mirror of
https://github.com/fofolee/uTools-Manuals.git
synced 2025-06-29 13:04:32 +08:00
0.0.1
This commit is contained in:
commit
7ca94f1141
77
README.md
Normal file
77
README.md
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,77 @@
|
||||
# 程序员手册 V0.0.1
|
||||
|
||||
### 简介
|
||||
|
||||
内置了多个实用的离线中文手册,目前包括:Linux命令、PHP函数、Python库、C函数、Vim命令、Git命令、Docker命令、Sql语句、uTools API
|
||||
|
||||
手册具有以下两个特色:
|
||||
|
||||
- 离线使用
|
||||
- 90%以上是中文
|
||||
|
||||
前身是之前发布的两个插件:
|
||||
|
||||
[PHP函数查询助手](https://yuanliao.info/d/329) [Linux命令查询手册](https://yuanliao.info/d/336)
|
||||
|
||||
### 更新
|
||||
|
||||
相较于之前两版,做了比较大的更新:
|
||||
|
||||
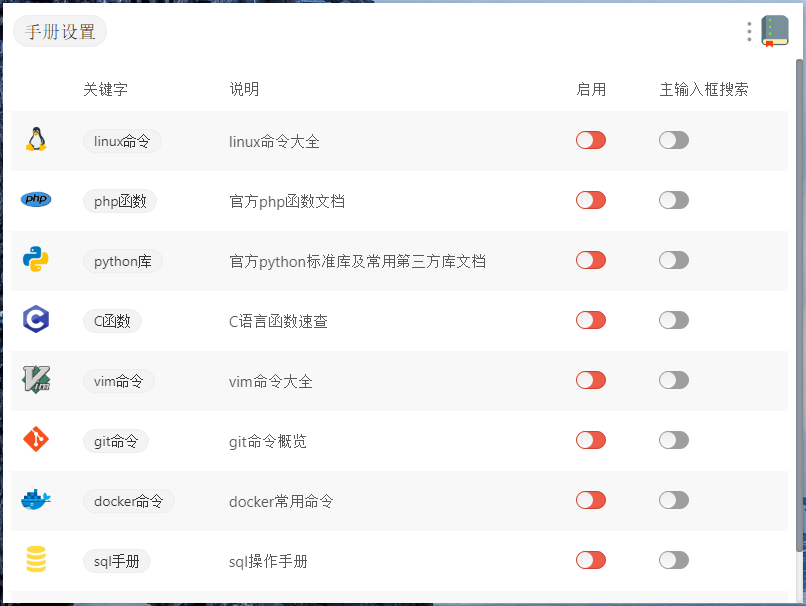
- 整合所有手册到一个插件当中,现在有多达**九个**语言或工具的手册
|
||||
- 添加了一个配置页面,可以选择需要启动的功能(注:默认情况下所有手册均未启用,需要先通过`手册设置`命令进行配置)
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
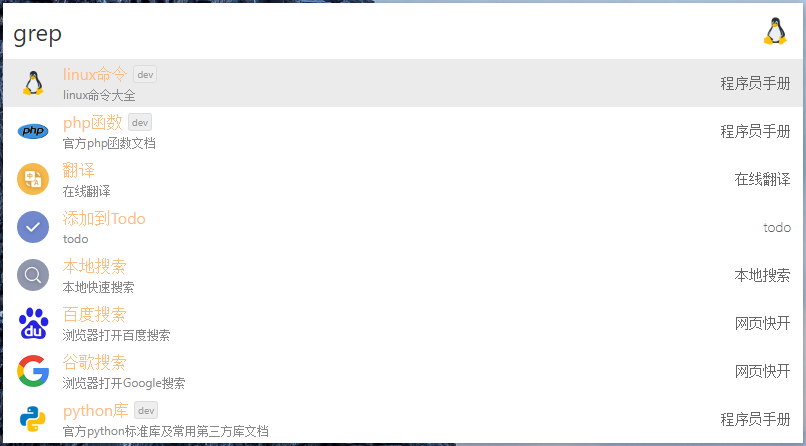
- 支持直接在`uTools`主输入框进行快速搜索查询(或复制文本后5s内呼出`uTools`),可在配置页面选择开启
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
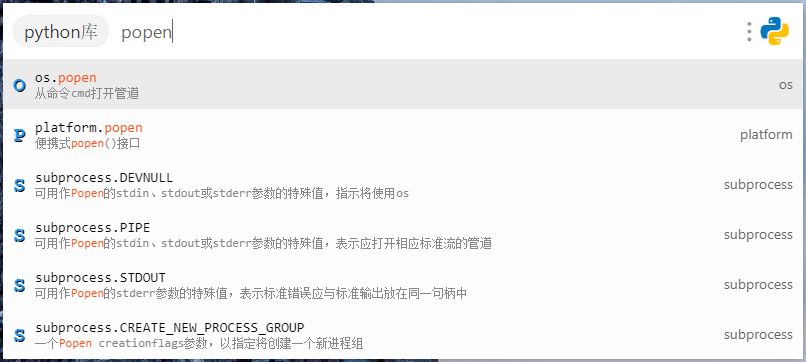
- 子输入框功能增强。
|
||||
|
||||
在**列表界面**用来搜索函数/命令,并高亮匹配文本
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
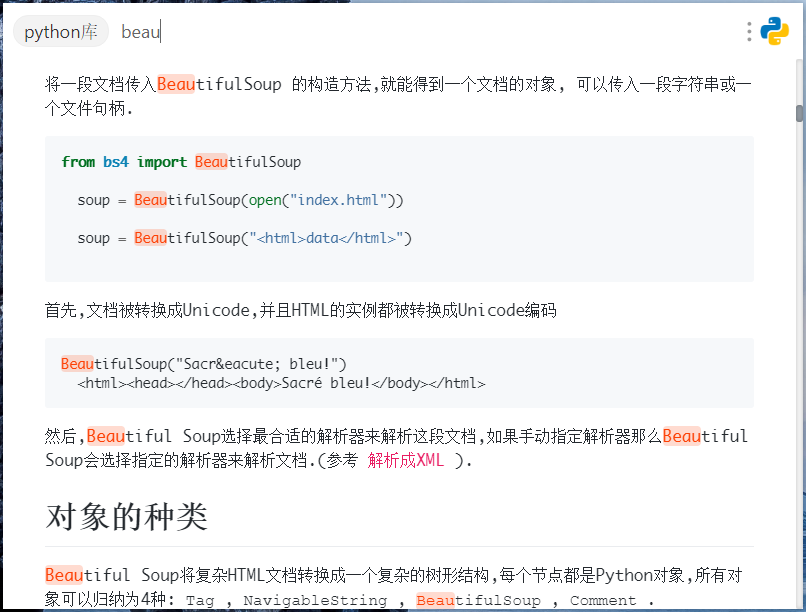
在**手册界面**则可以进行当前文档内容的搜索(回车键跳转到匹配文本位置)
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
- 添加了一个快捷键`TAB`,以在列表界面和手册界面之间进行切换
|
||||
|
||||
- 现在支持点击手册里的外部链接跳转到相应网址(通过默认浏览器打开,之前并不支持,不知道你们发现没~~)
|
||||
|
||||
- 界面微调
|
||||
|
||||
- 一些BUG修复
|
||||
|
||||
### 其他预览
|
||||
|
||||
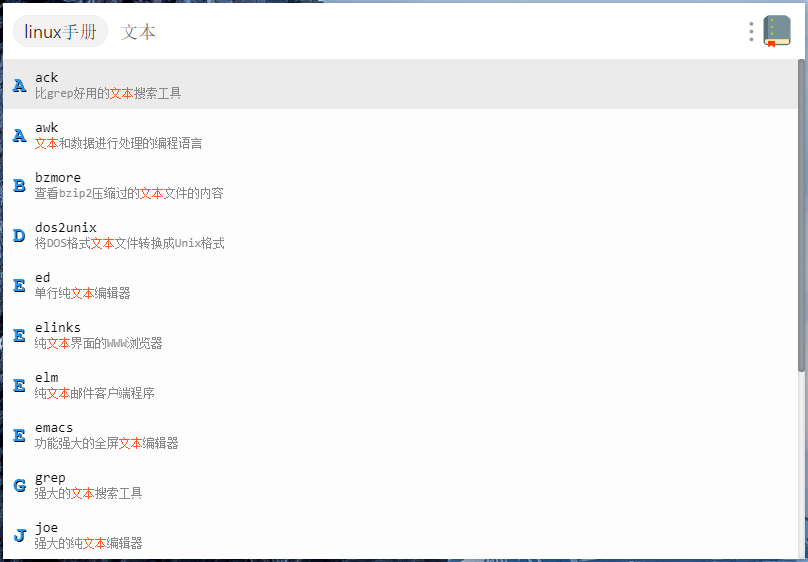
|
||||
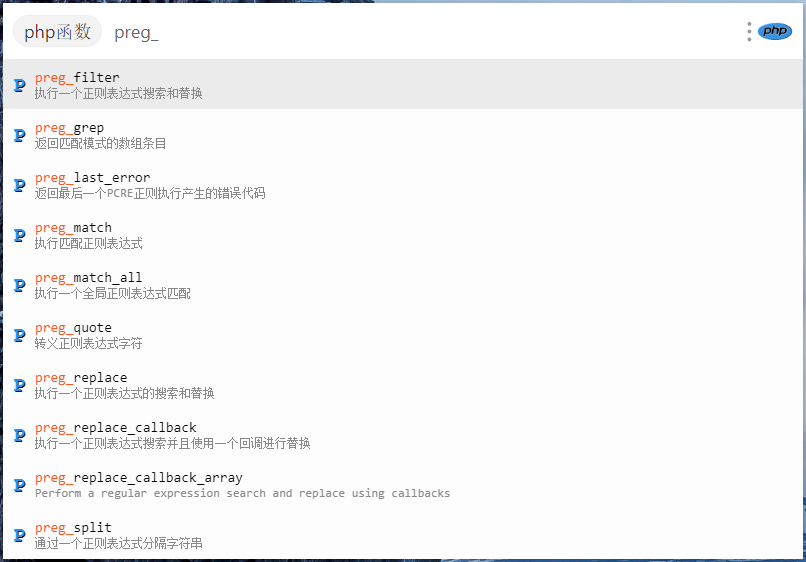
|
||||
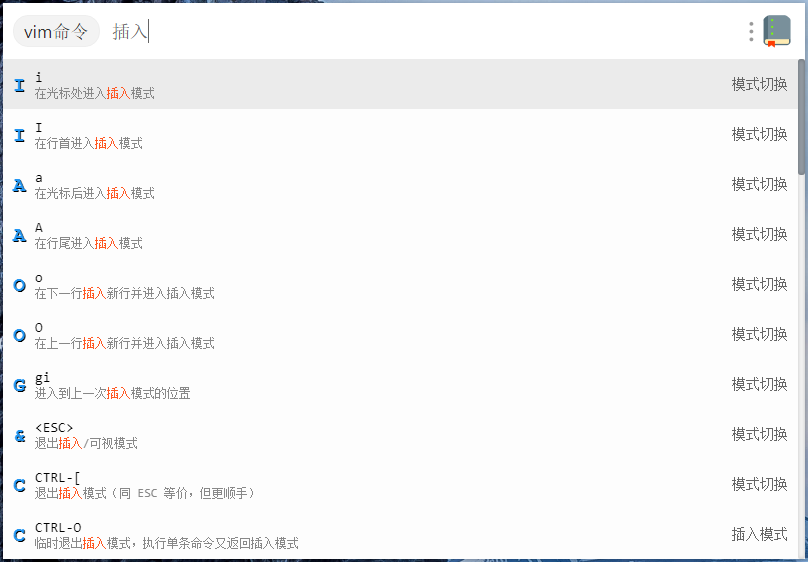
|
||||
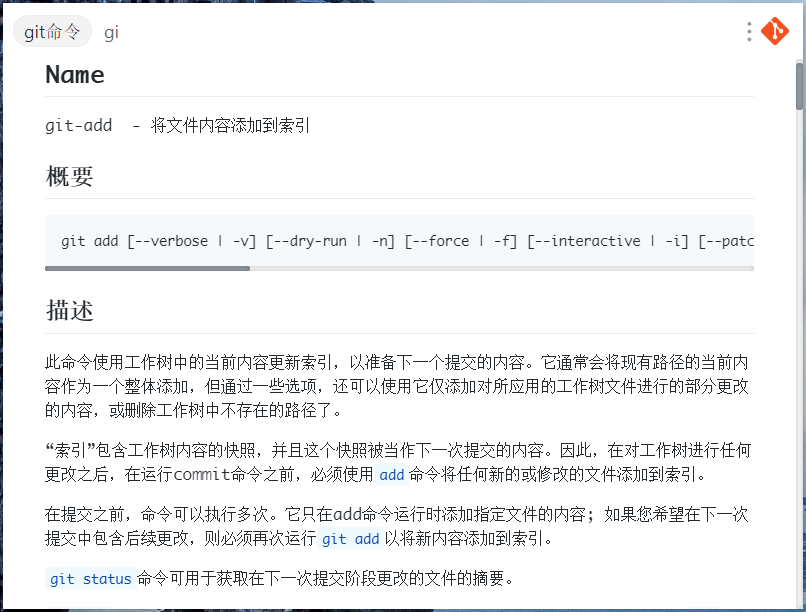
|
||||
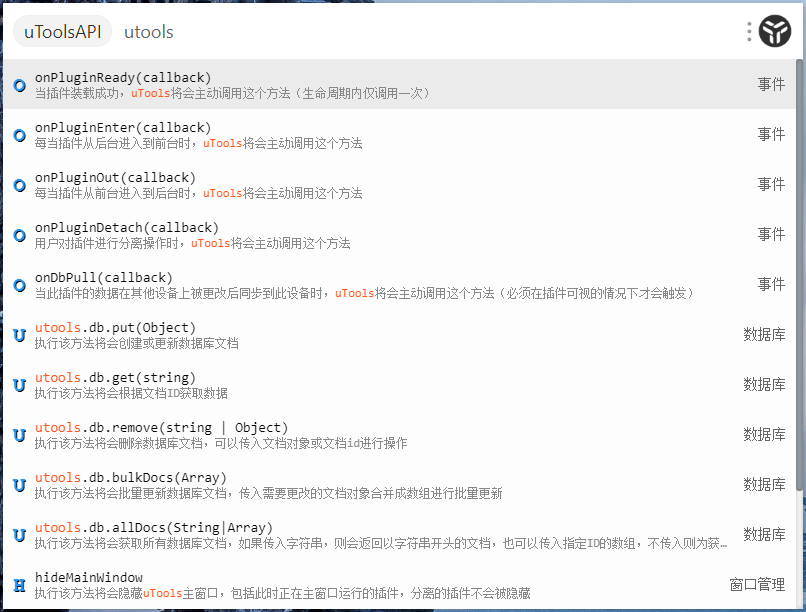
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
### 下载
|
||||
|
||||
[百度网盘](https://pan.baidu.com/s/188sFN_oktGulGTdvnCQPqw) 提取码: `yfh7`
|
||||
|
||||
[插件发布页](https://yuanliao.info/d/356)
|
||||
|
||||
### 安装方法
|
||||
|
||||
将`upx`文件拖入`uTools`输入框中安装即可
|
||||
|
||||
### 关键字
|
||||
|
||||
`手册设置` `linux命令` `php函数` `python库` `C函数` `vim命令` `git命令` `docker命令` `sql手册` `uToolsAPI`
|
||||
|
||||
### 手册来源
|
||||
|
||||
- php手册: [官方中文文档](https://www.php.net/download-docs.php)
|
||||
- linux手册: [离线手册:linux-command@jaywcjlove](https://github.com/jaywcjlove/linux-command) [原始数据:linuxde.net](http://man.linuxde.net/)
|
||||
- python手册: [官方文档一译翻译版(比官方中文翻译的要多不少)](https://yiyibooks.cn/xx/python_352/library/index.html)及其他第三方库的官方中文文档
|
||||
- C函数: C语言函数速查(Knocker 2004.7.7 版本 0.5)
|
||||
- vim命令: [awesome-cheatsheets](https://github.com/skywind3000/awesome-cheatsheets/blob/master/editors/vim.txt)
|
||||
- git命令: [php中文网git开发手册](http://www.php.cn/manual/view/34942.html)
|
||||
- sql手册: [php中文网sql参考手册](http://www.php.cn/manual/view/21301.html)
|
||||
- uTools API: [uTools官方文档](https://u.tools/docs/developer/api.html)
|
||||
71
assets/highlight.js
Normal file
71
assets/highlight.js
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,71 @@
|
||||
/*
|
||||
|
||||
highlight v3 !! Modified by Jon Raasch (http://jonraasch.com) to fix IE6 bug !!
