||
|
||||
${prefix} - ${spring.active.profile} . ${content-type}
|
||||
|
||||
* `prefix` 默认为 `spring.application.name` 的值,也可以通过配置项 `spring.cloud.nacos.config.prefix`来配置。
|
||||
|
||||
* `spring.active.profile` 即为当前环境对应的 profile,详情可以参考 [Spring Boot文档](https://docs.spring.io/spring-boot/docs/current/reference/html/boot-features-profiles.html#boot-features-profiles)
|
||||
|
||||
**注意,当 activeprofile 为空时,对应的连接符 `-` 也将不存在,dataId 的拼接格式变成 `${prefix}`.`${context.type}`**
|
||||
|
||||
* `content-type` 为配置内容的数据格式,可以通过配置项 `spring.cloud.nacos.config.content-type`来配置。
|
||||
目前只支持 `properties` 类型。
|
||||
|
||||
#### group
|
||||
* `group` 默认为 `DEFAULT_GROUP`,可以通过 `spring.cloud.nacos.config.group` 配置。
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
### 自动注入
|
||||
Nacos Config Starter 实现了 `org.springframework.cloud.bootstrap.config.PropertySourceLocator`接口,并将优先级设置成了最高。
|
||||
|
||||
在 Spring Cloud 应用启动阶段,会主动从 Nacos Server 端获取对应的数据,并将获取到的数据转换成 PropertySource 且注入到 Environment 的 PropertySources 属性中,所以使用 @Value 注解也能直接获取 Nacos Server 端配置的内容。
|
||||
|
||||
### 动态刷新
|
||||
|
||||
Nacos Config Starter 默认为所有获取数据成功的 Nacos 的配置项添加了监听功能,在监听到服务端配置发生变化时会实时触发 `org.springframework.cloud.context.refresh.ContextRefresher` 的 refresh 方法 。
|
||||
|
||||
如果需要对 Bean 进行动态刷新,请参照 Spring 和 Spring Cloud 规范。推荐给类添加 `@RefreshScope` 或 `@ConfigurationProperties ` 注解,
|
||||
|
||||
更多详情请参考 [ContextRefresher Java Doc](http://static.javadoc.io/org.springframework.cloud/spring-cloud-context/2.0.0.RELEASE/org/springframework/cloud/context/refresh/ContextRefresher.html)。
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
## Endpoint 信息查看
|
||||
|
||||
Spring Boot 应用支持通过 Endpoint 来暴露相关信息,Nacos Config Starter 也支持这一点。
|
||||
|
||||
在使用之前需要在 maven 中添加 `spring-boot-starter-actuator`依赖,并在配置中允许 Endpoints 的访问。
|
||||
|
||||
* Spring Boot 1.x 中添加配置 management.security.enabled=false
|
||||
* Spring Boot 2.x 中添加配置 management.endpoints.web.exposure.include=*
|
||||
|
||||
Spring Boot 1.x 可以通过访问 http://127.0.0.1:18084/nacos_config 来查看 Nacos Endpoint 的信息。
|
||||
|
||||
Spring Boot 2.x 可以通过访问 http://127.0.0.1:18084/actuator/nacos-config 来访问。
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
如上图所示,Sources 表示此客户端从哪些 Nacos Config 配置项中获取了信息,RefreshHistory 表示动态刷新的历史记录,最多保存20条,NacosConfigProperties 则为 Nacos Config Starter 本身的配置。
|
||||
|
||||
## More
|
||||
|
||||
#### 更多配置项
|
||||
配置项|key|默认值|说明
|
||||
----|----|-----|-----
|
||||
服务端地址|spring.cloud.nacos.config.server-addr||
|
||||
DataId前缀|spring.cloud.nacos.config.prefix||spring.application.name
|
||||
Group|spring.cloud.nacos.config.group|DEFAULT_GROUP|
|
||||
dataID后缀及数据格式|spring.cloud.nacos.config.content-type|properties|目前只支持 properties
|
||||
配置内容的编码方式|spring.cloud.nacos.config.encode|UTF-8|配置的编码
|
||||
获取配置的超时时间|spring.cloud.nacos.config.timeout|3000|单位为 ms
|
||||
配置的命名空间|spring.cloud.nacos.config.namespace||常用场景之一是不同环境的配置的区分隔离,例如开发测试环境和生产环境的资源隔离等。
|
||||
AccessKey|spring.cloud.nacos.config.access-key||
|
||||
SecretKey|spring.cloud.nacos.config.secret-key||
|
||||
相对路径|spring.cloud.nacos.config.context-path||服务端 API 的相对路径
|
||||
接入点|spring.cloud.nacos.config.endpoint|UTF-8|地域的某个服务的入口域名,通过此域名可以动态地拿到服务端地址
|
||||
是否开启监听和自动刷新|spring.cloud.nacos.config.refresh.enabled|true|
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
#### 更多介绍
|
||||
Nacos为用户提供包括动态服务发现,配置管理,服务管理等服务基础设施,帮助用户更灵活,更轻松地构建,交付和管理他们的微服务平台,基于Nacos, 用户可以更快速的构建以“服务”为中心的现代云原生应用。Nacos可以和Spring Cloud、Kubernetes/CNCF、Dubbo 等微服务生态无缝融合,为用户提供更卓越的体验。更多 Nacos 相关的信息,请参考 [Nacos 项目](https://github.com/alibaba/Nacos)。
|
||||
|
||||
如果您对 Spring Cloud Nacos Config Starter 有任何建议或想法,欢迎在 issue 中或者通过其他社区渠道向我们提出。
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -0,0 +1,193 @@
|
||||
# Nacos Config Example
|
||||
|
||||
## Project Instruction
|
||||
|
||||
This example illustrates how to use Nacos Config Starter implement externalized configuration for Spring Cloud applications.
|
||||
|
||||
[Nacos](https://github.com/alibaba/Nacos) an easy-to-use dynamic service discovery, configuration and service management platform for building cloud native applications.
|
||||
|
||||
## Demo
|
||||
|
||||
### Connect to Nacos Config
|
||||
Before we start the demo, let's learn how to connect Nacos Config to a Spring Cloud application. **Note: This section is to show you how to connect to Nacos Config. The configurations have been completed in the following example, so you don't need modify the code any more.**
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
1. Add dependency spring-cloud-starter-alibaba-nacos-config in the pom.xml file in your Spring Cloud project.
|
||||
|
||||
<dependency>
|
||||
<groupId>org.springframework.cloud</groupId>
|
||||
<artifactId>spring-cloud-starter-alibaba-nacos-config</artifactId>
|
||||
</dependency>
|
||||
|
||||
2. Add Nacos server address configurations to file /src/main/resources/bootstrap.properties
|
||||
|
||||
spring.cloud.nacos.config.server-addr=127.0.0.1:8080
|
||||
|
||||
3. After completing the above two steps, the application will get the externalized configuration from Nacos Server and put it in the Spring Environment's PropertySources.We use the @Value annotation to inject the corresponding configuration into the userName and age fields of the SampleController, and add @RefreshScope to turn on dynamic refresh .
|
||||
@RefreshScope
|
||||
class SampleController {
|
||||
|
||||
@Value("${user.name}")
|
||||
String userName;
|
||||
|
||||
@Value("${user.age}")
|
||||
int age;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
### Start Nacos Server
|
||||
|
||||
1. Install Nacos Server by downloading or build from source code.**Recommended latest version Nacos Server**
|
||||
|
||||
1. Download: Download Nacos Server [download page](https://github.com/alibaba/nacos/releases)
|
||||
2. Build from source code: Get source code by git clone git@github.com:alibaba/Nacos.git from Github Nacos and build your code. See [build reference](https://nacos.io/en-us/docs/quick-start.html) for details.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
2. Unzip the downloaded file and go to the nacos/bin folder(), And according to the actual situation of the operating system, execute the following command。[see reference for more detail](https://nacos.io/en-us/docs/quick-start.html)。
|
||||
|
||||
1. Linux/Unix/Mac , execute `sh startup.sh -m standalone`
|
||||
1. Windows , execute `cmd startup.cmd`
|
||||
|
||||
3. Execute the following command to add a configuration to Nacos Server.
|
||||
|
||||
curl -X POST "http://127.0.0.1:8080/nacos/v1/cs/configs?dataId=nacos-config-example.properties&group=DEFAULT_GROUP&content=user.id=1%0Auser.name=james%0Auser.age=17"
|
||||
|
||||
**Note: You can also add it in other ways. If you are using the Nacos version with its own console, it is recommended to configure it directly using the console.**
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
Details of the added configuration are as follows
|
||||
|
||||
dataId is nacos-config-example.properties
|
||||
group is DEFAULT_GROUP
|
||||
|
||||
content is
|
||||
|
||||
user.id=1
|
||||
user.name=james
|
||||
user.age=17
|
||||
|
||||
### Start Application
|
||||
|
||||
1. Add necessary configurations to file /src/main/resources/application.properties
|
||||
|
||||
spring.application.name=nacos-config-example
|
||||
server.port=18084
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
2. Start the application in IDE or by building a fatjar.
|
||||
|
||||
1. Start in IDE: Find main class `Application`, and execute the main method.
|
||||
2. Build a fatjar:Execute command `mvn clean package` to build a fatjar,and run command `java -jar nacos-config-example.jar` to start the application.