|
||||
|
||||
Highlights arbitrary terms.
|
||||
|
||||
<http://johannburkard.de/blog/programming/javascript/highlight-javascript-text-higlighting-jquery-plugin.html>
|
||||
|
||||
MIT license.
|
||||
|
||||
Johann Burkard
|
||||
<http://johannburkard.de>
|
||||
<mailto:jb@eaio.com>
|
||||
|
||||
*/
|
||||
|
||||
jQuery.fn.highlight = function(pat) {
|
||||
function innerHighlight(node, pat) {
|
||||
var skip = 0;
|
||||
if (node.nodeType == 3) {
|
||||
var pos = node.data.toUpperCase().indexOf(pat);
|
||||
if (pos >= 0) {
|
||||
var spannode = document.createElement('span');
|
||||
spannode.className = 'founds';
|
||||
var middlebit = node.splitText(pos);
|
||||
var endbit = middlebit.splitText(pat.length);
|
||||
var middleclone = middlebit.cloneNode(true);
|
||||
spannode.appendChild(middleclone);
|
||||
middlebit.parentNode.replaceChild(spannode, middlebit);
|
||||
skip = 1;
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
else if (node.nodeType == 1 && node.childNodes && !/(script|style)/i.test(node.tagName)) {
|
||||
for (var i = 0; i < node.childNodes.length; ++i) {
|
||||
i += innerHighlight(node.childNodes[i], pat);
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
return skip;
|
||||
}
|
||||
return this.each(function() {
|
||||
innerHighlight(this, pat.toUpperCase());
|
||||
});
|
||||
};
|
||||
|
||||
jQuery.fn.removeHighlight = function() {
|
||||
function newNormalize(node) {
|
||||
for (var i = 0, children = node.childNodes, nodeCount = children.length; i < nodeCount; i++) {
|
||||
var child = children[i];
|
||||
if (child.nodeType == 1) {
|
||||
newNormalize(child);
|
||||
continue;
|
||||
}
|
||||
if (child.nodeType != 3) { continue; }
|
||||
var next = child.nextSibling;
|
||||
if (next == null || next.nodeType != 3) { continue; }
|
||||
var combined_text = child.nodeValue + next.nodeValue;
|
||||
new_node = node.ownerDocument.createTextNode(combined_text);
|
||||
node.insertBefore(new_node, child);
|
||||
node.removeChild(child);
|
||||
node.removeChild(next);
|
||||
i--;
|
||||
nodeCount--;
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
return this.find("span.founds").each(function() {
|
||||
var thisParent = this.parentNode;
|
||||
thisParent.replaceChild(this.firstChild, this);
|
||||
newNormalize(thisParent);
|
||||
}).end();
|
||||
};
|
||||
223
assets/index.js
Normal file
223
assets/index.js
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,223 @@
|
||||
// 显示列表
|
||||
showList = (text, index, listnum) => {
|
||||
window.info = [];
|
||||
Object.keys(index).filter(path => {
|
||||
let description = index[path];
|
||||
let p = path.split('.html#')
|
||||
if (p.length == 2) {
|
||||
var type = `<div class="type">${p[0]}</div>`;
|
||||
var name = p[1];
|
||||
} else {
|
||||
var type = '';
|
||||
name = p[0].replace('.html', '');
|
||||
}
|
||||
let reg = new RegExp(text, "i");
|
||||
let match1 = reg.exec(name);
|
||||
let match2 = reg.exec(description)
|
||||
if (match1 || match2) {
|
||||
let index = name.slice(0, 1).toUpperCase();
|
||||
if (match1) name = highlightList(name, match1[0]);
|
||||
if (match2) description = highlightList(description, match2[0]);
|
||||
window.info.push(`<div class='info' path='${path}'>
|
||||
<div class="index">${index}</div>
|
||||
${type}
|
||||
<div class="name">${name}</div>
|
||||
<div class="description">${description}</div>
|
||||
</div>`);
|
||||
}
|
||||
})
|
||||
$("#mainlist").html(window.info.slice(0, listnum).join(''));
|
||||
$(".info:first").addClass('select');
|
||||
let num = $(".info").length
|
||||
utools.setExpendHeight(num > 11 ? 550 : 50 * num);
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// 显示手册
|
||||
showManual = path => {
|
||||
utools.setExpendHeight(550);
|
||||
if (/^((ht|f)tps?):\/\//.test(path)) {
|
||||
window.open(path);
|
||||
} else {
|
||||
let p = path.split('.html#')
|
||||
if (p.length == 2) {
|
||||
var file = p[0] + '.html';
|
||||
var id = '#' + p[1];
|
||||
} else {
|
||||
var file = p[0]
|
||||
}
|
||||
window.read(`docs/${window.code}/${file}`, (err, data) => {
|
||||
if (!err) {
|
||||
$("#mainlist").fadeOut();
|
||||
$("#content").fadeOut().promise().done(() => {
|
||||
$("#content").html(`<div id="head">${data}</head>`).fadeIn();
|
||||
if (p.length == 2) {
|
||||
location.href = id;
|
||||
} else {
|
||||
location.href = '#head'
|
||||
}
|
||||
})
|
||||
}
|
||||
})
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// 手册搜索结果高亮
|
||||
highlightManual = text => {
|
||||
$("#content").removeHighlight() ;
|
||||
if (text) {
|
||||
$("#content").highlight(text);
|
||||
window.findex = 0;
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// 列表搜索结果高亮
|
||||
highlightList = (string, match) => string.replace(match, `<span style="color:#ff5722">${match}</span>`)
|
||||
|
||||
// 隐藏所有窗口
|
||||
init = () => {
|
||||
$("#mainlist").fadeOut(0);
|
||||
$("#options").fadeOut(0);
|
||||
$("#content").fadeOut(0);
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// 切换列表和手册视图
|
||||
toggleView = () => {
|
||||
if ($('#content').is(':hidden')) {
|
||||
$('#content').fadeIn();
|
||||
$("#mainlist").fadeOut();
|
||||
} else {
|
||||
$("#content").fadeOut();
|
||||
$("#mainlist").fadeIn();
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// 加载剩余列表
|
||||
loadList = listnum => {
|
||||
if ($(window).scrollTop() >= (listnum * 50 - 550) && $(".info").length <= listnum) {
|
||||
$("#mainlist").append(window.info.slice(listnum).join(''));
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// 进入插件
|
||||
utools.onPluginEnter(({ code, type, payload }) => {
|
||||
init();
|
||||
if (code == 'options') {
|
||||
showOptions();
|
||||
} else {
|
||||
window.code = code;
|
||||
$("#mainlist").fadeIn();
|
||||
// 读取目录文件
|
||||
window.read(`index/${code}.json`, (err, data) => {
|
||||
let index = JSON.parse(data);
|
||||
if (type == 'over') {
|
||||
showList(payload, index, 500)
|
||||
} else {
|
||||
showList('', index, 500)
|
||||
}
|
||||
// 子输入框
|
||||
utools.setSubInput(({ text }) => {
|
||||
if ($('#content').is(':hidden')) {
|
||||
showList(text, index, 500);
|
||||
} else {
|
||||
highlightManual(text);
|
||||
}
|
||||
}, '输入名称或功能进行查询');
|
||||
});
|
||||
}
|
||||
});
|
||||
|
||||
// 单击列表,显示手册
|
||||
$("#mainlist").on('mousedown', '.info', function (e) {
|
||||
if (1 == e.which) {
|
||||
showManual($(".select").attr('path'));
|
||||
}
|
||||
});
|
||||
|
||||
// 鼠标滑过列表,高亮
|
||||
$("#mainlist").on('mouseover', '.info', function () {
|
||||
$(".select").removeClass('select');
|
||||
$(this).addClass('select');
|
||||
});
|
||||
|
||||
// 右键单击手册,退出手册
|
||||
$("#content").on('mousedown', function (e) {
|
||||
if (3 == e.which) {
|
||||
toggleView();
|
||||
}
|
||||
})
|
||||
|
||||
// 手册中a标签
|
||||
$("#content").on('mousedown', 'a', function (e) {
|
||||
if (1 == e.which) {
|
||||
showManual($(this).attr('href'));
|
||||
}
|
||||
});
|
||||
|
||||
// 滚动到边界加载列表
|
||||
$(document).scroll(() => {
|
||||
loadList(500);
|
||||
})
|
||||
|
||||
// 按键监听
|
||||
$(document).keydown(e => {
|
||||
switch (e.keyCode) {
|
||||
// TAB
|
||||
case 9:
|
||||
toggleView();
|
||||
break;
|
||||
// 回车
|
||||
case 13:
|
||||
// 列表界面进入手册
|
||||
if ($('#content').is(':hidden')) {
|
||||
showManual($(".select").attr('path'));
|
||||
// 手册界面搜索下一个
|
||||
} else {
|
||||
if (window.findex > 0) {
|
||||
$(`.founds:eq(${window.findex - 1})`).removeClass('firstFound');
|
||||
} else {
|
||||
$('.founds:last').removeClass('firstFound');
|
||||
}
|
||||
$(`.founds:eq(${window.findex})`).addClass('firstFound');
|
||||
$('.firstFound').get(0).scrollIntoView({ behavior: "smooth", block: "nearest" });
|
||||
if (window.findex == $('.founds').length - 1) {
|
||||
window.findex = 0;
|
||||
} else {
|
||||
window.findex += 1;
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
break;
|
||||
// 上
|
||||
case 38:
|
||||
let pre = $(".select").prev();
|
||||
// 没有到达边界时移动选择条
|
||||
if(pre.length != 0){
|
||||
event.preventDefault();
|
||||
if(pre.offset().top < $(window).scrollTop()){
|
||||
$("html").animate({ scrollTop: "-=50" }, 0);
|
||||
}
|
||||
pre.addClass("select");
|
||||
$(".select:last").removeClass("select");
|
||||
// 到达边界闪烁移动选择条
|
||||
}else{
|
||||
$(".select").animate({"opacity":"0.3"}).delay(500).animate({"opacity":"1"})
|
||||
}
|
||||
break;
|
||||
// 下
|
||||
case 40:
|
||||
let next = $(".select").next();
|
||||
// 没有到达边界时移动选择条
|
||||
if(next.length !=0){
|
||||
event.preventDefault();
|
||||
if(next.offset().top >= $(window).scrollTop() + 500){
|
||||
$("html").animate({ scrollTop: "+=50" }, 0);
|
||||
}
|
||||
loadList(500);
|
||||
next.addClass("select");
|
||||
$(".select:first").removeClass("select");
|
||||
// 到达边界闪烁移动选择条
|
||||
}else{
|
||||
$(".select").animate({"opacity":"0.3"}).delay(500).animate({"opacity":"1"})
|
||||
}
|
||||
break;
|
||||
}
|
||||
});
|
||||
2
assets/jquery-3.3.1.min.js
vendored
Normal file
2
assets/jquery-3.3.1.min.js
vendored
Normal file
File diff suppressed because one or more lines are too long
1346
assets/manual.css
Normal file
1346
assets/manual.css
Normal file
File diff suppressed because it is too large
Load Diff
157
assets/options.css
Normal file
157
assets/options.css
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,157 @@
|
||||
#options {
|
||||
display: none;
|
||||
font-size: 15px;
|
||||
color: #595959
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
#options *{
|
||||
margin: 0;
|
||||
padding: 0;
|
||||
box-sizing: border-box;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
#options .switch-btn {
|
||||
position: relative;
|
||||
display: inline-block;
|
||||
vertical-align: top;
|
||||
width: 80px;
|
||||
height: 30px;
|
||||
border-radius: 18px;
|
||||
cursor: pointer;
|
||||
zoom: 0.6;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
#options .checked-switch {
|
||||
position: absolute;
|
||||
top: 0;
|
||||
left: 0;
|
||||
opacity: 0;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
#options .text-switch {
|
||||
background-color: #ed5b49;
|
||||
border: 1px solid #d2402e;
|
||||
border-radius: inherit;
|
||||
color: #fff;
|
||||
display: block;
|
||||
font-size: 15px;
|
||||
width: 50px;
|
||||
height: inherit;
|
||||
position: relative;
|
||||
text-transform: uppercase;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
#options .text-switch:before,
|
||||
#options .text-switch:after {
|
||||
position: absolute;
|
||||
top: 50%;
|
||||
margin-top: -.5em;
|
||||
line-height: 1;
|
||||
-webkit-transition: inherit;
|
||||
-moz-transition: inherit;
|
||||
-o-transition: inherit;
|
||||
transition: inherit;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
#options .text-switch:before {
|
||||
content: attr(data-no);
|
||||
right: 11px;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
#options .text-switch:after {
|
||||
content: attr(data-yes);
|
||||
left: 11px;
|
||||
color: #FFFFFF;
|
||||
opacity: 0;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
#options .checked-switch:checked~.text-switch {
|
||||
background-color: #00af2c;
|
||||
border: 1px solid #068506;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
#options .checked-switch:disabled~.text-switch {
|
||||
background-color: #9E9E9E!important;
|
||||
border: 1px solid #9E9E9E !important;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
#options .checked-switch:checked~.text-switch:before {
|
||||
opacity: 0;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
#options .checked-switch:checked~.text-switch:after {
|
||||
opacity: 1;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
#options .toggle-btn {
|
||||
background: linear-gradient(#eee, #fafafa);
|
||||
border-radius: 100%;
|
||||
height: 28px;
|
||||
left: 1px;
|
||||
position: absolute;
|
||||
top: 1px;
|
||||
width: 28px;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
#options .checked-switch:checked~.toggle-btn {
|
||||
left: 20px;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
#options .text-switch,
|
||||
#options .toggle-btn {
|
||||
transition: All 0.3s ease;
|
||||
-webkit-transition: All 0.3s ease;
|
||||
-moz-transition: All 0.3s ease;
|
||||
-o-transition: All 0.3s ease;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
#options .no-radius,
|
||||
#options .no-radius .toggle-btn {
|
||||
border-radius: 0;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
#options .circle-style .toggle-btn::before {
|
||||
background: linear-gradient(#dedede, #cacaca);
|
||||
border-radius: 50%;
|
||||
content: "";
|
||||
height: 14px;
|
||||
margin-top: 6px;
|
||||
padding: 0;
|
||||
width: 14px;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
#options table {
|
||||
border-collapse: collapse;
|
||||
width: 100%;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
#options table td {
|
||||
border-collapse: collapse;
|
||||
padding: 12px 9px;
|
||||
word-break: break-all;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
#options table tr:nth-child(odd) {
|
||||
background-color: #fff !important;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
#options table tr:nth-child(even) {
|
||||
background-color: #f8f8f8 !important;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
#options .keyword {
|
||||
display: inline-block;
|
||||
font-size: 14px;
|
||||
color: #333;
|
||||
border: 1px solid #eee;
|
||||
border-radius: 12px;
|
||||
height: 24px;
|
||||
line-height: 22px;
|
||||
padding: 0 10px;
|
||||
background-color: #f3f3f3;
|
||||
margin-right: 5px
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
#options img{
|
||||
width: 32px;
|
||||
}
|
||||
124
assets/options.js
Normal file
124
assets/options.js
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,124 @@
|
||||
// 默认手册
|
||||
getDefaultFeatures = () => {
|
||||
return {
|
||||
"linux": {
|
||||
"code": "linux",
|
||||
"explain": "linux命令大全",
|
||||
"cmds": ["linux命令"],
|
||||
"icon": "logo/linux.png"
|
||||
},
|
||||
"php": {
|
||||
"code": "php",
|
||||
"explain": "官方php函数文档",
|
||||
"cmds": ["php函数"],
|
||||
"icon": "logo/php.png"
|
||||
},
|
||||
"python": {
|
||||
"code": "python",
|
||||
"explain": "官方python标准库及常用第三方库文档",
|
||||
"cmds": ["python库"],
|
||||
"icon": "logo/python.png"
|
||||
},
|
||||
"c": {
|
||||
"code": "c",
|
||||
"explain": "C语言函数速查",
|
||||
"cmds": ["C函数"],
|
||||
"icon": "logo/c.png"
|
||||
},
|
||||
"vim": {
|
||||
"code": "vim",
|
||||
"explain": "vim命令大全",
|
||||
"cmds": ["vim命令"],
|
||||
"icon": "logo/vim.png"
|
||||
},
|
||||
"git": {
|
||||
"code": "git",
|
||||
"explain": "git命令概览",
|
||||
"cmds": ["git命令"],
|
||||
"icon": "logo/git.png"
|
||||
},
|
||||
"docker": {
|
||||
"code": "docker",
|
||||
"explain": "docker常用命令",
|
||||
"cmds": ["docker命令"],
|
||||
"icon": "logo/docker.png"
|
||||
},
|
||||
"sql": {
|
||||
"code": "sql",
|
||||
"explain": "sql操作手册",
|
||||
"cmds": ["sql手册"],
|
||||
"icon": "logo/sql.png"
|
||||
},
|
||||
"utools": {
|
||||
"code": "utools",
|
||||
"explain": "uTools的API文档",
|
||||
"cmds": ["uToolsAPI"],
|
||||
"icon": "logo/utools.png"
|
||||
}
|
||||
};
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// 配置页面
|
||||
showOptions = () => {
|
||||
$("#options").show();
|
||||
const dFeatures = getDefaultFeatures();
|
||||
var cFeatures = utools.getFeatures();
|
||||
let featureList = '<table><tr><td></td><td>关键字</td><td>说明</td><td>启用</td><td>主输入框搜索</td></tr>';
|
||||
for (var f in dFeatures) {
|
||||
var cmds = '';
|
||||
dFeatures[f].cmds.forEach(cmd => {
|
||||
if (typeof (cmd) == "string") cmds += `<span class="keyword">${cmd}</span>`;
|
||||
});
|
||||
var isChecked1 = '';
|
||||
var isChecked2 = '';
|
||||
var isDisabled = 'disabled';
|
||||
for(var c of cFeatures){
|
||||
if (c.code == dFeatures[f].code) {
|
||||
isChecked1 = 'checked';
|
||||
isDisabled = '';
|
||||
if (typeof(c.cmds[c.cmds.length - 1]) != 'string') isChecked2 = 'checked';
|
||||
break;
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
featureList += `<tr><td><img src="logo/${dFeatures[f].code}.png"></td>
|
||||
<td>${cmds}</td><td>${dFeatures[f].explain}</td><td>
|
||||
<label class="switch-btn">
|
||||
<input class="checked-switch" id="${dFeatures[f].code}_1" type="checkbox" ${isChecked1}>
|
||||
<span class="text-switch"></span>
|
||||
<span class="toggle-btn"></span>
|
||||
</label></td><td>
|
||||
<label class="switch-btn">
|
||||
<input class="checked-switch" id="${dFeatures[f].code}_2" type="checkbox" ${isDisabled} ${isChecked2}>
|
||||
<span class="text-switch"></span>
|
||||
<span class="toggle-btn"></span>
|
||||
</label></td>`
|
||||
};
|
||||
featureList += '</tr></table>'
|
||||
$("#options").html(featureList);
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// 监听开关
|
||||
$("#options").on('change', 'input[type=checkbox]', function () {
|
||||
const dFeatures = getDefaultFeatures();
|
||||
var id = $(this).attr('id').split('_');
|
||||
var code = id[0]
|
||||
if (id[1] == '1') {
|
||||
if (!utools.removeFeature(code)) {
|
||||
utools.setFeature(dFeatures[code]);
|
||||
$(`#${code}_2`).prop('disabled', false);
|
||||
} else {
|
||||
$(`#${code}_2`).prop('checked', false);
|
||||
$(`#${code}_2`).prop('disabled', true);
|
||||
}
|
||||
} else {
|
||||
var featureConf = dFeatures[code];
|
||||
if($(this).prop('checked')){
|
||||
featureConf.cmds.push({
|
||||
"type": "over",
|
||||
"label": featureConf.cmds[0],
|
||||
"maxLength": 50
|
||||
});
|
||||
}
|
||||
utools.setFeature(featureConf);
|
||||
}
|
||||
});
|
||||
88
assets/style.css
Normal file
88
assets/style.css
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,88 @@
|
||||
#mainlist {
|
||||
position: absolute;
|
||||
left: 0;
|
||||
right: 0;
|
||||
top: 0;
|
||||
bottom: 0;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
#mainlist .info {
|
||||
background: #f5f5f533;
|
||||
cursor: pointer;
|
||||
height: 50px;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
#mainlist .name {
|
||||
padding-top: 10px;
|
||||
font-family: "consolas";
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
#mainlist .type {
|
||||
float: right;
|
||||
margin: 15px 10px;
|
||||
height: 20px;
|
||||
color: #666666
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
#mainlist .description {
|
||||
color: #888888;
|
||||
font-size: small;
|
||||
font-family: "consolas";
|
||||
white-space: nowrap;
|
||||
overflow: hidden;
|
||||
text-overflow: ellipsis
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
#mainlist .index {
|
||||
float: left;
|
||||
margin: 15px 10px;
|
||||
height: 20px;
|
||||
font-size: 20px;
|
||||
font-weight: bold;
|
||||
font-family: "courier new",微软雅黑;
|
||||
color: #2196F3;
|
||||
text-shadow: 1px 1px black;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
#mainlist .select{
|
||||
background: #ebebeb;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
#content {
|
||||
position: fixed;
|
||||
left: 0;
|
||||
right: 0;
|
||||
top: 0;
|
||||
bottom: 0;
|
||||
display: none;
|
||||
overflow: auto;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
.founds {
|
||||
background-color: #ff572236;
|
||||
color: #fd4005;
|
||||
border-radius: 4px;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
.firstFound{
|
||||
box-shadow: 0px 0px 5px 1px #FF5722;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
::-webkit-scrollbar
|
||||
{
|
||||
width: 7px;
|
||||
height: 5px;
|
||||
background-color: #F5F5F5;
|
||||
}
|
||||
::-webkit-scrollbar-track
|
||||
{
|
||||
box-shadow:inset 0 0 6px rgba(0, 0, 0, 0.2);
|
||||
border-radius:5px;
|
||||
background-color:#F5F5F5;
|
||||
}
|
||||
::-webkit-scrollbar-thumb
|
||||
{
|
||||
border-radius:5px;
|
||||
box-shadow:inset 0 0 6px rgba(0,0,0,.3);
|
||||
background-color:#959da5;
|
||||
}
|
||||
30
docs/c/ClearScreen.html
Normal file
30
docs/c/ClearScreen.html
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,30 @@
|
||||
<h1>标准库函数 - ClearScreen</h1>
|
||||
<p>原型:extern void clrscr(void);<br>
|
||||
extern void ClearScreen(void);</p>
|
||||
<p>用法:#include <system.h></p>
|
||||
<p>功能:清屏</p>
|
||||
<p>说明:清除屏幕缓冲区及液晶显示缓冲区
|
||||
<p>光标位置回到屏幕左上角。</p>
|
||||
|
||||
举例:
|
||||
<pre>
|
||||
// clrscr.c
|
||||
|
||||
#include <system.h>
|
||||
|
||||
main()
|
||||
{
|
||||
clrscr();
|
||||
textmode(0x00);
|
||||
|
||||
printf("Press a key");
|
||||
getchar();
|
||||
ClearScreen();
|
||||
|
||||
printf("Another Screen");
|
||||
getchar();
|
||||
return 0;
|
||||
}
|
||||
</pre>
|
||||
相关函数:无
|
||||
|
||||
45
docs/c/DispBCD.html
Normal file
45
docs/c/DispBCD.html
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,45 @@
|
||||
<h1>标准库函数 - DispBCD</h1>
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
<p>原型:extern void DispBCD(int);</p>
|
||||
|
||||
<p>用法:#include <system.h></p>
|
||||
|
||||
<p>功能:显示七段数码管数字</p>
|
||||
|
||||
<p>说明:调用后在屏幕左侧图标区显示对应数字。</p>
|
||||
显示最大值为999。
|
||||
|
||||
举例:<pre>
|
||||
|
||||
// DispBCD.c
|
||||
|
||||
#include <system.h>
|
||||
|
||||
main()
|
||||
{
|
||||
int i;
|
||||
|
||||
i=9;
|
||||
clrscr();
|
||||
printf("Now Display 9");
|
||||
DispBCD(9);
|
||||
getchar();
|
||||
|
||||
i=99;
|
||||
clrscr();
|
||||
printf("Now Display 99");
|
||||
DispBCD(99);
|
||||
getchar();
|
||||
|
||||
i=999;
|
||||
clrscr();
|
||||
printf("Now Display 99");
|
||||
DispBCD(999);
|
||||
getchar();
|
||||
|
||||
return 0;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
</pre>相关函数:无
|
||||
|
||||
36
docs/c/SetScrollBar.html
Normal file
36
docs/c/SetScrollBar.html
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,36 @@
|
||||
<h1>标准库函数 - SetScrollBar</h1>
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
<p>原型:extern void SetDispBar(int sum, int cur);</p>
|
||||
|
||||
<p>用法:#include <system.h></p>
|
||||
|
||||
<p>功能:显示滚动条</p>
|
||||
|
||||
<p>说明:调用后在屏幕左侧图标区显示百分比滚动条。</p>
|
||||
sum为总长度,cur为当前位置。
|
||||
|
||||
举例:<pre>
|
||||
|
||||
// SetScrollBar.c
|
||||
|
||||
#include <system.h>
|
||||
|
||||
main()
|
||||
{
|
||||
int i;
|
||||
|
||||
clrscr();
|
||||
printf("Scroll Bar Test");
|
||||
for(i=0;i<60;i+=5)
|
||||
{
|
||||
SetScrollBar(60,i);
|
||||
sleep(1);
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
getchar();
|
||||
return 0;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
</pre>相关函数:无
|
||||
|
||||
43
docs/c/TextOut.html
Normal file
43
docs/c/TextOut.html
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,43 @@
|
||||
<h1>标准库函数 - TextOut</h1>
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
<p>原型:extern void TextOut(int x, int y, char *str, int mode);</p>
|
||||
|
||||
<p>用法:#include <system.h></p>
|
||||
|
||||
<p>功能:在屏幕上指定位置输出字符串</p>
|
||||
|
||||
<p>说明:outtextxy为指向TextOut的宏,用法相同。</p>
|
||||
<pre>
|
||||
|
||||
str所指向字符串可以为中文或英文。中文显示成16x16点阵,英文显示成8x16点阵。
|
||||
mode决定往屏幕上写的方式,其值含义如下:
|
||||
0:背景透明,点阵中为0的点不显示。
|
||||
1:正常方式,即点阵中为0的点擦除,为1的点显示。
|
||||
2:反显方式,即点阵中为1的点擦除,为0的点显示。
|
||||
3:异或方式,即点阵中点的值和屏幕当前位置的值作异或后取值,为0则擦除,为1显示。
|
||||
</pre>
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
举例:<pre>
|
||||
|
||||
// TextOut.c
|
||||
|
||||
#include <system.h>
|
||||
|
||||
main()
|
||||
{
|
||||
clrscr();
|
||||
|
||||
TextOut(0,0,"文曲星",1);
|
||||
TextOut(10,10,"文曲星",0);
|
||||
|
||||
TextOut(20,20,"您好",2);
|
||||
TextOut(30,30,"GGV-金远见",3);
|
||||
|
||||
getchar();
|
||||
return 0;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
</pre>相关函数:无
|
||||
|
||||
56
docs/c/UpdateLCD.html
Normal file
56
docs/c/UpdateLCD.html
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,56 @@
|
||||
<h1>标准库函数 - UpdateLCD</h1>
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
<p>原型:extern void UpdateLCD(unsigned int mode);</p>
|
||||
|
||||
<p>用法:#include <system.h></p>
|
||||
|
||||
<p>功能:以指定模式刷新屏幕</p>
|
||||
|
||||
<p>说明:文曲星屏幕可以按大行(行高16点)或小行(行高8点)显示。</p>
|
||||
<pre>
|
||||
以CC300的屏幕为例,液晶分辨率为112*48即横向可显示112点,纵向可显示48点
|
||||
由于一个大行占据16点,小行占据8点,故可显示48/16=3大行,或48/8=6小行。
|
||||
大行和小行可以同屏显示。具体哪一行为大行,娜一行为小行由mode来决定。
|
||||
mode低字节从bit7-bit0每一位代表一行,为1表示大行,为0表示小行。举例如下:
|
||||
mode值 对应二进制值 屏幕显示状态
|
||||
0xE0 11100000 三大行
|
||||
0xC0 11000000 两大行,两小行
|
||||
0x80 10000000 一大行,四小行
|
||||
0x00 00000000 六小行
|
||||
0x20 00100000 两小行,一大行,两小行
|
||||
0x40 01000000 一小行,一大行,三小行
|
||||
...