|
||||
|
||||
### Verification
|
||||
|
||||
#### Automatic Injection
|
||||
Enter `http://127.0.0.1:18084/user` in the browser address bar and click Go to, we can see the data successfully obtained from Nacos Config Server.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
#### Dynamic Refresh
|
||||
1. Run the following command to modify the configuration data on the Nacos Server side.
|
||||
|
||||
curl -X POST "http://127.0.0.1:8080/nacos/v1/cs/configs?dataId=nacos-config-example.properties&group=DEFAULT_GROUP&content=user.id=1%0Auser.name=james%0Auser.age=18"
|
||||
|
||||
2. Enter `http://127.0.0.1:18084/user` in the browser address bar and click Go to,
|
||||
We can see that the app got the latest data from Nacos Server and the age becomes 18.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
## Principle
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
### Nacos Config Data Structure
|
||||
|
||||
Nacos Config primarily determines a piece of config through dataId and group, and we assume that you already know this background. If you don't understand, please refer to [Nacos Doc](https://nacos.io/en-us/docs/concepts.html)。
|
||||
|
||||
Nacos Client gets data from Nacos Server through this method. `ConfigService.getConfig(String dataId, String group, long timeoutMs)`。
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
### Spring Cloud Retrieve Data
|
||||
|
||||
#### dataID
|
||||
|
||||
In Nacos Config Starter, the splicing format of dataId is as follows
|
||||
|
||||
${prefix} - ${spring.active.profile} . ${content-type}
|
||||
|
||||
* `prefix` default value is `spring.application.name` value, which can also be configured via the configuration item `spring.cloud.nacos.config.prefix`.
|
||||
|
||||
* `spring.active.profile` is the profile corresponding to the current environment. For details, please refer to [Spring Boot Doc](https://docs.spring.io/spring-boot/docs/current/reference/html/boot-features-profiles.html#boot-features-profiles)
|
||||
|
||||
**Note: when the activeprofile is empty, the corresponding connector `-` will also not exist, and the splicing format of the dataId becomes `${prefix}`.`${context.type}`**
|
||||
|
||||
* `content-type` is the data format of the configuration content, which can be configured by the configuration item `spring.cloud.nacos.config.content-type`.
|
||||
Currently only the `properties` type is supported.
|
||||
|
||||
#### group
|
||||
* `group` defaults to `DEFAULT_GROUP` and can be configured via `spring.cloud.nacos.config.group`.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
### Automatic Injection
|
||||
Nacos Config Starter implement `org.springframework.cloud.bootstrap.config.PropertySourceLocator` interface, and set order to 0.
|
||||
|
||||
In the startup phase of the Spring Cloud application, the corresponding data is obtained from the Nacos Server side, and the acquired data is converted into a PropertySource and injected into the PropertySources property of the Spring Environment. so the @Value annotation can also directly obtain the configuration of the Nacos Server side.
|
||||
|
||||
### Dynamic Refresh
|
||||
|
||||
By default, Nacos Config Starter adds a listening function to all Nacos configuration items that have successfully acquired data. It will trigger `org.springframework.cloud.context.refresh.ContextRefresher` 's refresh method in real time when it detects changes in the server configuration.
|
||||
|
||||
If you need to dynamically refresh a bean, please refer to the Spring and Spring Cloud specifications. It is recommended to add `@RefreshScope` or `@ConfigurationProperties ` annotations to the class.
|
||||
|
||||
Please refer to[ContextRefresher Java Doc](http://static.javadoc.io/org.springframework.cloud/spring-cloud-context/2.0.0.RELEASE/org/springframework/cloud/context/refresh/ContextRefresher.html) for more details.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
## Endpoint
|
||||
|
||||
Nacos Config starter also supports the implementation of Spring Boot actuator endpoints.
|
||||
|
||||
**Prerequisite:**
|
||||
|
||||
Add dependency spring-boot-starter-actuator to your pom.xml file, and configure your endpoint security strategy.
|
||||
|
||||
Spring Boot 1.x: Add configuration management.security.enabled=false
|
||||
Spring Boot 2.x: Add configuration management.endpoints.web.exposure.include=*
|
||||
To view the endpoint information, visit the following URLS:
|
||||
|
||||
Spring Boot1.x: Nacos Config Endpoint URL is http://127.0.0.1:18083/nacos_config.
|
||||
Spring Boot2.x: Nacos Config Endpoint URL is http://127.0.0.1:18083/actuator/nacos-config.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
As shown in the figure above, Sources indicates which Nacos Config configuration items the client has obtained information, RefreshHistory indicates the dynamic refresh history, and up to 20, and NacosConfigProperties is the configuration of Nacos Config Starter itself.
|
||||
|
||||
## More
|
||||
|
||||
#### More configuration items
|
||||
|
||||
Configuration item|key|default value|Description
|
||||
----|----|-----|-----
|
||||
server address|spring.cloud.nacos.config.server-addr||
|
||||
DataId prefix|spring.cloud.nacos.config.prefix||spring.application.name
|
||||
Group|spring.cloud.nacos.config.group|DEFAULT_GROUP|
|
||||
dataID content type|spring.cloud.nacos.config.content-type|properties|currently only support properties
|
||||
encoding |spring.cloud.nacos.config.encode|UTF-8|Content encoding
|
||||
timeout|spring.cloud.nacos.config.timeout|3000|Get the configuration timeout period,unit is ms
|
||||
namespace|spring.cloud.nacos.config.namespace||One of the common scenarios is the separation of the configuration of different environments, such as the development of the test environment and the resource isolation of the production environment.
|
||||
AccessKey|spring.cloud.nacos.config.access-key||
|
||||
SecretKey|spring.cloud.nacos.config.secret-key||
|
||||
context-path|spring.cloud.nacos.config.context-path||Relative path of the server API
|
||||
endpoint|spring.cloud.nacos.config.endpoint|UTF-8|The domain name of a service, through which the server address can be dynamically obtained.
|
||||
refresh|spring.cloud.nacos.config.refresh.enabled|true|enable auto refresh
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
#### More introduction
|
||||
[Nacos](https://github.com/alibaba/Nacos) is committed to help you discover, configure, and manage your microservices. It provides a set of simple and useful features enabling you to realize dynamic service discovery, service configuration, service metadata and traffic management.
|
||||
|
||||
Nacos makes it easier and faster to construct, deliver and manage your microservices platform. It is the infrastructure that supports a service-centered modern application architecture with a microservices or cloud-native approach.
|
||||
|
||||
If you have any ideas or suggestions for Nacos Config starter, please don't hesitate to tell us by submitting github issues.
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -0,0 +1,54 @@
|
||||
package org.springframework.cloud.alibaba.cloud.examples;
|
||||
|
||||
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Value;
|
||||
import org.springframework.boot.ApplicationArguments;
|
||||
import org.springframework.boot.ApplicationRunner;
|
||||
import org.springframework.boot.SpringApplication;
|
||||
import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.SpringBootApplication;
|
||||
import org.springframework.cloud.context.config.annotation.RefreshScope;
|
||||
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
|
||||
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;
|
||||
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController;
|
||||
|
||||
/**
|
||||
* @author xiaojing
|
||||
*/
|
||||
@SpringBootApplication
|
||||
public class Application {
|
||||
|
||||
public static void main(String[] args) {
|
||||
SpringApplication.run(Application.class, args);
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
@Component
|
||||
class SampleRunner implements ApplicationRunner {
|
||||
|
||||
@Value("${user.name}")
|
||||
String userName;
|
||||
|
||||
@Value("${user.age}")
|
||||
int userAge;
|
||||
|
||||
@Override
|
||||
public void run(ApplicationArguments args) throws Exception {
|
||||
System.out.println(userName);
|
||||
System.out.println(userAge);
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
@RestController
|
||||
@RefreshScope
|
||||
class SampleController {
|
||||
|
||||
@Value("${user.name}")
|
||||
String userName;
|
||||
|
||||
@Value("${user.age}")
|
||||
int age;
|
||||
|
||||
@RequestMapping("/user")
|
||||
public String simple() {
|
||||
return "Hello Nacos Config!" + "Hello " + userName + " " + age + "!";
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
@@ -0,0 +1,3 @@
|
||||
spring.application.name=nacos-config-example
|
||||
server.port=18084
|
||||
management.endpoints.web.exposure.include=*
|
||||
@@ -0,0 +1 @@
|
||||
spring.cloud.nacos.config.server-addr=127.0.0.1:8080
|
||||
@@ -0,0 +1,62 @@
|
||||
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
|
||||
<project xmlns="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
|
||||
xsi:schemaLocation="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0 http://maven.apache.org/xsd/maven-4.0.0.xsd">
|
||||
|
||||
<parent>
|
||||
<groupId>org.springframework.cloud</groupId>
|
||||
<artifactId>nacos-discovery-example</artifactId>
|
||||
<version>0.1.0.BUILD-SNAPSHOT</version>
|
||||
</parent>
|
||||
<modelVersion>4.0.0</modelVersion>
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
<artifactId>nacos-discovery-consumer-example</artifactId>
|
||||
<packaging>jar</packaging>
|
||||
<description>Example demonstrating how to use nacos discovery</description>
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
<dependencies>
|
||||
<dependency>
|
||||
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
|
||||
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-web</artifactId>
|
||||
</dependency>
|
||||
<dependency>
|
||||
<groupId>org.springframework.cloud</groupId>
|
||||
<artifactId>spring-cloud-starter-alibaba-nacos-discovery</artifactId>
|
||||
</dependency>
|
||||
|
||||
<dependency>
|
||||
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
|
||||
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-actuator</artifactId>
|
||||
</dependency>
|
||||
|
||||
<dependency>
|
||||
<groupId>org.springframework.cloud</groupId>
|
||||
<artifactId>spring-cloud-starter-netflix-ribbon</artifactId>
|
||||
</dependency>
|
||||
|
||||
<dependency>
|
||||
<groupId>org.springframework.cloud</groupId>
|
||||
<artifactId>spring-cloud-starter-feign</artifactId>
|
||||
</dependency>
|
||||
|
||||
</dependencies>
|
||||
|
||||
<build>
|
||||
<plugins>
|
||||
<plugin>
|
||||
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
|
||||
<artifactId>spring-boot-maven-plugin</artifactId>
|
||||
</plugin>
|
||||
<plugin>
|
||||
<groupId>org.apache.maven.plugins</groupId>
|
||||
<artifactId>maven-deploy-plugin</artifactId>
|
||||
<version>${maven-deploy-plugin.version}</version>
|
||||
<configuration>
|
||||
<skip>true</skip>
|
||||
</configuration>
|
||||
</plugin>
|
||||
</plugins>
|
||||
</build>
|
||||
|
||||
</project>
|
||||
@@ -0,0 +1,41 @@
|
||||
package org.springframework.cloud.alibaba.cloud.examples;
|
||||
|
||||
import org.springframework.boot.SpringApplication;
|
||||
import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.SpringBootApplication;
|
||||
import org.springframework.cloud.client.discovery.EnableDiscoveryClient;
|
||||
import org.springframework.cloud.client.loadbalancer.LoadBalanced;
|
||||
import org.springframework.cloud.netflix.feign.EnableFeignClients;
|
||||
import org.springframework.cloud.netflix.feign.FeignClient;
|
||||
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
|
||||
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.PathVariable;
|
||||
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;
|
||||
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMethod;
|
||||
import org.springframework.web.client.RestTemplate;
|
||||
|
||||
/**
|
||||
* @author xiaojing
|
||||
*/
|
||||
@SpringBootApplication
|
||||
@EnableDiscoveryClient
|
||||
@EnableFeignClients
|
||||
public class ConsumerApplication {
|
||||
|
||||
@LoadBalanced
|
||||
@Bean
|
||||
public RestTemplate restTemplate() {
|
||||
return new RestTemplate();
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
public static void main(String[] args) {
|
||||
SpringApplication.run(ConsumerApplication.class, args);
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
@FeignClient(name = "service-provider")
|
||||
public interface EchoService {
|
||||
@RequestMapping(value = "/echo/{str}", method = RequestMethod.GET)
|
||||
String echo(@PathVariable("str") String str);
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
@@ -0,0 +1,45 @@
|
||||
package org.springframework.cloud.alibaba.cloud.examples;
|
||||
|
||||
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
|
||||
import org.springframework.cloud.alibaba.cloud.examples.ConsumerApplication.EchoService;
|
||||
import org.springframework.cloud.client.discovery.DiscoveryClient;
|
||||
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.PathVariable;
|
||||
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;
|
||||
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMethod;
|
||||
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController;
|
||||
import org.springframework.web.client.RestTemplate;
|
||||
|
||||
/**
|
||||
* @author xiaojing
|
||||
*/
|
||||
@RestController
|
||||
public class TestController {
|
||||
|
||||
@Autowired
|
||||
private RestTemplate restTemplate;
|
||||
@Autowired
|
||||
private EchoService echoService;
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
@Autowired
|
||||
private DiscoveryClient discoveryClient;
|
||||
|
||||
@RequestMapping(value = "/echo-rest/{str}", method = RequestMethod.GET)
|
||||
public String rest(@PathVariable String str) {
|
||||
return restTemplate.getForObject("http://service-provider/echo/" + str, String.class);
|
||||
}
|
||||
@RequestMapping(value = "/echo-feign/{str}", method = RequestMethod.GET)
|
||||
public String feign(@PathVariable String str) {
|
||||
return echoService.echo(str);
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
@RequestMapping(value="/services/{service}",method = RequestMethod.GET)
|
||||
public Object client(@PathVariable String service){
|
||||
return discoveryClient.getInstances(service);
|
||||
}
|
||||
@RequestMapping(value="/services",method = RequestMethod.GET)
|
||||
public Object services(){
|
||||
return discoveryClient.getServices();
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
@@ -0,0 +1,4 @@
|
||||
spring.application.name=service-consumer
|
||||
server.port=18083
|
||||
management.endpoints.web.exposure.include=*
|
||||
spring.cloud.nacos.discovery.server-addr=127.0.0.1:8080
|
||||