|
||||
|
||||
以此类推。
|
||||
</pre>
|
||||
举例:<pre>
|
||||
|
||||
// TextOut.c
|
||||
|
||||
#include <system.h>
|
||||
|
||||
main()
|
||||
{
|
||||
clrscr();
|
||||
printf("Line 1\n");
|
||||
printf("Line 2\n");
|
||||
printf("Line 3\n");
|
||||
printf("Line 4\n");
|
||||
printf("Line 5\n");
|
||||
printf("Line 6\n");
|
||||
|
||||
UpdateLCD(0x00); // all are visible
|
||||
getchar();
|
||||
UpdateLCD(0xE0); // only first 3 lines visible
|
||||
getchar();
|
||||
UpdateLCD(0x40); // line 6 invisible
|
||||
getchar();
|
||||
UpdateLCD(0x20); // line 6 invisible
|
||||
|
||||
getchar();
|
||||
return 0;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
</pre>相关函数:<a href="textmode.html">textmode</a>
|
||||
|
||||
37
docs/c/abs.html
Normal file
37
docs/c/abs.html
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,37 @@
|
||||
<h1>数学函数 - abs</h1>
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
<p>原型:extern int abs(int x);</p>
|
||||
|
||||
<p>用法:#include <math.h></p>
|
||||
|
||||
<p>功能:求整数x的绝对值</p>
|
||||
|
||||
<p>说明:计算|x|, 当x不为负时返回x,否则返回-x</p>
|
||||
|
||||
举例:<pre>
|
||||
|
||||
// abs.c
|
||||
|
||||
#include <syslib.h>
|
||||
#include <math.h>
|
||||
|
||||
main()
|
||||
{
|
||||
int x;
|
||||
|
||||
clrscr(); // clear screen
|
||||
|
||||
x=-5;
|
||||
printf("|%d|=%d\n",x,abs(x));
|
||||
x=0;
|
||||
printf("|%d|=%d\n",x,abs(x));
|
||||
x=+5;
|
||||
printf("|%d|=%d\n",x,abs(x));
|
||||
|
||||
getchar();
|
||||
return 0;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
</pre>相关函数:<a href="fabs.html">fabs</a>
|
||||
|
||||
34
docs/c/acos.html
Normal file
34
docs/c/acos.html
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,34 @@
|
||||
<h1>数学函数 - acos</h1>
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
<p>原型:extern float acos(float x);</p>
|
||||
|
||||
<p>用法:#include <math.h></p>
|
||||
|
||||
<p>功能:求x(弧度表示)的反余弦值</p>
|
||||
|
||||
<p>说明:x的定义域为[-1.0,1.0],值域为[0,π]。</p>
|
||||
|
||||
举例:<pre>
|
||||
|
||||
// acos.c
|
||||
|
||||
#include <syslib.h>
|
||||
#include <math.h>
|
||||
|
||||
main()
|
||||
{
|
||||
float x;
|
||||
|
||||
clrscr(); // clear screen
|
||||
textmode(0x00); // 6 lines per LCD screen
|
||||
|
||||
x=0.32;
|
||||
printf("acos(%.2f)=%.4f",x,acos(x));
|
||||
|
||||
getchar();
|
||||
return 0;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
</pre>相关函数:<a href="asin.html">asin</a>,<a href="atan.html">atan</a>,<a href="atan2.html">atan2</a>,<a href="sin.html">sin</a>,<a href="cos.html">cos</a>,<a href="tan.html">tan</a>
|
||||
|
||||
34
docs/c/asin.html
Normal file
34
docs/c/asin.html
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,34 @@
|
||||
<h1>数学函数 - asin</h1>
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
<p>原型:extern float asin(float x);</p>
|
||||
|
||||
<p>用法:#include <math.h></p>
|
||||
|
||||
<p>功能:求x(弧度表示)的反正弦值</p>
|
||||
|
||||
<p>说明:x的定义域为[-1.0,1.0],值域为[-π/2,+π/2]。</p>
|
||||
|
||||
举例:<pre>
|
||||
|
||||
// asin.c
|
||||
|
||||
#include <syslib.h>
|
||||
#include <math.h>
|
||||
|
||||
main()
|
||||
{
|
||||
float x;
|
||||
|
||||
clrscr(); // clear screen
|
||||
textmode(0x00); // 6 lines per LCD screen
|
||||
|
||||
x=0.32;
|
||||
printf("asin(%.2f)=%.4f",x,asin(x));
|
||||
|
||||
getchar();
|
||||
return 0;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
</pre>相关函数:<a href="acos.html">acos</a>,<a href="atan.html">atan</a>,<a href="atan2.html">atan2</a>,<a href="sin.html">sin</a>,<a href="cos.html">cos</a>,<a href="tan.html">tan</a>
|
||||
|
||||
34
docs/c/atan.html
Normal file
34
docs/c/atan.html
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,34 @@
|
||||
<h1>数学函数 - atan</h1>
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
<p>原型:extern float atan(float x);</p>
|
||||
|
||||
<p>用法:#include <math.h></p>
|
||||
|
||||
<p>功能:求x(弧度表示)的反正切值</p>
|
||||
|
||||
<p>说明:值域为(-π/2,+π/2)。</p>
|
||||
|
||||
举例:<pre>
|
||||
|
||||
// atan.c
|
||||
|
||||
#include <syslib.h>
|
||||
#include <math.h>
|
||||
|
||||
main()
|
||||
{
|
||||
float x;
|
||||
|
||||
clrscr(); // clear screen
|
||||
textmode(0x00); // 6 lines per LCD screen
|
||||
|
||||
x=0.32;
|
||||
printf("atan(%.2f)=%.4f",x,atan(x));
|
||||
|
||||
getchar();
|
||||
return 0;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
</pre>相关函数:<a href="asin.html">asin</a>,<a href="acos.html">acos</a>,<a href="atan2.html">atan2</a>,<a href="sin.html">sin</a>,<a href="cos.html">cos</a>,<a href="tan.html">tan</a>
|
||||
|
||||
35
docs/c/atan2.html
Normal file
35
docs/c/atan2.html
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,35 @@
|
||||
<h1>数学函数 - atan2</h1>
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
<p>原型:extern float atan2(float y, float x);</p>
|
||||
|
||||
<p>用法:#include <math.h></p>
|
||||
|
||||
<p>功能:求y/x(弧度表示)的反正切值</p>
|
||||
|
||||
<p>说明:值域为(-π/2,+π/2)。</p>
|
||||
|
||||
举例:<pre>
|
||||
|
||||
// atan2.c
|
||||
|
||||
#include <syslib.h>
|
||||
#include <math.h>
|
||||
|
||||
main()
|
||||
{
|
||||
float x,y;
|
||||
|
||||
clrscr(); // clear screen
|
||||
textmode(0x00); // 6 lines per LCD screen
|
||||
|
||||
x=0.064;
|
||||
y=0.2;
|
||||
printf("atan2(%.3f,%.2f)=%.4f",y,x,atan2(y,x));
|
||||
|
||||
getchar();
|
||||
return 0;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
</pre>相关函数:<a href="asin.html">asin</a>,<a href="acos.html">acos</a>,<a href="atan.html">atan</a>,<a href="sin.html">sin</a>,<a href="cos.html">cos</a>,<a href="tan.html">tan</a>
|
||||
|
||||
42
docs/c/bcmp.html
Normal file
42
docs/c/bcmp.html
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,42 @@
|
||||
<h1>字符串函数 - bcmp</h1>
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
<p>原型:extern int bcmp(const void *s1, const void *s2, int n);</p>
|
||||
|
||||
<p>用法:#include <string.h></p>
|
||||
|
||||
<p>功能:比较字符串s1和s2的前n个字节是否相等</p>
|
||||
|
||||
<p>说明:如果s1=s2或n=0则返回零,否则返回非零值。bcmp不检查NULL。</p>
|
||||
|
||||
举例:<pre>
|
||||
|
||||
// bcmp.c
|
||||
|
||||
#include <syslib.h>
|
||||
#include <string.h>
|
||||
|
||||
main()
|
||||
{
|
||||
char *s1="Golden Global View";
|
||||
char *s2="Golden global view";;
|
||||
|
||||
clrscr(); // clear screen
|
||||
if(!bcmp(s1,s2,7))
|
||||
printf("s1 equal to s2 in first 7 bytes");
|
||||
else
|
||||
printf("s1 not equal to s2 in first 7 bytes");
|
||||
|
||||
getchar();
|
||||
clrscr();
|
||||
if(!bcmp(s1,s2,12))
|
||||
printf("s1 equal to s2 in first 12 bytes");
|
||||
else
|
||||
printf("s1 not equal to s2 in first 12 bytes");
|
||||
|
||||
getchar();
|
||||
return 0;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
</pre>相关函数:<a href="bcopy.html">bcopy</a>,<a href="bzero.html">bzero</a>
|
||||
|
||||
42
docs/c/bcopy.html
Normal file
42
docs/c/bcopy.html
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,42 @@
|
||||
<h1>字符串函数 - bcopy</h1>
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
<p>原型:extern void bcopy(const void *src, void *dest, int n);</p>
|
||||
|
||||
<p>用法:#include <string.h></p>
|
||||
|
||||
<p>功能:将字符串src的前n个字节复制到dest中</p>
|
||||
|
||||
<p>说明:bcopy不检查字符串中的空字节NULL,函数没有返回值。</p>
|
||||
|
||||
举例:<pre>
|
||||
|
||||
// bcopy.c
|
||||
|
||||
#include <syslib.h>
|
||||
#include <string.h>
|
||||
|
||||
main()
|
||||
{
|
||||
char *s="Golden Global View";
|
||||
char d[20];
|
||||
|
||||
clrscr(); // clear screen
|
||||
bcopy(s,d,6);
|
||||
printf("s: %s\n",s);
|
||||
printf("d: %s\n",d);
|
||||
|
||||
getchar();
|
||||
clrscr();
|
||||
s[13]=0;
|
||||
bcopy(s+7,d,11); // bcopy ignore null in string
|
||||
printf("%s\n",s+7);
|
||||
for(i=0;i<11;i++)
|
||||
putchar(d[i]);
|
||||
|
||||
getchar();
|
||||
return 0;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
</pre>相关函数:<a href="bcmp.html">bcmp</a>,<a href="bzero.html">bzero</a>
|
||||
|
||||
39
docs/c/bell.html
Normal file
39
docs/c/bell.html
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,39 @@
|
||||
<h1>标准库函数 - bell</h1>
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
<p>原型:extern void bell(void);</p>
|
||||
|
||||
<p>用法:#include <system.h></p>
|
||||
|
||||
<p>功能:响铃</p>
|
||||
|
||||
<p>说明:当在文曲星中,如果所按键在当前功能中不可用,便会发出类似声音。</p>
|
||||
|
||||
举例:<pre>
|
||||
|
||||
// bell.c
|
||||
|
||||
#include <system.h>
|
||||
|
||||
main()
|
||||
{
|
||||
int c;
|
||||
|
||||
clrscr();
|
||||
printf("press any key\n");
|
||||
c=getchar();
|
||||
|
||||
while(c!=0x1b)
|
||||
{
|
||||
bell();
|
||||
c=getchar();
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
printf("Thank you!");
|
||||
|
||||
getchar();
|
||||
return 0;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
</pre>相关函数:无
|
||||
|
||||
45
docs/c/block.html
Normal file
45
docs/c/block.html
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,45 @@
|
||||
<h1>标准库函数 - block</h1>
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
<p>原型:extern void block(int left, int top, int right, int bottom, int mode);</p>
|
||||
|
||||
<p>用法:#include <system.h></p>
|
||||
|
||||
<p>功能:在屏幕上画一矩形并填充。</p>
|
||||
|
||||
<p>说明:(left,top)指定左上角坐标,(right,bottom)指定右下角坐标。<br>
|
||||
mode决定画图方式,其值含义如下:<br>
|
||||
0:清除方式<br>
|
||||
1:正常方式<br>
|
||||
2:反相方式<br>
|
||||
</p>
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
举例:<pre>
|
||||
|
||||
// block.c
|
||||
|
||||
#include <system.h>
|
||||
|
||||
main()
|
||||
{
|
||||
int c;
|
||||
|
||||
clrscr();
|
||||
gotoxy(10,10); // Hide cursor(moved out of screen)
|
||||
|
||||
block(1,0,111,47,1);
|
||||
getchar();
|
||||
|
||||
block(20,10,100,30,0);
|
||||
getchar();
|
||||
|
||||
block(40,0,80,47,2);
|
||||
getchar();
|
||||
|
||||
getchar();
|
||||
return 0;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
</pre>相关函数:<a href="rectangle.html">rectangle</a>
|
||||
|
||||
41
docs/c/bzero.html
Normal file
41
docs/c/bzero.html
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,41 @@
|
||||
<h1>字符串函数 - bzero</h1>
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
<p>原型:extern void bzero(void *s, int n);</p>
|
||||
|
||||
<p>用法:#include <string.h></p>
|
||||
|
||||
<p>功能:置字节字符串s的前n个字节为零。</p>
|
||||
|
||||
<p>说明:bzero无返回值。</p>
|
||||
|
||||
举例:<pre>
|
||||
|
||||
// bzero.c
|
||||
|
||||
#include <syslib.h>
|
||||
#include <string.h>
|
||||
|
||||
main()
|
||||
{
|
||||
struct
|
||||
{
|
||||
int a;
|
||||
char s[5];
|
||||
float f;
|
||||
} tt;
|
||||
|
||||
char s[20];
|
||||
|
||||
bzero(&tt,sizeof(tt)); // struct initialization to zero
|
||||
bzero(s,20);
|
||||
|
||||
clrscr();
|
||||
printf("Initail Success");
|
||||
|
||||