@@ -0,0 +1,52 @@
|
||||
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
|
||||
<project xmlns="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
|
||||
xsi:schemaLocation="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0 http://maven.apache.org/xsd/maven-4.0.0.xsd">
|
||||
|
||||
<parent>
|
||||
<groupId>org.springframework.cloud</groupId>
|
||||
<artifactId>nacos-discovery-example</artifactId>
|
||||
<version>0.1.0.BUILD-SNAPSHOT</version>
|
||||
</parent>
|
||||
<modelVersion>4.0.0</modelVersion>
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
<artifactId>nacos-discovery-provider-example</artifactId>
|
||||
<packaging>jar</packaging>
|
||||
<description>Example demonstrating how to use nacos discovery</description>
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
<dependencies>
|
||||
<dependency>
|
||||
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
|
||||
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-web</artifactId>
|
||||
</dependency>
|
||||
<dependency>
|
||||
<groupId>org.springframework.cloud</groupId>
|
||||
<artifactId>spring-cloud-starter-alibaba-nacos-discovery</artifactId>
|
||||
</dependency>
|
||||
|
||||
<dependency>
|
||||
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
|
||||
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-actuator</artifactId>
|
||||
</dependency>
|
||||
|
||||
</dependencies>
|
||||
|
||||
<build>
|
||||
<plugins>
|
||||
<plugin>
|
||||
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
|
||||
<artifactId>spring-boot-maven-plugin</artifactId>
|
||||
</plugin>
|
||||
<plugin>
|
||||
<groupId>org.apache.maven.plugins</groupId>
|
||||
<artifactId>maven-deploy-plugin</artifactId>
|
||||
<version>${maven-deploy-plugin.version}</version>
|
||||
<configuration>
|
||||
<skip>true</skip>
|
||||
</configuration>
|
||||
</plugin>
|
||||
</plugins>
|
||||
</build>
|
||||
|
||||
</project>
|
||||
@@ -0,0 +1,29 @@
|
||||
package org.springframework.cloud.alibaba.cloud.examples;
|
||||
|
||||
import org.springframework.boot.SpringApplication;
|
||||
import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.SpringBootApplication;
|
||||
import org.springframework.cloud.client.discovery.EnableDiscoveryClient;
|
||||
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.PathVariable;
|
||||
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;
|
||||
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMethod;
|
||||
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController;
|
||||
|
||||
/**
|
||||
* @author xiaojing
|
||||
*/
|
||||
@SpringBootApplication
|
||||
@EnableDiscoveryClient
|
||||
public class ProviderApplication {
|
||||
|
||||
public static void main(String[] args) {
|
||||
SpringApplication.run(ProviderApplication.class, args);
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
@RestController
|
||||
class EchoController {
|
||||
@RequestMapping(value = "/echo/{string}", method = RequestMethod.GET)
|
||||
public String echo(@PathVariable String string) {
|
||||
return "hello Nacos Discovery " + string;
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
@@ -0,0 +1,4 @@
|
||||
server.port=18082
|
||||
spring.application.name=service-provider
|
||||
spring.cloud.nacos.discovery.server-addr=127.0.0.1:8080
|
||||
management.endpoints.web.exposure.include=*
|
||||
@@ -0,0 +1,25 @@
|
||||
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
|
||||
<project xmlns="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
|
||||
xsi:schemaLocation="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0 http://maven.apache.org/xsd/maven-4.0.0.xsd">
|
||||
|
||||
<parent>
|
||||
<groupId>org.springframework.cloud</groupId>
|
||||
<artifactId>spring-cloud-alibaba-examples</artifactId>
|
||||
<version>0.1.0.BUILD-SNAPSHOT</version>
|
||||
<relativePath>../../pom.xml</relativePath>
|
||||
</parent>
|
||||
<modelVersion>4.0.0</modelVersion>
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
<artifactId>nacos-discovery-example</artifactId>
|
||||
<packaging>pom</packaging>
|
||||
<description>Example demonstrating how to use nacos discovery</description>
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
<modules>
|
||||
<module>nacos-discovery-consumer-example</module>
|
||||
<module>nacos-discovery-provider-example</module>
|
||||
</modules>
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
</project>
|
||||
@@ -0,0 +1,209 @@
|
||||
# Nacos Discovery Example
|
||||
|
||||
## 项目说明
|
||||
|
||||
本项目演示如何使用 Nacos Discovery Starter 完成 Spring Cloud 应用的服务注册与发现。
|
||||
|
||||
[Nacos](https://github.com/alibaba/Nacos) 是阿里巴巴开源的一个更易于构建云原生应用的动态服务发现、配置管理和服务管理平台。
|
||||
|
||||
## 示例
|
||||
|
||||
### 如何接入
|
||||
在启动示例进行演示之前,我们先了解一下 Spring Cloud 应用如何接入 Nacos Discovery。
|
||||
**注意 本章节只是为了便于您理解接入方式,本示例代码中已经完成接入工作,您无需再进行修改。**
|
||||
|
||||
1. 首先,修改 pom.xml 文件,引入 Nacos Discovery Starter。
|
||||
|
||||
<dependency>
|
||||
<groupId>org.springframework.cloud</groupId>
|
||||
<artifactId>spring-cloud-starter-alibaba-nacos-discovery</artifactId>
|
||||
</dependency>
|
||||
|
||||
2. 在应用的 /src/main/resources/application.properties 配置文件中配置 Nacos Server 地址
|
||||
|
||||
spring.cloud.nacos.discovery.server-addr=127.0.0.1:8080
|
||||
|
||||
3. 使用 @EnableDiscoveryClient 注解开启服务注册与发现功能
|
||||
|
||||
@SpringBootApplication
|
||||
@EnableDiscoveryClient
|
||||
public class ProviderApplication {
|
||||
|
||||
public static void main(String[] args) {
|
||||
SpringApplication.run(Application.class, args);
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
@RestController
|
||||
class EchoController {
|
||||
@RequestMapping(value = "/echo/{string}", method = RequestMethod.GET)
|
||||
public String echo(@PathVariable String string) {
|
||||
return string;
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
### 启动 Nacos Server
|
||||
|
||||
1. 首先需要获取 Nacos Server,支持直接下载和源码构建两种方式。
|
||||
|
||||
1. 直接下载:[Nacos Server 下载页](https://github.com/alibaba/nacos/releases)
|
||||
2. 源码构建:进入 Nacos [Github 项目页面](https://github.com/alibaba/nacos),将代码 git clone 到本地自行编译打包,[参考此文档](https://nacos.io/zh-cn/docs/quick-start.html)。**推荐使用源码构建方式以获取最新版本**
|
||||
|
||||
2. 启动 Server,进入解压后文件夹或编译打包好的文件夹,找到如下相对文件夹 nacos/bin,并对照操作系统实际情况之下如下命令。
|
||||
|
||||
1. Linux/Unix/Mac 操作系统,执行命令 `sh startup.sh -m standalone`
|
||||
1. Windows 操作系统,执行命令 `cmd startup.cmd`
|
||||
|
||||
### 应用启动
|
||||
|
||||
1. 增加配置,在 nacos-discovery-provider-example 项目的 /src/main/resources/application.properties 中添加基本配置信息
|
||||
|
||||
spring.application.name=service-provider
|
||||
server.port=18082
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
2. 启动应用,支持 IDE 直接启动和编译打包后启动。
|
||||
|
||||
1. IDE直接启动:找到 nacos-discovery-provider-example 项目的主类 `ProviderApplication`,执行 main 方法启动应用。
|
||||
2. 打包编译后启动:在 nacos-discovery-provider-example 项目中执行 `mvn clean package` 将工程编译打包,然后执行 `java -jar nacos-discovery-provider-example.jar`启动应用。
|
||||
|
||||
### 验证
|
||||
|
||||
#### 查询服务
|
||||
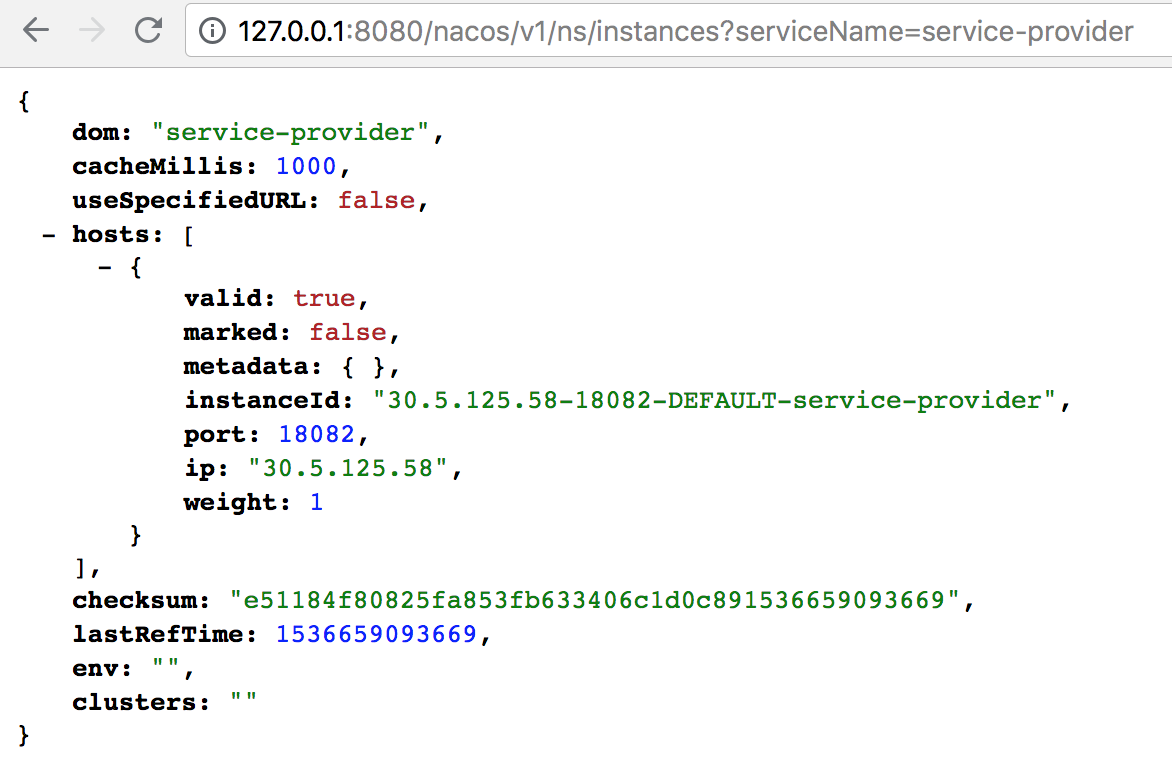
在浏览器输入此地址 `http://127.0.0.1:8080/nacos/v1/ns/instances?serviceName=service-provider`,并点击跳转,可以看到服务节点已经成功注册到 Nacos Server。
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
### 服务发现
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
#### 集成 Ribbon
|
||||
为了便于使用,NacosServerList 实现了 com.netflix.loadbalancer.ServerList<Server> 接口,并在 @ConditionOnMissingBean 的条件下进行自动注入。如果您有定制化的需求,可以自己实现自己的 ServerList。
|
||||
|
||||
Nacos Discovery Starter 默认集成了 Ribbon ,所以对于使用了 Ribbon 做负载均衡的组件,可以直接使用 Nacos 的服务发现。
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
#### 使用 RestTemplate 和 FeignClient
|
||||
|
||||
下面将分析 nacos-discovery-consumer-example 项目的代码,演示如何 RestTemplate 与 FeignClient。
|
||||
|
||||
**注意 本章节只是为了便于您理解接入方式,本示例代码中已经完成接入工作,您无需再进行修改。此处只涉及Ribbon、RestTemplate、FeignClient相关的内容,如果已经使用了其他服务发现组件,可以通过直接替换依赖来接入 Nacos Discovery。**
|
||||
|
||||
1. 添加 @LoadBlanced 注解,使得 RestTemplate 接入 Ribbon
|
||||
|
||||
@Bean
|
||||
@LoadBalanced
|
||||
public RestTemplate restTemplate() {
|
||||
return new RestTemplate();
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