getchar();
|
||||
return 0;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
</pre>相关函数:<a href="bcmp.html">bcmp</a>,<a href="bcopy.html">bcopy</a>
|
||||
|
||||
39
docs/c/calloc.html
Normal file
39
docs/c/calloc.html
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,39 @@
|
||||
<h1>动态内存 - calloc</h1>
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
<p>原型:extern void *calloc(int num_elems, int elem_size);</p>
|
||||
|
||||
<p>用法:#include <alloc.h></p>
|
||||
|
||||
<p>功能:为具有num_elems个长度为elem_size元素的数组分配内存</p>
|
||||
|
||||
<p>说明:如果分配成功则返回指向被分配内存的指针,否则返回空指针NULL。<br>
|
||||
当内存不再使用时,应使用free()函数将内存块释放。</p>
|
||||
|
||||
举例:<pre>
|
||||
|
||||
// calloc.c
|
||||
|
||||
#include <syslib.h>
|
||||
#include <alloc.h>
|
||||
|
||||
main()
|
||||
{
|
||||
char *p;
|
||||
|
||||
clrscr(); // clear screen
|
||||
|
||||
p=(char *)calloc(100,sizeof(char));
|
||||
if(p)
|
||||
printf("Memory Allocated at: %x",p);
|
||||
else
|
||||
printf("Not Enough Memory!\n");
|
||||
|
||||
free(p);
|
||||
|
||||
getchar();
|
||||
return 0;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
</pre>相关函数:<a href="free.html">free</a>,<a href="malloc.html">malloc</a>,<a href="realloc.html">realloc</a>
|
||||
|
||||
36
docs/c/ceil.html
Normal file
36
docs/c/ceil.html
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,36 @@
|
||||
<h1>数学函数 - ceil</h1>
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
<p>原型:extern float ceil(float x);</p>
|
||||
|
||||
<p>用法:#include <math.h></p>
|
||||
|
||||
<p>功能:求不小于x的最小整数</p>
|
||||
|
||||
<p>说明:返回x的上限,如74.12的上限为75,-74.12的上限为-74。返回值为float类型。</p>
|
||||
|
||||
举例:<pre>
|
||||
|
||||
// ceil.c
|
||||
|
||||
#include <syslib.h>
|
||||
#include <math.h>
|
||||
|
||||
main()
|
||||
{
|
||||
float x;
|
||||
|
||||
clrscr(); // clear screen
|
||||
textmode(0x00); // 6 lines per LCD screen
|
||||
|
||||
x=74.12;
|
||||
printf("ceil(%.2f)=%.0f\n",x,ceil(x));
|
||||
x=-74.12;
|
||||
printf("ceil(%.2f)=%.0f\n",x,ceil(x));
|
||||
|
||||
getchar();
|
||||
return 0;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
</pre>相关函数:<a href="floor.html">floor</a>
|
||||
|
||||
35
docs/c/clrscr.html
Normal file
35
docs/c/clrscr.html
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,35 @@
|
||||
<h1>标准库函数 - clrscr</h1>
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
<p>原型:extern void clrscr(void);</p>
|
||||
extern void ClearScreen(void);
|
||||
|
||||
<p>用法:#include <system.h></p>
|
||||
|
||||
<p>功能:清屏</p>
|
||||
|
||||
<p>说明:清除屏幕缓冲区及液晶显示缓冲区<br>
|
||||
光标位置回到屏幕左上角。</p>
|
||||
|
||||
举例:<pre>
|
||||
|
||||
// clrscr.c
|
||||
|
||||
#include <system.h>
|
||||
|
||||
main()
|
||||
{
|
||||
clrscr();
|
||||
textmode(0x00);
|
||||
|
||||
printf("Press a key");
|
||||
getchar();
|
||||
ClearScreen();
|
||||
|
||||
printf("Another Screen");
|
||||
getchar();
|
||||
return 0;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
</pre>相关函数:无
|
||||
|
||||
34
docs/c/cos.html
Normal file
34
docs/c/cos.html
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,34 @@
|
||||
<h1>数学函数 - cos</h1>
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
<p>原型:extern float cos(float x);</p>
|
||||
|
||||
<p>用法:#include <math.h></p>
|
||||
|
||||
<p>功能:求x(弧度表示)的余弦值</p>
|
||||
|
||||
<p>说明:返回值在[-1.0,1.0]之间。</p>
|
||||
|
||||
举例:<pre>
|
||||
|
||||
// cos.c
|
||||
|
||||
#include <syslib.h>
|
||||
#include <math.h>
|
||||
|
||||
main()
|
||||
{
|
||||
float x;
|
||||
|
||||
clrscr(); // clear screen
|
||||
textmode(0x00); // 6 lines per LCD screen
|
||||
|
||||
x=PI/4.;
|
||||
printf("cos(%.4f)=%.4f\n",x,cos(x));
|
||||
|
||||
getchar();
|
||||
return 0;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
</pre>相关函数:<a href="asin.html">asin</a>,<a href="acos.html">acos</a>,<a href="atan.html">atan</a>,<a href="atan2.html">atan2</a>,<a href="sin.html">sin</a>,<a href="tan.html">tan</a>
|
||||
|
||||
34
docs/c/cosh.html
Normal file
34
docs/c/cosh.html
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,34 @@
|
||||
<h1>数学函数 - cosh</h1>
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
<p>原型:extern float cosh(float x);</p>
|
||||
|
||||
<p>用法:#include <math.h></p>
|
||||
|
||||
<p>功能:求x的双曲余弦值</p>
|
||||
|
||||
<p>说明:cosh(x)=(e^x+e^(-x))/2</p>
|
||||
|
||||
举例:<pre>
|
||||
|
||||
// cosh.c
|
||||
|
||||
#include <syslib.h>
|
||||
#include <math.h>
|
||||
|
||||
main()
|
||||
{
|
||||
float x;
|
||||
|
||||
clrscr(); // clear screen
|
||||
textmode(0x00); // 6 lines per LCD screen
|
||||
|
||||
x=PI/4.;
|
||||
printf("cosh(%.4f)=%.4f\n",x,cosh(x));
|
||||
|
||||
getchar();
|
||||
return 0;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
</pre>相关函数:<a href="sinh.html">sinh</a>,<a href="tanh.html">tanh</a>
|
||||
|
||||
29
docs/c/cursor.html
Normal file
29
docs/c/cursor.html
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,29 @@
|
||||
<h1>标准库函数 - cursor</h1>
|
||||
<pre>原型:extern void cursor(int mode);</pre>
|
||||
<pre>用法:#include <system.h></pre>
|
||||
<pre>功能:设定光标形态</pre>
|
||||
<pre>说明:mode值含义如下:0x00:块状光标(默认); 0x80:下划线光标; 其它值无意义</pre>
|
||||
|
||||
举例:
|
||||
<pre>
|
||||
// cursor.c
|
||||
|
||||
#include <system.h>
|
||||
|
||||
main()
|
||||
{
|
||||
int c;
|
||||
|
||||
clrscr();
|
||||
cursor(0x00);
|
||||
printf("press key to change cursor");
|
||||
|
||||
getchar();
|
||||
cursor(0x80);
|
||||
|
||||
getchar();
|
||||
return 0;
|
||||
}
|
||||
</pre>
|
||||
相关函数:无
|
||||
|
||||
35
docs/c/delay.html
Normal file
35
docs/c/delay.html
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,35 @@
|
||||
<h1>标准库函数 - delay</h1>
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
<p>原型:extern void delay(unsigned int msec);</p>
|
||||
|
||||
<p>用法:#include <system.h></p>
|
||||
|
||||
<p>功能:短暂延时</p>
|
||||
|
||||
<p>说明:延时msec*4毫秒</p>
|
||||
|
||||
举例:<pre>
|
||||
|
||||
// delay.c
|
||||
|
||||
#include <system.h>
|
||||
|
||||
main()
|
||||
{
|
||||
int c;
|
||||
|
||||
clrscr();
|
||||
printf("\nHello, world!");
|
||||
|
||||
delay(250); // 250*4=1000msec=1sec
|
||||
|
||||
clrscr();
|
||||
printf("\nHi, guys");
|
||||
|
||||
getchar();
|
||||
return 0;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
</pre>相关函数:<a href="sleep.html">sleep</a>
|
||||
|
||||
42
docs/c/exit.html
Normal file
42
docs/c/exit.html
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,42 @@
|
||||
<h1>标准库函数 - exit</h1>
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
<p>原型:extern void exit(int retval);</p>
|
||||
|
||||
<p>用法:#include <stdlib.h></p>
|
||||
|
||||
<p>功能:结束程序</p>
|
||||
|
||||
<p>说明:返回值将被忽略</p>
|
||||
|
||||
举例:<pre>
|
||||
|
||||
// exit.c
|
||||
|
||||
#include <syslib.h>
|
||||
#include <stdlib.h>
|
||||
|
||||
main()
|
||||
{
|
||||
int i;
|
||||
|
||||
clrscr(); // clear screen
|
||||
textmode(0x00);
|
||||
|
||||
for(i=0;i<10;i++)
|
||||
{
|
||||
if(i==5) exit(0);
|
||||
else
|
||||
{
|
||||
clrscr();
|
||||
printf("%d",i);
|
||||
getchar();
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
getchar();
|
||||
return 0;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
</pre>相关函数:无
|
||||
|
||||
31
docs/c/exp.html
Normal file
31
docs/c/exp.html
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,31 @@
|
||||
<h1>数学函数 - exp</h1>
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
<p>原型:extern float exp(float x);</p>
|
||||
|
||||
<p>用法:#include <math.h></p>
|
||||
|
||||
<p>功能:求e的x次幂</p>
|
||||
|
||||
<p>说明:e=2.718281828...</p>
|
||||
|
||||
举例:<pre>
|
||||
|
||||
// exp.c
|
||||
|
||||
#include <syslib.h>
|
||||
#include <math.h>
|
||||
|
||||
main()
|
||||
{
|
||||
clrscr(); // clear screen
|
||||
textmode(0x00); // 6 lines per LCD screen
|
||||
|
||||
printf("e=%f\n",exp(1.0));
|
||||
|
||||
getchar();
|
||||
return 0;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
</pre>相关函数:无
|
||||
|
||||
38
docs/c/fabs.html
Normal file
38
docs/c/fabs.html
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,38 @@
|
||||
<h1>数学函数 - fabs</h1>
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
<p>原型:extern float fabs(float x);</p>
|
||||
|
||||
<p>用法:#include <math.h></p>
|
||||
|
||||
<p>功能:求浮点数x的绝对值</p>
|
||||
|
||||
<p>说明:计算|x|, 当x不为负时返回x,否则返回-x</p>
|
||||
|
||||
举例:<pre>
|
||||
|
||||
// fabs.c
|
||||
|
||||
#include <syslib.h>
|
||||
#include <math.h>
|
||||
|
||||
main()
|
||||
{
|
||||
float x;
|
||||
|
||||
clrscr(); // clear screen
|
||||
textmode(0x00); // 6 lines per LCD screen
|
||||
|
||||
x=-74.12;
|
||||
printf("|%f|=%f\n",x,fabs(x));
|
||||
x=0;
|
||||
printf("|%f|=%f\n",x,fabs(x));
|
||||
x=74.12;
|
||||
printf("|%f|=%f\n",x,fabs(x));
|
||||
|
||||
getchar();
|
||||
return 0;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
</pre>相关函数:<a href="abs.html">abs</a>
|
||||
|
||||
36
docs/c/floor.html
Normal file
36
docs/c/floor.html
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,36 @@
|
||||
<h1>数学函数 - floor</h1>
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
<p>原型:extern float floor(float x);</p>
|
||||
|
||||
<p>用法:#include <math.h></p>
|
||||
|
||||
<p>功能:求不大于x的最达整数</p>
|
||||
|
||||
<p>说明:返回x的下限,如74.12的下限为74,-74.12的下限为-75。返回值为float类型。</p>
|
||||
|
||||
举例:<pre>
|
||||
|
||||
// floor.c
|
||||
|
||||
#include <syslib.h>
|
||||
#include <math.h>
|
||||
|
||||
main()
|
||||
{
|
||||
float x;
|
||||
|
||||
clrscr(); // clear screen
|
||||
textmode(0x00); // 6 lines per LCD screen
|
||||
|
||||
x=74.12;
|
||||
printf("floor(%.2f)=%.0f\n",x,floor(x));
|
||||
x=-74.12;
|
||||
printf("floor(%.2f)=%.0f\n",x,floor(x));
|
||||
|
||||
getchar();
|
||||
return 0;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
</pre>相关函数:<a href="ceil.html">ceil</a>
|
||||
|
||||
38
docs/c/fmod.html
Normal file
38
docs/c/fmod.html
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,38 @@
|
||||
<h1>数学函数 - fmod</h1>
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
<p>原型:extern float fmod(float x, float y);</p>
|
||||
|
||||
<p>用法:#include <math.h></p>
|
||||
|
||||
<p>功能:计算x/y的余数</p>
|
||||
|
||||
<p>说明:返回x-n*y,符号同y。n=[x/y](向离开零的方向取整)</p>
|
||||
|
||||
举例:<pre>
|
||||
|
||||
// fmod.c
|
||||
|
||||
#include <syslib.h>
|
||||
#include <math.h>
|
||||
|
||||
main()
|
||||
{
|
||||
float x,y;
|
||||
|
||||
clrscr(); // clear screen
|
||||
textmode(0x00); // 6 lines per LCD screen
|
||||
|
||||
x=74.12;
|
||||
y=6.4;
|
||||
printf("74.12/6.4: %f\n",fmod(x,y));
|
||||
x=74.12;
|
||||
y=-6.4;
|
||||
printf("74.12/(-6.4): %f\n",fmod(x,y));
|
||||
|
||||
getchar();
|
||||
return 0;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
</pre>相关函数:无
|
||||
|
||||
49
docs/c/free.html
Normal file
49
docs/c/free.html
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,49 @@
|
||||
<h1>动态内存 - free</h1>
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
<p>原型:extern void free(void *p);</p>
|
||||
|
||||
<p>用法:#include <alloc.h></p>
|
||||
|
||||
<p>功能:释放指针p所指向的的内存空间。</p>
|
||||
|
||||
<p>说明:p所指向的内存空间必须是用calloc,malloc,realloc所分配的内存。
|
||||
如果p为NULL或指向不存在的内存块则不做任何操作。</p>
|
||||
|
||||
举例:<pre>
|
||||
|
||||
// free.c
|
||||
|
||||
#include <syslib.h>
|
||||
#include <alloc.h>
|
||||
|
||||
main()
|
||||
{
|
||||
char *p;
|
||||
|
||||
clrscr(); // clear screen
|
||||
textmode(0x00);
|
||||
|
||||
p=(char *)malloc(100);
|
||||
if(p)
|
||||
printf("Memory Allocated at: %x",p);
|
||||
else
|
||||
printf("Not Enough Memory!\n");
|
||||
|
||||
getchar();
|
||||
free(p); // release memory to reuse it
|
||||
|
||||
p=(char *)calloc(100,1);
|
||||
if(p)
|
||||
printf("Memory Reallocated at: %x",p);
|
||||
else
|
||||
printf("Not Enough Memory!\n");
|
||||
|
||||
free(p); // release memory at program end
|
||||
|
||||
getchar();
|
||||
return 0;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
</pre>相关函数:<a href="calloc.html">calloc</a>,<a href="malloc.html">malloc</a>,<a href="realloc.html">realloc</a>
|
||||
|
||||
35
docs/c/frexp.html
Normal file
35
docs/c/frexp.html
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,35 @@
|
||||
<h1>数学函数 - frexp</h1>
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
<p>原型:extern float frexp(float x, int *exp);</p>
|
||||
|
||||
<p>用法:#include <math.h></p>
|
||||
|
||||
<p>功能:把浮点数x分解成尾数和指数。</p>
|
||||
|
||||
<p>说明:x=m*2^exp,m为规格化小数。返回尾数m,并将指数存入exp中。</p>
|
||||
|
||||
举例:<pre>
|
||||
|
||||
// frexp.c
|
||||
|
||||
#include <syslib.h>
|
||||
#include <math.h>
|
||||
|
||||
main()
|
||||
{
|
||||
float x;
|
||||
int exp;
|
||||
|
||||
clrscr(); // clear screen
|
||||
textmode(0x00); // 6 lines per LCD screen
|
||||
|
||||
x=frexp(64.0,&exp);
|
||||
printf("64=%.2f*2^%d",x,exp);
|
||||
|
||||
getchar();
|
||||
return 0;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
</pre>相关函数:<a href="ldexp.html">ldexp</a>,<a href="modf.html">modf</a>
|
||||
|
||||
63
docs/c/get_chi_font.html
Normal file
63
docs/c/get_chi_font.html
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,63 @@
|
||||
<h1>标准库函数 - get_chi_font</h1>
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
<p>原型:extern void get_chi_font(char *str, char *buf);</p>
|
||||
|
||||
<p>用法:#include <system.h></p>
|
||||
|
||||
<p>功能:取春鹤值阏 </p>
|
||||
<p>说明:把str所指向的汉字的16*16点阵信息存放在buf中。</p>
|
||||
<pre>
|
||||
|
||||
buf必须有足够的空间(>32字节)来容纳返回的数据。
|
||||
只返回str指向的第一个汉字的点阵数据。返回的点阵排列如下:
|
||||
|
||||
第一字节 十六字节
|
||||
第二字节 十七字节
|
||||
... ...
|
||||
十四字节 第30字节
|
||||
十五字节 第31字节
|
||||
</pre>
|
||||
|
||||
举例:<pre>
|
||||
|
||||
// get_chi_font.c
|
||||
|
||||
#include <system.h>
|
||||
|
||||
main()
|
||||
{
|
||||
char buf[32];
|
||||
char *s="文曲星",*p;
|
||||
int i,j,k; // Loop variable
|
||||
int x=0,y=0; // screen location to display HZ
|
||||
int r; // current byte
|
||||
|
||||
clrscr();
|
||||
gotoxy(10,10); // Hide Cursor
|
||||
|
||||
p=s;
|
||||
while(*p)
|
||||
{
|
||||
get_chi_font(p,buf);
|
||||
for(i=0;i<2;i++)
|
||||
{
|
||||
for(j=0;j<16;j++)
|
||||
{
|
||||
r=buf[i*16+j];
|
||||
for(k=0;k<8;k++)
|
||||
{
|
||||
putpixel(x+i*8+k,y+j,((r<<k)&0x80)?1:0);
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
p+=2; // forward a Chinese Character(HZ), two bytes
|
||||
x+=16;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
getchar();
|
||||
return 0;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
</pre>相关函数:<a href="write_chi_font.html">write_chi_font</a>
|
||||
|
||||
75
docs/c/get_eng_font.html
Normal file
75
docs/c/get_eng_font.html
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,75 @@
|
||||
<h1>标准库函数 - get_eng_font</h1>
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
<p>原型:extern void get_eng_font(char ch, char *buf, int mode);</p>
|
||||
|
||||
<p>用法:#include <system.h></p>
|
||||
|
||||
<p>功能:取英文字符的点阵</p>
|
||||
|
||||
<p>说明:把字符ch的点阵信息存放在buf中。</p>
|
||||
<pre>
|
||||
|
||||
buf必须有足够的空间容纳返回的数据。
|
||||
mode=0时返回8x16点阵信息,mode=1时返回8x8点阵信息。
|
||||
</pre>
|
||||
|
||||
举例:<pre>
|
||||
|
||||
// get_eng_font.c
|
||||
|
||||
#include <system.h>
|
||||
|
||||
main()
|
||||
{
|
||||
char buf[32];
|
||||
char *s="Global View",*p;
|
||||
int i,j,k; // Loop variable
|
||||
int x=0,y=0; // screen location to display HZ
|
||||
int r; // current byte
|
||||
|
||||
clrscr();
|
||||
gotoxy(10,10); // Hide Cursor
|
||||
|
||||
x=y=0;
|
||||
|
||||
p=s;
|
||||
while(*p)
|
||||
{
|
||||
get_eng_font(*p,buf,0);
|
||||
for(j=0;j<16;j++)
|
||||
{
|
||||
r=buf[j];
|
||||
for(k=0;k<8;k++)
|
||||
{
|
||||
putpixel(x+k,y+j,((r<<k)&0x80)?1:0);
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
p++; // forward to next character
|
||||
x+=8;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
x=0,y=16;
|
||||
|
||||
p=s;
|
||||
while(*p)
|
||||
{
|
||||
get_eng_font(*p,buf,1);
|
||||
for(j=0;j<8;j++)
|
||||
{
|
||||
r=buf[j];
|
||||
for(k=0;k<8;k++)
|
||||
{
|
||||
putpixel(x+k,y+j,((r<<k)&0x80)?1:0);
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
p++; // forward to next character
|
||||
x+=8;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
getchar();
|
||||
return 0;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
</pre>相关函数:<a href="write_eng_font.html">write_eng_font</a>
|
||||
|
||||
33
docs/c/getchar.html
Normal file
33
docs/c/getchar.html
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,33 @@
|
||||
<h1>输入输出 - getchar</h1>
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
<p>原型:extern int getchar(void);</p>
|
||||
|
||||
<p>用法:#include <ctype.h></p>
|
||||
|
||||
<p>功能:读键</p>
|
||||
|
||||
<p>说明:从键盘上读取一个键,并返回该键的键值</p>
|
||||
getch是到getchar的宏定义
|
||||
|
||||
举例:<pre>
|
||||
|
||||
// getchar.c
|
||||
|
||||
#include <stdio.h>
|
||||
|
||||
main()
|
||||
{
|
||||
int c;
|
||||
|
||||
clrscr();
|
||||
printf("Press key...");
|
||||
while((c=getchar())!='Q')
|
||||
{
|
||||
clrscr();
|
||||
printf("key: %c\nvalue: %x",c,c);
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
</pre>相关函数:<font color=gray>getkey</font>,<a href="kbhit.html">kbhit</a>
|
||||
|
||||
32
docs/c/getkey.html
Normal file
32
docs/c/getkey.html
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,32 @@
|
||||
<h1>标准库函数 - getkey</h1>
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
<p>原型:extern int getkey(void);</p>
|
||||
|
||||
<p>用法:#include <system.h></p>
|
||||
|
||||
<p>功能:读键</p>
|
||||
|
||||
<p>说明:功能同getchar</p>
|
||||
|
||||
举例:<pre>
|
||||
|
||||
// getkey.c
|
||||
|
||||
#include <system.h>
|
||||
|
||||
main()
|
||||
{
|
||||
int c;
|
||||
|
||||
clrscr();
|
||||
printf("Press key...");
|
||||
while((c=getkey())!='Q')
|
||||
{
|
||||
clrscr();
|
||||
printf("key: %c\nvalue: %x",c,c);
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
</pre>相关函数:<font color=gray>getch,getchar,kbhit</font>
|
||||
|
||||
40
docs/c/getpixel.html
Normal file
40
docs/c/getpixel.html
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,40 @@
|
||||
<h1>标准库函数 - getpixel</h1>
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
<p>原型:extern int getpixel(int x, int y);</p>
|
||||
|
||||
<p>用法:#include <system.h></p>
|
||||
|
||||
<p>功能:返回屏幕上指定点的状态</p>
|
||||
|
||||
<p>说明:(x,y)为屏幕上点的坐标,如果点为清除状态返回零,否则返回非零值。</p>
|
||||
|
||||
举例:<pre>
|
||||
|
||||
// pixel.c
|
||||
|
||||
#include <system.h>
|
||||
|
||||
main()
|
||||
{
|
||||
int i,j;
|
||||
|
||||
clrscr();
|
||||
printf("V");
|
||||
gotoxy(10,10); // Hide cursor
|
||||
|
||||
for(i=0;i<8;i++)
|
||||
for(j=0;j<16;j++)
|
||||
{
|
||||
if(getpixel(i,j))
|
||||
putpixel(10+i,10+j,1);
|
||||
else
|
||||
putpixel(10+i,10+j,0);
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
getchar();
|
||||
return 0;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
</pre>相关函数:<a href="putpixel.html">putpixel</a>
|
||||
|
||||
41
docs/c/gotoxy.html
Normal file
41
docs/c/gotoxy.html
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,41 @@
|
||||
<h1>标准库函数 - gotoxy</h1>
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
<p>原型:extern void gotoxy(int x, int y);</p>
|
||||
|
||||
<p>用法:#include <system.h></p>
|
||||
|
||||
<p>功能:将光标移动到指定位置</p>
|
||||
|
||||
<p>说明:gotoxy(x,y)将光标移动到指定行y和列x。</p>
|
||||
gotoxy(0,0)将光标移动到屏幕左上角。
|
||||
move(row,col)是到gotoxy的宏,将光标移动到指定行row和列col
|
||||
move(1,1)将光标移动到屏幕左上角。
|
||||
举例:<pre>
|
||||
|
||||
// gotoxy.c
|
||||
|
||||
#include <system.h>
|
||||
|
||||
main()
|
||||
{
|
||||
int i;
|
||||
char *scrbuf=(char *)0x280;
|
||||
|
||||
/* write to ScreenBuf, faster than printf or putchar */
|
||||
for(i=0;i<85;i++) scrbuf[i]='+';
|
||||
UpdateLCD(0x00);
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
gotoxy(2,2); // row 3, col 3
|
||||
|
||||
getchar();
|
||||
|
||||
move(2,2); // row 2, col 2
|
||||
|
||||
getchar();
|
||||
return 0;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
</pre>相关函数:无
|
||||
|
||||
32
docs/c/hypot.html
Normal file
32
docs/c/hypot.html
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,32 @@
|
||||
<h1>数学函数 - hypot</h1>
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
<p>原型:extern float hypot(float x, float y);</p>
|
||||
|
||||
<p>用法:#include <math.h></p>
|
||||
|
||||
<p>功能:对于给定的直角三角形的两个直角边,求其斜边的长度。</p>
|
||||
|
||||
<p>说明:返回斜边值。</p>
|
||||
|
||||
举例:<pre>
|
||||
|
||||
// hypot.c
|
||||
|
||||
#include <syslib.h>
|
||||
#include <math.h>
|
||||
|
||||
main()
|
||||
{
|
||||
clrscr(); // clear screen
|
||||
textmode(0x00); // 6 lines per LCD screen
|
||||
|
||||
printf("3^2+4^2=%.0f^2\n",hypot(3.,4.));
|
||||
printf("3.2^2+4.3^2=%.2f^2",hypot(x,y));
|
||||
|
||||
getchar();
|
||||
return 0;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
</pre>相关函数:<a href="frexp.html">frexp</a>,<a href="ldexp.html">ldexp</a>
|
||||
|
||||
35
docs/c/isalnum.html
Normal file
35
docs/c/isalnum.html
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,35 @@
|
||||
<h1>字符函数 - isalnum</h1>
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
<p>原型:extern int isalnum(int c);</p>
|
||||
|
||||
<p>用法:#include <ctype.h></p>
|
||||
|
||||
<p>功能:判断字符c是否为字母或数字</p>
|
||||
|
||||
<p>说明:当c为数字0-9或字母a-z及A-Z时,返回非零值,否则返回零。</p>
|
||||
|
||||
举例:<pre>
|
||||
|
||||