1. FeignClient 已经默认集成了 Ribbon ,此处演示如何配置一个 FeignClient。
|
||||
|
||||
@FeignClient(name = "service-provider")
|
||||
public interface EchoService {
|
||||
@RequestMapping(value = "/echo/{str}", method = RequestMethod.GET)
|
||||
String echo(@PathVariable("str") String str);
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
使用 @FeignClient 注解将 EchoService 这个接口包装成一个 FeignClient,属性 name 对应服务名 service-provider。
|
||||
|
||||
echo 方法上的 @RequestMapping 注解将 echo 方法与 URL "/echo/{str}" 相对应,@PathVariable 注解将 URL 路径中的 `{str}` 对应成 echo 方法的参数 str。
|
||||
|
||||
1. 完成以上配置后,将两者自动注入到 TestController 中。
|
||||
|
||||
@RestController
|
||||
public class TestController {
|
||||
|
||||
@Autowired
|
||||
private RestTemplate restTemplate;
|
||||
@Autowired
|
||||
private EchoService echoService;
|
||||
|
||||
@RequestMapping(value = "/echo-rest/{str}", method = RequestMethod.GET)
|
||||
public String rest(@PathVariable String str) {
|
||||
return restTemplate.getForObject("http://service-provider/echo/" + str, String.class);
|
||||
}
|
||||
@RequestMapping(value = "/echo-feign/{str}", method = RequestMethod.GET)
|
||||
public String feign(@PathVariable String str) {
|
||||
return echoService.echo(str);
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
1. 配置必要的配置,在 nacos-discovery-consumer-example 项目的 /src/main/resources/application.properties 中添加基本配置信息
|
||||
|
||||
spring.application.name=service-consumer
|
||||
server.port=18083
|
||||
|
||||
1. 启动应用,支持 IDE 直接启动和编译打包后启动。
|
||||
|
||||
1. IDE直接启动:找到 nacos-discovery-consumer-example 项目的主类 `ConsumerApplication`,执行 main 方法启动应用。
|
||||
2. 打包编译后启动:在 nacos-discovery-consumer-example 项目中执行 `mvn clean package` 将工程编译打包,然后执行 `java -jar nacos-discovery-consumer-example.jar`启动应用。
|
||||
|
||||
#### 验证
|
||||
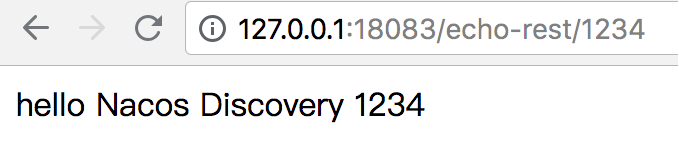
1. 在流量器地址栏中输入 http://127.0.0.1:18083/echo-rest/1234,点击跳转,可以看到浏览器显示了 nacos-discovery-provider-example 返回的消息 "hello Nacos Discovery 1234",证明服务发现生效。
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
1. 在流量器地址栏中输入 http://127.0.0.1:18083/echo-feign/12345,点击跳转,可以看到浏览器显示 nacos-discovery-provider-example 返回的消息 "hello Nacos Discovery 12345",证明服务发现生效。
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
## 原理
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
### 服务注册
|
||||
Spring Cloud Nacos Discovery 遵循了 spring cloud common 标准,实现了 AutoServiceRegistration、ServiceRegistry、Registration 这三个接口。
|
||||
|
||||
在 spring cloud 应用的启动阶段,监听了 ServletWebServerInitializedEvent 事件,当Web容器初始化完成后,即收到 ServletWebServerInitializedEvent 事件后,会触发注册的动作,调用 ServiceRegistry 的 register 方法,将服务注册到 Nacos Server。
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
### 服务发现
|
||||
NacosServerList 实现了 com.netflix.loadbalancer.ServerList<Server> 接口,并在 @ConditionOnMissingBean 的条件下进行自动注入,默认集成了Ribbon。
|
||||
|
||||
如果需要有更加自定义的可以使用 @Autowired 注入一个 NacosRegistration 实例,通过其持有的 NamingService 字段内容直接调用 Nacos API。
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
## Endpoint 信息查看
|
||||
|
||||
Spring Boot 应用支持通过 Endpoint 来暴露相关信息,Nacos Discovery Starter 也支持这一点。
|
||||
|
||||
在使用之前需要在 maven 中添加 `spring-boot-starter-actuator`依赖,并在配置中允许 Endpoints 的访问。
|
||||
|
||||
* Spring Boot 1.x 中添加配置 management.security.enabled=false
|
||||
* Spring Boot 2.x 中添加配置 management.endpoints.web.exposure.include=*
|
||||
|
||||
Spring Boot 1.x 可以通过访问 http://127.0.0.1:18083/nacos_discovery 来查看 Nacos Endpoint 的信息。
|
||||
|
||||
Spring Boot 2.x 可以通过访问 http://127.0.0.1:18083/actuator/nacos-discovery 来访问。
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
如上图所示,NacosDiscoveryProperties 则为 Spring Cloud Nacos Discovery 本身的配置,也包括本机注册的内容,subscribe 为本机已订阅的服务信息。
|
||||
|
||||
## More
|
||||
|
||||
#### 更多配置项
|
||||
配置项|key|默认值|说明
|
||||
----|----|-----|-----
|
||||
服务端地址|spring.cloud.nacos.discovery.server-addr||
|
||||
服务名|spring.cloud.nacos.discovery.service|spring.application.name|
|
||||
权重|spring.cloud.nacos.discovery.weight|1|取值范围 1 到 100,数值越大,权重越大
|
||||
网卡名|spring.cloud.nacos.discovery.network-interface||当IP未配置时,注册的IP为此网卡所对应的IP地址,如果此项也未配置,则默认取第一块网卡的地址
|
||||
注册的IP地址|spring.cloud.nacos.discovery.ip||优先级最高
|
||||
注册的端口|spring.cloud.nacos.discovery.port|-1|默认情况下不用配置,会自动探测
|
||||
命名空间|spring.cloud.nacos.discovery.namespace||常用场景之一是不同环境的注册的区分隔离,例如开发测试环境和生产环境的资源(如配置、服务)隔离等。
|
||||
AccessKey|spring.cloud.nacos.discovery.access-key||
|
||||
SecretKey|spring.cloud.nacos.discovery.secret-key||
|
||||
Metadata|spring.cloud.nacos.discovery.metadata||使用Map格式配置
|
||||
日志文件名|spring.cloud.nacos.discovery.log-name||
|
||||
接入点|spring.cloud.nacos.discovery.enpoint|UTF-8|地域的某个服务的入口域名,通过此域名可以动态地拿到服务端地址
|
||||
是否集成Ribbon|ribbon.nacos.enabled|true|
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
#### 更多介绍
|
||||
Nacos为用户提供包括动态服务发现,配置管理,服务管理等服务基础设施,帮助用户更灵活,更轻松地构建,交付和管理他们的微服务平台,基于Nacos, 用户可以更快速的构建以“服务”为中心的现代云原生应用。Nacos可以和Spring Cloud、Kubernetes/CNCF、Dubbo 等微服务生态无缝融合,为用户提供更卓越的体验。更多 Nacos 相关的信息,请参考 [Nacos 项目](https://github.com/alibaba/Nacos)。
|
||||
|
||||
如果您对 Spring Cloud Nacos Discovery 有任何建议或想法,欢迎在 issue 中或者通过其他社区渠道向我们提出。
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -0,0 +1,220 @@
|
||||
# Nacos Discovery Example
|
||||
|
||||
## Project Instruction
|
||||
|
||||
This example illustrates how to use Nacos Discovery Starter implement Service discovery for Spring Cloud applications.
|
||||
|
||||
[Nacos](https://github.com/alibaba/Nacos) an easy-to-use dynamic service discovery, configuration and service management platform for building cloud native applications.
|
||||
|
||||
## Demo
|
||||
|
||||
### Connect to Nacos Discovery
|
||||
Before we start the demo, let's learn how to connect Nacos Config to a Spring Cloud application. **Note: This section is to show you how to connect to Nacos Discovery. The configurations have been completed in the following example, so you don't need modify the code any more.**
|
||||
|
||||
1. Add dependency spring-cloud-starter-alibaba-nacos-discovery in the pom.xml file in your Spring Cloud project.
|
||||
|
||||
<dependency>
|
||||
<groupId>org.springframework.cloud</groupId>
|
||||
<artifactId>spring-cloud-starter-alibaba-nacos-discovery</artifactId>
|
||||
</dependency>
|
||||
|
||||
2. Add Nacos server address configurations to file /src/main/resources/application.properties.
|
||||
|
||||
spring.cloud.nacos.discovery.server-addr=127.0.0.1:8080
|
||||
|
||||
3. Use the @EnableDiscoveryClient annotation to turn on service registration and discovery.
|
||||
|
||||
@SpringBootApplication
|
||||
@EnableDiscoveryClient
|
||||
public class ProviderApplication {
|
||||
|
||||
public static void main(String[] args) {
|
||||
SpringApplication.run(Application.class, args);
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
@RestController
|
||||
class EchoController {
|
||||
@RequestMapping(value = "/echo/{string}", method = RequestMethod.GET)
|
||||
public String echo(@PathVariable String string) {
|
||||
return string;
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
### Start Nacos Server
|
||||
|
||||
1. Install Nacos Server by downloading or build from source code.**Recommended latest version Nacos Server**
|
||||
|
||||
1. Download: Download Nacos Server [download page](https://github.com/alibaba/nacos/releases)
|
||||
2. Build from source code: Get source code by git clone git@github.com:alibaba/Nacos.git from Github Nacos and build your code. See [build reference](https://nacos.io/en-us/docs/quick-start.html) for details.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
2. Unzip the downloaded file and go to the nacos/bin folder(), And according to the actual situation of the operating system, execute the following command。[see reference for more detail](https://nacos.io/en-us/docs/quick-start.html)。
|
||||
|
||||
1. Linux/Unix/Mac , execute `sh startup.sh -m standalone`
|
||||
1. Windows , execute `cmd startup.cmd`
|
||||
|
||||
### Start Application
|
||||
|
||||
1. Add necessary configurations to project `nacos-discovery-provider-example`, file /src/main/resources/application.properties.