// isalnum.c
|
||||
|
||||
#include <syslib.h>
|
||||
#include <ctype.h>
|
||||
|
||||
main()
|
||||
{
|
||||
int c;
|
||||
|
||||
clrscr(); // clear screen
|
||||
c='a';
|
||||
printf("%c:%s\n",c,isalnum(c)?"yes":"no");
|
||||
c='7';
|
||||
printf("%c:%s\n",c,isalnum(c)?"yes":"no");
|
||||
c='@';
|
||||
printf("%c:%s\n",c,isalnum(c)?"yes":"no");
|
||||
getchar();
|
||||
return 0;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
</pre>相关函数:<a href="isalpha.html">isalpha</a>,<a href="isdigit.html">isdigit</a>,<a href="isxdigit.html">isxdigit</a>,<a href="iscntrl.html">iscntrl</a>,<a href="isgraph.html">isgraph</a>,<a href="isprint.html">isprint</a>,<a href="ispunct.html">ispunct</a>,<a href="isspace.html">isspace</a>
|
||||
|
||||
31
docs/c/isalpha.html
Normal file
31
docs/c/isalpha.html
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,31 @@
|
||||
<h1>字符函数 - isalpha</h1>
|
||||
<p>原型:extern int isalpha(int c);</p>
|
||||
<p>用法:#include <ctype.h></p>
|
||||
<p>功能:判断字符c是否为英文字母</p>
|
||||
<p>说明:当c为英文字母a-z或A-Z时,返回非零值,否则返回零</p>
|
||||
|
||||
举例:
|
||||
<pre>
|
||||
// isalpha.c
|
||||
|
||||
#include <syslib.h>
|
||||
#include <ctype.h>
|
||||
#include <stdio.h>
|
||||
|
||||
main()
|
||||
{
|
||||
int c;
|
||||
|
||||
clrscr(); // clear screen
|
||||
printf("Press a key");
|
||||
for(;;)
|
||||
{
|
||||
c=getchar();
|
||||
clrscr();
|
||||
printf("%c: %s letter",c,isalpha(c)?"is":"not");
|
||||
}
|
||||
return 0; // just to avoid warnings by compiler
|
||||
}
|
||||
</pre>
|
||||
相关函数:<a href="isalnum.html">isalnum</a>,<a href="isdigit.html">isdigit</a>,<a href="isxdigit.html">isxdigit</a>,<a href="iscntrl.html">iscntrl</a>,<a href="isgraph.html">isgraph</a>,<a href="isprint.html">isprint</a>,<a href="ispunct.html">ispunct</a>,<a href=isspace.html">isspace</a>
|
||||
|
||||
37
docs/c/isascii.html
Normal file
37
docs/c/isascii.html
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,37 @@
|
||||
<h1>字符函数 - isascii</h1>
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
<p>原型:extern int isascii(int c);</p>
|
||||
|
||||
<p>用法:#include <ctype.h></p>
|
||||
|
||||
<p>功能:判断字符c是否为ascii码</p>
|
||||
|
||||
<p>说明:当c为ascii码时,返回非零值,否则返回零。ascii码指0x00-0x7F之间的字符</p>
|
||||
|
||||
举例:<pre>
|
||||
|
||||
// isascii.c
|
||||
|
||||
#include <syslib.h>
|
||||
#include <ctype.h>
|
||||
|
||||
main()
|
||||
{
|
||||
char s[]="文曲星-BJGGV";
|
||||
int i=12; // length of string s
|
||||
|
||||
clrscr(); // clear screen
|
||||
textmode(0xE0); // make sure LCD mode is 3 big line
|
||||
printf("%s\n",s);
|
||||
for(i=0;i<12;i++)
|
||||
{
|
||||
if(isascii(s[i])) putchar('^');
|
||||
else putchar('.');
|
||||
}
|
||||
getchar();
|
||||
return 0;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
</pre>相关函数:无
|
||||
|
||||
33
docs/c/isblank.html
Normal file
33
docs/c/isblank.html
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,33 @@
|
||||
<h1>字符函数 - isblank</h1>
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
<p>原型:extern int isblank(int c);</p>
|
||||
|
||||
<p>用法:#include <ctype.h></p>
|
||||
|
||||
<p>功能:判断字符c是否为TAB或空格</p>
|
||||
|
||||
<p>说明:当c为TAB或空格时,返回非零值,否则返回零。</p>
|
||||
|
||||
举例:<pre>
|
||||
|
||||
// isalnum.c
|
||||
|
||||
#include <syslib.h>
|
||||
#include <ctype.h>
|
||||
|
||||
main()
|
||||
{
|
||||
int c;
|
||||
|
||||
clrscr(); // clear screen
|
||||
c='a';
|
||||
printf("%c:%s\n",c,isalnum(c)?"yes":"no");
|
||||
c='7';
|
||||
printf("%c:%s\n",c,isalnum(c)?"yes":"no");
|
||||
c='@';
|
||||
printf("%c:%s\n",c,isalnum(c)?"yes":"no");
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
</pre>相关函数:<a href="isalpha.html">isalnum</a>,<a href="isalpha.html">isalpha</a>,<a href="iscntrl.html">iscntrl</a>,<a href="isgraph.html">isgraph</a>,<a href="isprint.html">isprint</a>,<a href="ispunct.html">ispunct</a>,<a href=isspace.html">isspace</a>
|
||||
|
||||
35
docs/c/iscntrl.html
Normal file
35
docs/c/iscntrl.html
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,35 @@
|
||||
<h1>字符函数 - iscntrl</h1>
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
<p>原型:extern int iscntrl(int c);</p>
|
||||
|
||||
<p>用法:#include <ctype.h></p>
|
||||
|
||||
<p>功能:判断字符c是否为控制字符</p>
|
||||
|
||||
<p>说明:当c在0x00-0x1F之间或等于0x7F(DEL)时,返回非零值,否则返回零。</p>
|
||||
|
||||
举例:<pre>
|
||||
|
||||
// iscntrl.c
|
||||
|
||||
#include <syslib.h>
|
||||
#include <ctype.h>
|
||||
|
||||
main()
|
||||
{
|
||||
int c;
|
||||
|
||||
clrscr(); // clear screen
|
||||
c='a';
|
||||
printf("%x:%s\n",c,iscntrl(c)?"yes":"no");
|
||||
c=0x0d;
|
||||
printf("%x:%s\n",c,iscntrl(c)?"yes":"no");
|
||||
c=0x7f;
|
||||
printf("%x:%s\n",c,iscntrl(c)?"yes":"no");
|
||||
getchar();
|
||||
return 0;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
</pre>相关函数:<a href="isalnum.html">isalnum</a>,<a href="isalpha.html">isalpha</a>,<a href="isdigit.html">isdigit</a>,<a href="isxdigit.html">isxdigit</a>,<a href="isgraph.html">isgraph</a>,<a href="isprint.html">isprint</a>,<a href="ispunct.html">ispunct</a>,<a href=isspace.html">isspace</a>
|
||||
|
||||
35
docs/c/isdigit.html
Normal file
35
docs/c/isdigit.html
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,35 @@
|
||||
<h1>字符函数 - isdigit</h1>
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
<p>原型:extern int isdigit(int c);</p>
|
||||
|
||||
<p>用法:#include <ctype.h></p>
|
||||
|
||||
<p>功能:判断字符c是否为数字</p>
|
||||
|
||||
<p>说明:当c为数字0-9时,返回非零值,否则返回零。</p>
|
||||
|
||||
举例:<pre>
|
||||
|
||||
// isdigit.c
|
||||
|
||||
#include <syslib.h>
|
||||
#include <ctype.h>
|
||||
|
||||
main()
|
||||
{
|
||||
int c;
|
||||
|
||||
clrscr(); // clear screen
|
||||
c='a';
|
||||
printf("%c:%s\n",c,isdigit(c)?"yes":"no");
|
||||
c='9';
|
||||
printf("%c:%s\n",c,isdigit(c)?"yes":"no");
|
||||
c='*';
|
||||
printf("%c:%s\n",c,isdigit(c)?"yes":"no");
|
||||
getchar();
|
||||
return 0;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
</pre>相关函数:<a href="isalnum.html">isalnum</a>,<a href="isalpha.html">isalpha</a>,<a href="isxdigit.html">isxdigit</a>,<a href="iscntrl.html">iscntrl</a>,<a href="isgraph.html">isgraph</a>,<a href="isprint.html">isprint</a>,<a href="ispunct.html">ispunct</a>,<a href=isspace.html">isspace</a>
|
||||
|
||||
30
docs/c/isgraph.html
Normal file
30
docs/c/isgraph.html
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,30 @@
|
||||
<h1>字符函数 - isgraph</h1>
|
||||
<p>原型:extern int isgraph(int c);<p>
|
||||
<p>用法:#include <ctype.h><p>
|
||||
<p>功能:判断字符c是否为除空格外的可打印字符<p>
|
||||
<p>说明:当c为可打印字符(0x21-0x7e)时,返回非零值,否则返回零。<p>
|
||||
举例:
|
||||
<pre>
|
||||
// isgraph.c
|
||||
|
||||
#include <syslib.h>
|
||||
#include <ctype.h>
|
||||
|
||||
main()
|
||||
{
|
||||
int c;
|
||||
|
||||
clrscr(); // clear screen
|
||||
c='a';
|
||||
printf("%c:%s\n",c,isgraph(c)?"yes":"no");
|
||||
c=' '; // 0x20
|
||||
printf("%c:%s\n",c,isgraph(c)?"yes":"no");
|
||||
c=0x7f;
|
||||
printf("%c:%s\n",c,isgraph(c)?"yes":"no");
|
||||
|
||||
getchar();
|
||||
return 0;
|
||||
}
|
||||
</pre>
|
||||
相关函数:<a href="isprint.html">isprint</a>
|
||||
|
||||
35
docs/c/islower.html
Normal file
35
docs/c/islower.html
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,35 @@
|
||||
<h1>字符函数 - islower</h1>
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
<p>原型:extern int islower(int c);</p>
|
||||
|
||||
<p>用法:#include <ctype.h></p>
|
||||
|
||||
<p>功能:判断字符c是否为小写英文字母</p>
|
||||
|
||||
<p>说明:当c为小写英文字母(a-z)时,返回非零值,否则返回零。</p>
|
||||
|
||||
举例:<pre>
|
||||
|
||||
// islower.c
|
||||
|
||||
#include <syslib.h>
|
||||
#include <ctype.h>
|
||||
|
||||
main()
|
||||
{
|
||||
int c;
|
||||
|
||||
clrscr(); // clear screen
|
||||
c='a';
|
||||
printf("%c:%s\n",c,islower(c)?"yes":"no");
|
||||
c='A';
|
||||
printf("%c:%s\n",c,islower(c)?"yes":"no");
|
||||
c='7';
|
||||
printf("%c:%s\n",c,islower(c)?"yes":"no");
|
||||
getchar();
|
||||
return 0;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
</pre>相关函数:<a href="isupper.html">isupper</a>
|
||||
|
||||
36
docs/c/isprint.html
Normal file
36
docs/c/isprint.html
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,36 @@
|
||||
<h1>字符函数 - isprint</h1>
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
<p>原型:extern int isprint(int c);</p>
|
||||
|
||||
<p>用法:#include <ctype.h></p>
|
||||
|
||||
<p>功能:判断字符c是否为可打印字符(含空格)</p>
|
||||
|
||||
<p>说明:当c为可打印字符(0x20-0x7e)时,返回非零值,否则返回零。</p>
|
||||
|
||||
举例:<pre>
|
||||
|
||||
// isprint.c
|
||||
|
||||
#include <syslib.h>
|
||||
#include <ctype.h>
|
||||
|
||||
main()
|
||||
{
|
||||
int c;
|
||||
|
||||
clrscr(); // clear screen
|
||||
c='a';
|
||||
printf("%c:%s\n",c,isprint(c)?"yes":"no");
|
||||
c=' ';
|
||||
printf("%c:%s\n",c,isprint(c)?"yes":"no");
|
||||
c=0x7f;
|
||||
printf("%c:%s\n",c,isprint(c)?"yes":"no");
|
||||
|
||||
getchar();
|
||||
return 0;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
</pre>相关函数:<a href="isgraph.html">isgraph</a>
|
||||
|
||||
40
docs/c/ispunct.html
Normal file
40
docs/c/ispunct.html
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,40 @@
|
||||
<h1>字符函数 - ispunct</h1>
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
<p>原型:extern int ispunct(int c);</p>
|
||||
|
||||
<p>用法:#include <ctype.h></p>
|
||||
|
||||
<p>功能:判断字符c是否为标点符号</p>
|
||||
|
||||
<p>说明:当c为标点符号时,返回非零值,否则返回零。
|
||||
标点符号指那些既不是字母数字,也不是空格的可打印字符。</p>
|
||||
|
||||
举例:<pre>
|
||||
|
||||
// ispunct.c
|
||||
|
||||
#include <syslib.h>
|
||||
#include <ctype.h>
|
||||
#include <string.h>
|
||||
|
||||
main()
|
||||
{
|
||||
char s[]="Hello, Rain!";
|
||||
int i;
|
||||
|
||||
clrscr(); // clear screen
|
||||
printf("%s\n",s);
|
||||
for(i=0;i<strlen(s);i++)
|
||||
{
|
||||
if(ispunct(s[i])) printf("^");
|
||||
else printf(".");
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
getchar();
|
||||
return 0;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
</pre>相关函数:<a href="isalnum.html">isalnum</a>,<a href="isalpha.html">isalpha</a>,<a href="isdigit.html">isdigit</a>,<a href="isxdigit.html">isxdigit</a>,<a href="iscntrl.html">iscntrl</a>,<a href="isgraph.html">isgraph</a>,<a href="isprint.html">isprint</a>,<a href=isspace.html">isspace</a>
|
||||
|
||||
36
docs/c/isspace.html
Normal file
36
docs/c/isspace.html
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,36 @@
|
||||
<h1>字符函数 - isspace</h1>
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
<p>原型:extern int isspace(int c);</p>
|
||||
|
||||
<p>用法:#include <ctype.h></p>
|
||||
|
||||
<p>功能:判断字符c是否为空白符</p>
|
||||
|
||||
<p>说明:当c为空白符时,返回非零值,否则返回零。</p>