|
||||
|
||||
spring.application.name=service-provider
|
||||
server.port=18082
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
2. Start the application in IDE or by building a fatjar.
|
||||
|
||||
1. Start in IDE: Find main class `ProviderApplication ` in project `nacos-discovery-provider-example`, and execute the main method.
|
||||
2. Build a fatjar:Execute command `mvn clean package` in project ` nacos-discovery-provider-example ` to build a fatjar,and run command `java -jar nacos-discovery-provider-example.jar` to start the application.
|
||||
|
||||
### Verification
|
||||
|
||||
#### Query Service
|
||||
|
||||
Enter `http://127.0.0.1:8080/nacos/v1/ns/instances?serviceName=service-provider` in the browser address bar and click Go to, we can see that the service node has been successfully registered to Nacos Server.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
### Service Discovery
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
#### Integration Ribbon
|
||||
|
||||
For ease of use, NacosServerList implements the com.netflix.loadbalancer.ServerList<Server> interface and auto-injects under the @ConditionOnMissingBean condition. If you have customized requirements, you can implement your own ServerList yourself.
|
||||
|
||||
Nacos Discovery Starter integrates Ribbon by default, so for components that use Ribbon for load balancing, you can use Nacos Service discovery directly.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
#### Use RestTemplate and FeignClient
|
||||
|
||||
The code of `nacos-discovery-consumer-example` project will be analyzed below, demonstrating how RestTemplate and FeignClient.
|
||||
|
||||
**Note This section is to show you how to connect to Nacos Discovery. The configurations have been completed in the following example, so you don't need modify the code any more.Only the contents related to Ribbon, RestTemplate, and FeignClient are involved here. If other service discovery components have been used, you can access Nacos Discovery by directly replacing the dependencies.**
|
||||
|
||||
1. Add the @LoadBlanced annotation to make RestTemplate accessible to the Ribbon
|
||||
|
||||
@Bean
|
||||
@LoadBalanced
|
||||
public RestTemplate restTemplate() {
|
||||
return new RestTemplate();
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
1. FeignClient has integrated the Ribbon by default, which shows how to configure a FeignClient.
|
||||
|
||||
@FeignClient(name = "service-provider")
|
||||
public interface EchoService {
|
||||
@RequestMapping(value = "/echo/{str}", method = RequestMethod.GET)
|
||||
String echo(@PathVariable("str") String str);
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
Use the @FeignClient annotation to wrap the `EchoService` interface as a FeignClient with the attribute name corresponding to the service name `service-provider`.
|
||||
|
||||
The `@RequestMapping` annotation on the `echo` method corresponds the echo method to the URL `/echo/{str}`, and the `@PathVariable` annotation maps `{str}` in the URL path to the argument `str` of the echo method.
|
||||
|
||||
1. After completing the above configuration, injected them into the TestController.
|
||||
|
||||
@RestController
|
||||
public class TestController {
|
||||
|
||||
@Autowired
|
||||
private RestTemplate restTemplate;
|
||||
@Autowired
|
||||
private EchoService echoService;
|
||||
|
||||
@RequestMapping(value = "/echo-rest/{str}", method = RequestMethod.GET)
|
||||
public String rest(@PathVariable String str) {
|
||||
return restTemplate.getForObject("http://service-provider/echo/" + str, String.class);
|
||||
}
|
||||
@RequestMapping(value = "/echo-feign/{str}", method = RequestMethod.GET)
|
||||
public String feign(@PathVariable String str) {
|
||||
return echoService.echo(str);
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
1. Add necessary configurations to project `nacos-discovery-consumer-example` file /src/main/resources/application.properties.
|
||||
|
||||
spring.application.name=service-consumer
|
||||
server.port=18083
|
||||
|
||||
1. Start the application in IDE or by building a fatjar.
|
||||
|
||||
1. Start in IDE: Find main class `ConsumerApplication ` in project `nacos-discovery-consumer-example`, and execute the main method.
|
||||
2. Build a fatjar:Execute command `mvn clean package` in project ` nacos-discovery-consumer-example ` to build a fatjar,and run command `java -jar nacos-discovery-consumer-example.jar` to start the application.
|
||||
|
||||
#### Verification
|
||||
1. Enter `http://127.0.0.1:18083/echo-rest/1234` in the browser address bar and click Go to, we can see that the browser displays the message "hello Nacos Discovery 1234" returned by nacos-discovery-provider-example to prove that the service discovery is in effect.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
1. Enter `http://127.0.0.1:18083/echo-feign/12345` in the browser address bar and click Go to, we can see that the browser displays the message "hello Nacos Discovery 12345" returned by nacos-discovery-provider-example to prove that the service discovery is in effect.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
## Principle
|
||||
|
||||
### Service Registry
|
||||
|
||||
Spring Cloud Nacos Discovery follows the spring cloud common standard and implements three interfaces: AutoServiceRegistration, ServiceRegistry, and Registration.
|
||||
|
||||
During the startup phase of the spring cloud application, the ServletWebServerInitializedEvent event is watched. When the ServletWebServerInitializedEvent event is received after the Web container is initialized, the registration action is triggered, and the ServiceRegistry register method is called to register the service to the Nacos Server.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
### Service Discovery
|
||||
|
||||
NacosServerList implements the com.netflix.loadbalancer.ServerList <Server> interface and auto-injects it under @ConditionOnMissingBean. The ribbon is integrated by default.
|
||||
|
||||
If you need to be more customizable, you can use @Autowired to inject a NacosRegistration bean and call the Nacos API directly through the contents of the NamingService field it holds.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
## Endpoint
|
||||
|
||||
Nacos Discovery Starter also supports the implementation of Spring Boot actuator endpoints.
|
||||
|
||||
**Prerequisite:**
|
||||
|
||||
Add dependency spring-boot-starter-actuator to your pom.xml file, and configure your endpoint security strategy.
|
||||
|
||||
Spring Boot 1.x: Add configuration management.security.enabled=false
|
||||
Spring Boot 2.x: Add configuration management.endpoints.web.exposure.include=*
|
||||
To view the endpoint information, visit the following URLS:
|
||||
|
||||
Spring Boot1.x: Nacos Discovery Endpoint URL is http://127.0.0.1:18083/nacos_discovery.
|
||||
Spring Boot2.x: Nacos Discovery Endpoint URL is http://127.0.0.1:18083/actuator/nacos-discovery.
|
||||
|
||||

|
||||
|
||||
As shown in the figure above, NacosDiscoveryProperties is the configuration of Nacos Discovery itself, and also includes the contents registered by the application, subscribe is the service information that the application has subscribed to.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
## More
|
||||
|
||||
#### More configuration items
|
||||
Configuration item|key|default value|Description
|
||||
----|----|-----|-----
|
||||
server address|spring.cloud.nacos.discovery.server-addr||
|
||||
service|spring.cloud.nacos.discovery.service|spring.application.name|service id to registry
|
||||
weight|spring.cloud.nacos.discovery.weight|1|value from 1 to 100, The larger the value, the larger the weight
|
||||
ip|spring.cloud.nacos.discovery.ip||ip address to registry, Highest priority
|
||||
network interface|spring.cloud.nacos.discovery.network-interface||When the IP is not configured, the registered IP address is the IP address corresponding to the network-interface. If this item is not configured, the address of the first network-interface is taken by default.
|
||||
port|spring.cloud.nacos.discovery.port|-1|port to registry, Automatically detect without configuration
|
||||
namesapce|spring.cloud.nacos.discovery.namespace||One of the common scenarios is the separation of the configuration of different environments, such as the development of the test environment and the resource isolation of the production environment.
|
||||
AccessKey|spring.cloud.nacos.discovery.access-key||
|
||||
SecretKey|spring.cloud.nacos.discovery.secret-key||
|
||||
Metadata|spring.cloud.nacos.discovery.metadata||Extended data, Configure using Map format
|
||||
log name|spring.cloud.nacos.discovery.log-name||
|
||||
endpoint|spring.cloud.nacos.discovery.enpoint||The domain name of a service, through which the server address can be dynamically obtained.
|
||||
Integration Ribbon|ribbon.nacos.enabled|true|
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
#### More introduction
|
||||
|
||||
[Nacos ](https://github.com/alibaba/Nacos) is committed to help you discover, configure, and manage your microservices. It provides a set of simple and useful features enabling you to realize dynamic service discovery, service configuration, service metadata and traffic management.
|
||||
|
||||
Nacos makes it easier and faster to construct, deliver and manage your microservices platform. It is the infrastructure that supports a service-centered modern application architecture with a microservices or cloud-native approach.
|
||||
|
||||
If you have any ideas or suggestions for Nacos Discovery starter, please don't hesitate to tell us by submitting github issues.
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -12,10 +12,13 @@
|
||||
|
||||
<artifactId>spring-cloud-alibaba-examples</artifactId>
|
||||
<packaging>pom</packaging>
|
||||
<name>Spring Cloud Alibaba Examples</name>
|
||||
<description>Example showing how to use features of Spring Cloud Alibaba</description>
|
||||
|
||||
<modules>
|
||||
<module>sentinel-example</module>
|
||||
<module>nacos-example/nacos-discovery-example</module>
|
||||
<module>nacos-example/nacos-config-example</module>
|
||||
<module>sentinel-dubbo-provider-example</module>
|
||||
<module>sentinel-dubbo-consumer-example</module>
|
||||
<module>sentinel-dubbo-api</module>
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -22,7 +22,7 @@
|
||||
|
||||
<dependency>
|
||||
<groupId>org.springframework.cloud</groupId>
|
||||
<artifactId>spring-cloud-starter-sentinel</artifactId>
|
||||
<artifactId>spring-cloud-starter-alibaba-sentinel</artifactId>
|
||||
</dependency>
|
||||
|
||||
<dependency>
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -10,45 +10,55 @@
|
||||
## 示例
|
||||
|
||||
### 如何接入
|
||||
|
||||
在启动示例进行演示之前,我们先了解一下如何接入 Sentinel。
|
||||
**注意 本章节只是为了便于您理解接入方式,本示例代码中已经完成接入工作,您无需再进行修改。**
|
||||
|
||||
1. 首先,修改 pom.xml 文件,引入 Sentinel starter。
|
||||
> **注意:本章节只是为了便于您理解接入方式,本示例代码中已经完成接入工作,您无需再进行修改。**
|
||||
|
||||
1. 首先,修改 `pom.xml` 文件,引入 Sentinel starter。
|
||||
|
||||
```xml
|
||||
<dependency>
|
||||
<groupId>org.springframework.cloud</groupId>
|
||||
<artifactId>spring-cloud-starter-alibaba-sentinel</artifactId>
|
||||
</dependency>
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
<dependency>
|
||||
<groupId>org.springframework.cloud</groupId>
|
||||
<artifactId>spring-cloud-starter-alibaba-sentinel</artifactId>
|
||||
</dependency>
|
||||
|
||||
2. 接入限流埋点
|
||||
- HTTP 埋点
|
||||
|
||||
1. HTTP埋点
|
||||
Sentinel starter 默认为所有的 HTTP 服务提供了限流埋点,如果只想对 HTTP 服务进行限流,那么只需要引入依赖,无需修改代码。
|
||||
- 自定义埋点
|
||||
|
||||
如果需要对某个特定的方法进行限流或降级,可以通过 `@SentinelResource` 注解来完成限流的埋点,示例代码如下:
|
||||
|
||||
```java
|
||||
@SentinelResource("resource")
|
||||
public String hello() {
|
||||
return "Hello";
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
2. 自定义埋点
|
||||
如果需要对某个特定的方法进行限流或降级,可以通过 @SentinelResource 来完成限流的埋点,示例代码如下
|
||||
当然也可以通过原始的 `SphU.entry(xxx)` 方法进行埋点,可以参见 [Sentinel 文档](https://github.com/alibaba/Sentinel/wiki/%E5%A6%82%E4%BD%95%E4%BD%BF%E7%94%A8#%E5%AE%9A%E4%B9%89%E8%B5%84%E6%BA%90)。
|
||||
|
||||
@SentinelResource("resource")
|
||||
public String hello() {
|
||||
return "Hello";
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
3. 配置限流规则
|
||||
|
||||
Sentinel提供了两种配置限流规则的方式,代码配置 和 控制台配置,本示例使用的方式为通过控制台配置。
|
||||
Sentinel 提供了两种配置限流规则的方式:代码配置 和 控制台配置。本示例使用的方式为通过控制台配置。
|
||||
|
||||
1. 通过代码来实现限流规则的配置。一个简单的限流规则配置示例代码如下,更多限流规则配置详情请参考 [Sentinel 文档](https://github.com/alibaba/Sentinel/wiki/%E5%A6%82%E4%BD%95%E4%BD%BF%E7%94%A8#%E5%AE%9A%E4%B9%89%E8%A7%84%E5%88%99)。
|
||||
|
||||
List<FlowRule> rules = new ArrayList<FlowRule>();
|
||||
FlowRule rule = new FlowRule();
|
||||
rule.setResource(str);
|
||||
// set limit qps to 10
|
||||
rule.setCount(10);
|
||||
rule.setGrade(RuleConstant.FLOW_GRADE_QPS);
|
||||
rule.setLimitApp("default");
|
||||
rules.add(rule);
|
||||
FlowRuleManager.loadRules(rules);
|
||||
|
||||
```java
|
||||
List<FlowRule> rules = new ArrayList<FlowRule>();
|
||||
FlowRule rule = new FlowRule();
|
||||
rule.setResource(str);
|
||||
// set limit qps to 10
|
||||
rule.setCount(10);
|
||||
rule.setGrade(RuleConstant.FLOW_GRADE_QPS);
|
||||
rule.setLimitApp("default");
|
||||
rules.add(rule);
|
||||
FlowRuleManager.loadRules(rules);
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
2. 通过控制台进行限流规则配置请参考文章后面的图文说明。
|
||||
|
||||
### 启动 Sentinel 控制台
|
||||
@@ -65,10 +75,12 @@
|
||||
|
||||
1. 增加配置,在应用的 /src/main/resources/application.properties 中添加基本配置信息
|
||||
|
||||
spring.application.name=sentinel-example
|
||||
server.port=18083
|
||||
spring.cloud.sentinel.dashboard=localhost:8080
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
spring.application.name=sentinel-example
|
||||
server.port=18083
|
||||
spring.cloud.sentinel.dashboard=localhost:8080
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
2. 启动应用,支持 IDE 直接启动和编译打包后启动。
|
||||
|
||||
1. IDE直接启动:找到主类 `ServiceApplication`,执行 main 方法启动应用。
|
||||
@@ -84,7 +96,8 @@
|
||||
### 配置限流规则并验证
|
||||
|
||||
1. 访问 http://localhost:8080 页面,可以在左侧看到 Sentinel-Example 应用已经注册到了控制台,单击 **流控规则** ,可以看到目前的流控规则为空。
|
||||
**注意 如果您在控制台没有找到应用,请调用一下进行了 Sentinel 埋点的 URL 或方法,因为 Sentinel 使用了 lazy load 策略**
|
||||
|
||||
> **注意:如果您在控制台没有找到应用,请调用一下进行了 Sentinel 埋点的 URL 或方法,因为 Sentinel 使用了 lazy load 策略。详细的排查过程请参见 [Sentinel FAQ](https://github.com/alibaba/Sentinel/wiki/FAQ)。**
|
||||
|
||||
<p align="center"><img src="https://cdn.nlark.com/lark/0/2018/png/54319/1532315951819-9ffd959e-0547-4f61-8f06-91374cfe7f21.png" width="1000" heigh='400' ></p>
|
||||
|
||||
@@ -94,7 +107,7 @@
|
||||
<p align="center"><img src="https://cdn.yuque.com/lark/0/2018/png/54319/1532078717483-62ab74cd-e5da-4241-a45d-66166b1bde99.png" width="480" heigh='180' ></p>
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
3. 配置自定义限流规则:点击新增流控规则,资源名填写 @SentinelResource 注解 value 字段的值,单机阈值选择需要限流的阈值,点击新增进行确认。(为了便于演示效果,这里将值设置成了 1)。
|
||||
3. 配置自定义限流规则:点击新增流控规则,资源名填写 `@SentinelResource` 注解 `value` 字段的值,单机阈值选择需要限流的阈值,点击新增进行确认。(为了便于演示效果,这里将值设置成了 1)。
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
<p align="center"><img src="https://cdn.yuque.com/lark/0/2018/png/54319/1532080384317-2943ce0a-daaf-495d-8afc-79a0248a119a.png" width="480" heigh='180' ></p>
|
||||
@@ -110,60 +123,82 @@
|
||||
## 自定义限流处理逻辑
|
||||
|
||||
1. URL 限流触发后默认处理逻辑是,直接返回 "Blocked by Sentinel (flow limiting)"。
|
||||
如果需要自定义处理逻辑,实现的方式如下
|
||||
如果需要自定义处理逻辑,实现的方式如下:
|
||||
|
||||
public class CustomUrlBlockHandler implements UrlBlockHandler {
|
||||
@Override
|
||||
public void blocked(HttpServletRequest httpServletRequest,
|
||||
HttpServletResponse httpServletResponse) throws IOException {
|
||||
// todo add your logic
|
||||
}
|
||||
```java
|
||||
public class CustomUrlBlockHandler implements UrlBlockHandler {
|
||||
@Override
|
||||
public void blocked(HttpServletRequest httpServletRequest, HttpServletResponse httpServletResponse) throws IOException {
|
||||
// todo add your logic
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
WebCallbackManager.setUrlBlockHandler(new CustomUrlBlockHandler());
|
||||
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
WebCallbackManager.setUrlBlockHandler(new CustomUrlBlockHandler());
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
2. 自定义限流触发后,默认的处理逻辑是抛出异常。
|
||||
如果需要自定义处理逻辑,填写@SentinelResource注解的blockHandler和blockHandlerClass属性,指定后会去blockHandlerClass类里找对应的blockHandler静态方法。示例实现如下
|
||||
|
||||
@SentinelResource(value = "resource", blockHandler = "", blockHandlerClass = ExceptionUtil.class)
|
||||
public String hello() {
|
||||
return "Hello";
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// ExceptionUtil.java
|
||||
public class ExceptionUtil {
|
||||
public static void handleException(BlockException ex) {
|
||||
System.out.println("Oops: " + ex.getClass().getCanonicalName());
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
如果需要自定义处理逻辑,填写 `@SentinelResource` 注解的 `blockHandler` 属性(针对所有类型的 `BlockException`,需自行判断)或 `fallback` 属性(针对熔断降级异常),注意**对应方法的签名和位置有限制**,详情见 [Sentinel 注解支持文档](https://github.com/alibaba/Sentinel/wiki/%E6%B3%A8%E8%A7%A3%E6%94%AF%E6%8C%81#sentinelresource-%E6%B3%A8%E8%A7%A3)。示例实现如下:
|
||||
|
||||
```java
|
||||
public class TestService {
|
||||
|
||||
// blockHandler 是位于 ExceptionUtil 类下的 handleException 静态方法,需符合对应的类型限制.
|
||||
@SentinelResource(value = "test", blockHandler = "handleException", blockHandlerClass = {ExceptionUtil.class})
|
||||
public void test() {
|
||||
System.out.println("Test");
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// blockHandler 是位于当前类下的 exceptionHandler 方法,需符合对应的类型限制.
|
||||
@SentinelResource(value = "hello", blockHandler = "exceptionHandler")
|
||||
public String hello(long s) {
|
||||
return String.format("Hello at %d", s);
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
public String exceptionHandler(long s, BlockException ex) {
|
||||
// Do some log here.
|
||||
ex.printStackTrace();
|
||||
return "Oops, error occurred at " + s;
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
```java
|
||||
public final class ExceptionUtil {
|
||||
|
||||
public static void handleException(BlockException ex) {
|
||||
System.out.println("Oops: " + ex.getClass().getCanonicalName());
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
一个简单的示例可以见 [sentinel-demo-annotation-spring-aop](https://github.com/alibaba/Sentinel/tree/master/sentinel-demo/sentinel-demo-annotation-spring-aop)。
|
||||
|
||||
## Endpoint 信息查看
|
||||
|
||||
Spring Boot 应用支持通过 Endpoint 来暴露相关信息,Sentinel Starter 也支持这一点。
|
||||
|
||||
在使用之前需要在 maven 中添加 `spring-boot-starter-actuator`依赖,并在配置中允许 Endpoints 的访问。
|
||||
* Spring Boot1.x 中添加配置 management.security.enabled=false
|
||||
* Spring Boot2.x 中添加配置 management.endpoints.web.exposure.include=*
|
||||
在使用之前需要在 Maven 中添加 `spring-boot-starter-actuator`依赖,并在配置中允许 Endpoints 的访问。
|
||||
* Spring Boot 1.x 中添加配置 `management.security.enabled=false`
|
||||
* Spring Boot 2.x 中添加配置 `management.endpoints.web.exposure.include=*`
|
||||
|
||||
Spring Boot1.x 可以通过访问 http://127.0.0.1:18083/sentinel 来查看 Sentinel Endpoint 的信息。Spring Boot2.x 可以通过访问 http://127.0.0.1:18083/acutator/sentinel 来访问。
|
||||
Spring Boot 1.x 可以通过访问 http://127.0.0.1:18083/sentinel 来查看 Sentinel Endpoint 的信息。Spring Boot 2.x 可以通过访问 http://127.0.0.1:18083/acutator/sentinel 来访问。
|
||||
|
||||
<p align="center"><img src="https://cdn.yuque.com/lark/0/2018/png/54319/1532084199224-1a41591d-7a06-4680-be8a-5de319ac635d.png" width="480" heigh='360' ></p>
|
||||
|
||||
## 查看实时监控
|
||||
Sentinel 控制台支持实时监控查看,您可以通过 Sentinel 控制台查看各链路的请求的通过数和被限流数等信息。
|
||||
其中 p_qps 为通过(pass) 流控的 QPS,b_qps 为被限流 (block) 的 QPS。
|
||||
其中 `p_qps` 为通过(pass) 流控的 QPS,`b_qps` 为被限流 (block) 的 QPS。
|
||||
|
||||
<p align="center"><img src="https://cdn.nlark.com/lark/0/2018/png/54319/1532313595369-8428cd7d-9eb7-4786-a149-acf0da4a2daf.png" width="480" heigh='180' ></p>
|
||||
|
||||
## DataSource支持
|
||||
## DataSource 支持
|
||||
|
||||
Sentinel内部提供了[动态规则的扩展实现DataSource](https://github.com/alibaba/Sentinel/wiki/%E5%8A%A8%E6%80%81%E8%A7%84%E5%88%99%E6%89%A9%E5%B1%95#datasource-%E6%89%A9%E5%B1%95)。
|
||||
Sentinel 内部提供了[动态规则的扩展实现 DataSource](https://github.com/alibaba/Sentinel/wiki/%E5%8A%A8%E6%80%81%E8%A7%84%E5%88%99%E6%89%A9%E5%B1%95#datasource-%E6%89%A9%E5%B1%95)。
|
||||
|
||||
Sentinel starter整合了目前存在的4类DataSource。只需要在配置文件中进行相关配置,即可在Spring容器中自动注册DataSource。
|
||||
Sentinel starter 整合了目前存在的几类 DataSource。只需要在配置文件中进行相关配置,即可在 Spring 容器中自动注册 DataSource。
|
||||
|
||||
比如要定义一个FileRefreshableDataSource,配置如下:
|
||||
比如要定义一个 `FileRefreshableDataSource`,配置如下:
|
||||
|
||||
spring.cloud.sentinel.datasource.type=file
|
||||
spring.cloud.sentinel.datasource.recommendRefreshMs=2000
|
||||
@@ -171,40 +206,40 @@ Sentinel starter整合了目前存在的4类DataSource。只需要在配置文
|
||||
spring.cloud.sentinel.datasource.charset=utf-8
|
||||
spring.cloud.sentinel.datasource.configParser=myParser
|
||||
spring.cloud.sentinel.datasource.file=/Users/you/rule.json
|
||||
|
||||
然后使用`@SentinelDataSource`注解修饰DataSource即可注入:
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
然后使用`@SentinelDataSource` 注解修饰 DataSource 即可注入:
|
||||
|
||||
@SentinelDataSource("spring.cloud.sentinel.datasource")
|
||||
private DataSource dataSource;
|
||||
|
||||
`@SentinelDataSource`注解的value属性可以不填。默认值就是spring.cloud.sentinel.datasource。
|
||||
|
||||
value属性代表配置前缀。示例中会去找spring.cloud.sentinel.datasource.xxx相关的配置。
|
||||
`@SentinelDataSource` 注解的 value 属性可以不填。默认值就是 `spring.cloud.sentinel.datasource`。
|
||||
|
||||
spring.cloud.sentinel.datasource.type就是对应的DataSource类型。
|
||||
`value` 属性代表配置前缀。示例中会去找 `spring.cloud.sentinel.datasource.xxx` 相关的配置。
|
||||
|
||||
spring.cloud.sentinel.datasource.recommendRefreshMs里的recommendRefreshMs对应相关DataSource的属性。
|
||||
`spring.cloud.sentinel.datasource.type` 就是对应的 DataSource 类型。
|
||||
|
||||
spring.cloud.sentinel.datasource.configParser代表ConfigParser在Spring容器里的name。如果没找到,会抛出异常。
|
||||
`spring.cloud.sentinel.datasource.recommendRefreshMs` 里的 `recommendRefreshMs` 对应相关 DataSource 的属性。
|
||||
|
||||
`spring.cloud.sentinel.datasource.configParser`代表 `ConfigParser` 在 Spring 容器里的 name。如果没找到,会抛出异常。
|
||||
|
||||
type目前支持file, nacos, zk, apollo。
|
||||
|
||||
### 自定义DataSource
|
||||
|
||||
自定义DataSource只需要两部。
|
||||
自定义DataSource只需要两步。
|
||||
|
||||
1. 定义DataSource
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
public class CustomDataSource implements DataSource {
|
||||
private String fieldA;
|
||||
private String fieldB;
|
||||
...
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
2. 装配DataSource。有两种方式处理。
|
||||
|
||||
* 直接构造DataSource
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
@Bean
|
||||
public CustomDataSource customDataSource() {
|
||||
CustomDataSource customDataSource =
|
||||
@@ -218,13 +253,13 @@ type目前支持file, nacos, zk, apollo。
|
||||
* 在classpath:/META-INF/sentinel-datasource.properties中管理DataSource信息
|
||||
|
||||
custom = yourpackage.CustomDataSource
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
在application.properties中定义DataSource
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
spring.cloud.sentinel.datasource.type = custom
|
||||
spring.cloud.sentinel.datasource.fieldA = valueA
|
||||
spring.cloud.sentinel.datasource.fieldB = valueB
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
注意:由于目前Sentinel的AbstractDataSource需要有个ConfigParser作为构造函数中的参数,并且它的子类的构造都是通过多个参数的构造函数构造的。
|
||||
所以目前所有的Sentinel starter中的DataSource都是基于FactoryBean并且通过设置属性构造的。如果有这方面的需求,需要再多加一个registerFactoryBean过程。
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
Reference in New Issue
Block a user