|
||||
空白符指空格、水平制表、垂直制表、换页、回车和换行符。
|
||||
|
||||
举例:<pre>
|
||||
|
||||
// isspace.c
|
||||
|
||||
#include <syslib.h>
|
||||
#include <ctype.h>
|
||||
|
||||
main()
|
||||
{
|
||||
char s[]="Test Line 1\tend\nTest Line 2\r";
|
||||
int i;
|
||||
|
||||
clrscr(); // clear screen
|
||||
for(i=0;i<strlen(s);i++)
|
||||
{
|
||||
if(isspace(s[i])) putchar('.');
|
||||
else putchar(s[i]);
|
||||
}
|
||||
getchar();
|
||||
return 0;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
</pre>相关函数:<a href="isalnum.html">isalnum</a>,<a href="isalpha.html">isalpha</a>,<a href="isdigit.html">isdigit</a>,<a href="isxdigit.html">isxdigit</a>,<a href="iscntrl.html">iscntrl</a>,<a href="isgraph.html">isgraph</a>,<a href="isprint.html">isprint</a>,<a href="ispunct.html">ispunct</a>
|
||||
|
||||
35
docs/c/isupper.html
Normal file
35
docs/c/isupper.html
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,35 @@
|
||||
<h1>字符函数 - isupper</h1>
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
<p>原型:extern int isupper(int c);</p>
|
||||
|
||||
<p>用法:#include <ctype.h></p>
|
||||
|
||||
<p>功能:判断字符c是否为大写英文字母</p>
|
||||
|
||||
<p>说明:当c为大写英文字母(A-Z)时,返回非零值,否则返回零。</p>
|
||||
|
||||
举例:<pre>
|
||||
|
||||
// isupper.c
|
||||
|
||||
#include <syslib.h>
|
||||
#include <ctype.h>
|
||||
|
||||
main()
|
||||
{
|
||||
int c;
|
||||
|
||||
clrscr(); // clear screen
|
||||
c='a';
|
||||
printf("%c:%s\n",c,isupper(c)?"yes":"no");
|
||||
c='A';
|
||||
printf("%c:%s\n",c,isupper(c)?"yes":"no");
|
||||
c='7';
|
||||
printf("%c:%s\n",c,isupper(c)?"yes":"no");
|
||||
getchar();
|
||||
return 0;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
</pre>相关函数:<a href="islower.html">islower</a>
|
||||
|
||||
36
docs/c/isxdigit.html
Normal file
36
docs/c/isxdigit.html
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,36 @@
|
||||
<h1>字符函数 - isxdigit</h1>
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
<p>原型:extern int isxdigit(int c);</p>
|
||||
|
||||
<p>用法:#include <ctype.h></p>
|
||||
|
||||
<p>功能:判断字符c是否为十六进制数字</p>
|
||||
|
||||
<p>说明:当c为A-F,a-f或0-9之间的十六进制数字时,返回非零值,否则返回零。</p>
|
||||
|
||||
举例:<pre>
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
// isxdigit.c
|
||||
|
||||
#include <syslib.h>
|
||||
#include <ctype.h>
|
||||
|
||||
main()
|
||||
{
|
||||
int c;
|
||||
|
||||
clrscr(); // clear screen
|
||||
c='a';
|
||||
printf("%c:%s\n",c,isxdigit(c)?"yes":"no");
|
||||
c='9';
|
||||
printf("%c:%s\n",c,isxdigit(c)?"yes":"no");
|
||||
c='*';
|
||||
printf("%c:%s\n",c,isxdigit(c)?"yes":"no");
|
||||
getchar();
|
||||
return 0;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
</pre>相关函数:<a href="isalnum.html">isalnum</a>,<a href="isalpha.html">isalpha</a>,<a href="isdigit.html">isdigit</a>,<a href="iscntrl.html">iscntrl</a>,<a href="isgraph.html">isgraph</a>,<a href="isprint.html">isprint</a>,<a href="ispunct.html">ispunct</a>,<a href=isspace.html">isspace</a>
|
||||
|
||||
34
docs/c/itoa.html
Normal file
34
docs/c/itoa.html
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,34 @@
|
||||
<h1>标准库函数 - itoa</h1>
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
<p>原型:extern char *itoa(int i);</p>
|
||||
|
||||
<p>用法:#include <stdlib.h></p>
|
||||
|
||||
<p>功能:把整数i转换成字符串</p>
|
||||
|
||||
<p>说明:返回指向转换后的字符串的指针</p>
|
||||
|
||||
举例:<pre>
|
||||
|
||||
// itoa.c
|
||||
|
||||
#include <syslib.h>
|
||||
#include <stdlib.h>
|
||||
|
||||
main()
|
||||
{
|
||||
int i=7412;
|
||||
|
||||
clrscr(); // clear screen
|
||||
textmode(0x00);
|
||||
|
||||
printf("%d",i);
|
||||
printf("%s",itoa(i));
|
||||
|
||||
getchar();
|
||||
return 0;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
</pre>相关函数:无
|
||||
|
||||
40
docs/c/kbhit.html
Normal file
40
docs/c/kbhit.html
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,40 @@
|
||||
<h1>输入输出 - kbhit</h1>
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
<p>原型:extern int kbhit(void);</p>
|
||||
|
||||
<p>用法:#include <stdio.h></p>
|
||||
|
||||
<p>功能:检测按键</p>
|
||||
|
||||
<p>说明:检测键盘是否有键按下。</p>
|
||||
如果有键按下,则返回对应键值;否则返回零。
|
||||
kbhit不等待键盘按键。无论有无按键都会立即返回。
|
||||
|
||||
举例:<pre>
|
||||
|
||||
// kbhit.c
|
||||
|
||||
#include <stdio.h>
|
||||
|
||||
main()
|
||||
{
|
||||
int i=0;
|
||||
|
||||
clrscr();
|
||||
|
||||
while(!kbhit())
|
||||
{
|
||||
clrscr();
|
||||
printf("%05d",i++);
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
clrscr();
|
||||
printf("End.");
|
||||
|
||||
getchar();
|
||||
return 0;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
</pre>相关函数:<font color=gray>getkey,getch</font>,<a href="getchar.html">getchar</a>
|
||||
|
||||
34
docs/c/ldexp.html
Normal file
34
docs/c/ldexp.html
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,34 @@
|
||||
<h1>数学函数 - ldexp</h1>
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
<p>原型:extern float ldexp(float x, int exp);</p>
|
||||
|
||||
<p>用法:#include <math.h></p>
|
||||
|
||||
<p>功能:装载浮点数。</p>
|
||||
|
||||
<p>说明:返回x*2^exp的值。</p>
|
||||
|
||||
举例:<pre>
|
||||
|
||||
// ldexp.c
|
||||
|
||||
#include <syslib.h>
|
||||
#include <math.h>
|
||||
|
||||
main()
|
||||
{
|
||||
float x;
|
||||
|
||||
clrscr(); // clear screen
|
||||
textmode(0x00); // 6 lines per LCD screen
|
||||
|
||||
x=ldexp(1.0,6); // 1.0*2^6
|
||||
printf("2^6=%.2f",x);
|
||||
|
||||
getchar();
|
||||
return 0;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
</pre>相关函数:<a href="frexp.html">frexp</a>,<a href="modf.html">modf</a>
|
||||
|
||||
41
docs/c/line.html
Normal file
41
docs/c/line.html
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,41 @@
|
||||
<h1>标准库函数 - line</h1>
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
<p>原型:extern void line(int left, int top, int right, int bottom, int mode);</p>
|
||||
|
||||
<p>用法:#include <system.h></p>
|
||||
|
||||
<p>功能:在屏幕上画直线</p>
|
||||
|
||||
<p>说明:(left,top)和(right,bottom)指定直线的两个端点坐标。mode决定划线的模式。</p>
|
||||
<pre> 超出屏幕的线将被裁端。
|
||||
mode值的含义:
|
||||
mode=0:清除方式
|
||||
=1:正常方式
|
||||
=2:取反方式
|
||||
</pre>
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
举例:<pre>
|
||||
|
||||
// line.c
|
||||
|
||||
#include <system.h>
|
||||
|
||||
main()
|
||||
{
|
||||
clrscr();
|
||||
move(10,10); // hide cursor
|
||||
|
||||
block(20,10,100,40,1);
|
||||
|
||||
line(1,1,111,47,1); // from top left to bottom right
|
||||
line(1,47,111,1,0); // from bottom left to top right
|
||||
line(112/2,1,112/2,47,2); // line vertically at the middle of the LCD
|
||||
|
||||
getchar();
|
||||
return 0;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
</pre>相关函数:无
|
||||
|
||||
32
docs/c/log.html
Normal file
32
docs/c/log.html
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,32 @@
|
||||
<h1>数学函数 - log</h1>
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
<p>原型:extern float log(float x);</p>
|
||||
|
||||
<p>用法:#include <math.h></p>
|
||||
|
||||
<p>功能:计算x的自然对数。</p>
|
||||
|
||||
<p>说明:x的值应大于零。</p>
|
||||
|
||||
举例:<pre>
|
||||
|
||||
// log.c
|
||||
|
||||
#include <syslib.h>
|
||||
#include <math.h>
|
||||
|
||||
main()
|
||||
{
|
||||
float x;
|
||||
clrscr(); // clear screen
|
||||
textmode(0x00); // 6 lines per LCD screen
|
||||
|
||||
printf("ln(e)=%f\n", log(M_E)); // M_E is 2.71828..., defined in math.h
|
||||
|
||||
getchar();
|
||||
return 0;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
</pre>相关函数:<a href="log10.html">log10</a>
|
||||
|
||||
32
docs/c/log10.html
Normal file
32
docs/c/log10.html
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,32 @@
|
||||
<h1>数学函数 - log10</h1>
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
<p>原型:extern float log10(float x);</p>
|
||||
|
||||
<p>用法:#include <math.h></p>
|
||||
|
||||
<p>功能:计算x的常用对数。</p>
|
||||
|
||||
<p>说明:x的值应大于零。</p>
|
||||
|
||||
举例:<pre>
|
||||
|
||||
// log10.c
|
||||
|
||||
#include <syslib.h>
|
||||
#include <math.h>
|
||||
|
||||
main()
|
||||
{
|
||||
float x;
|
||||
clrscr(); // clear screen
|
||||
textmode(0x00); // 6 lines per LCD screen
|
||||
|
||||
printf("lg(5)=%f\n", log10(5.0));
|
||||
|
||||
getchar();
|
||||
return 0;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
</pre>相关函数:<a href="log.html">log</a>
|
||||
|
||||
39
docs/c/malloc.html
Normal file
39
docs/c/malloc.html
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,39 @@
|
||||
<h1>动态内存 - malloc</h1>
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
<p>原型:extern void *malloc(unsigned int num_bytes);</p>
|
||||
|
||||
<p>用法:#include <alloc.h></p>
|
||||
|
||||
<p>功能:分配长度为num_bytes字节的内存块</p>
|
||||
|
||||
<p>说明:如果分配成功则返回指向被分配内存的指针,否则返回空指针NULL。</p>
|
||||
当内存不再使用时,应使用free()函数将内存块释放。
|
||||
|
||||
举例:<pre>
|
||||
|
||||
// malloc.c
|
||||
|
||||
#include <syslib.h>
|
||||
#include <alloc.h>
|
||||
|
||||
main()
|
||||
{
|
||||
char *p;
|
||||
|
||||
clrscr(); // clear screen
|
||||
|
||||
p=(char *)malloc(100);
|
||||
if(p)
|
||||
printf("Memory Allocated at: %x",p);
|
||||
else
|
||||
printf("Not Enough Memory!\n");
|
||||
|
||||
free(p);
|
||||
|
||||
getchar();
|
||||
return 0;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
</pre>相关函数:<a href="calloc.html">calloc</a>,<a href="free.html">free</a>,<a href="realloc.html">realloc</a>
|
||||
|
||||
41
docs/c/memccpy.html
Normal file
41
docs/c/memccpy.html
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,41 @@
|
||||
<h1>字符串函数 - memccpy</h1>
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
<p>原型:extern void *memccpy(void *dest, void *src, unsigned char ch, unsigned int count);</p>
|
||||
|
||||
<p>用法:#include <string.h></p>
|
||||
|
||||
<p>功能:由src所指内存区域复制不多于count个字节到dest所指内存区域,如果遇到字符ch则停止复制。</p>
|
||||
|
||||
<p>说明:返回指向字符ch后的第一个字符的指针,如果src前n个字节中不存在ch则返回NULL。ch被复制。</p>
|
||||
|
||||
举例:<pre>
|
||||
|
||||
// memccpy.c
|
||||
|
||||
#include <syslib.h>
|
||||
#include <string.h>
|
||||
|
||||
main()
|
||||
{
|
||||
char *s="Golden Global View";
|
||||
char d[20],*p;
|
||||
|
||||
clrscr();
|
||||
|
||||
p=memccpy(d,s,'x',strlen(s));
|
||||
if(p)
|
||||
{
|
||||
*p='\0'; // MUST Do This
|
||||
printf("Char found: %s.\n",d);
|
||||
}
|
||||
else
|
||||
printf("Char not found.\n");
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
getchar();
|
||||
return 0;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
</pre>相关函数:<a href="memcpy.html">memcpy</a>,<a href="strcpy.html">strcpy</a>
|
||||
|
||||
37
docs/c/memchr.html
Normal file
37
docs/c/memchr.html
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,37 @@
|
||||
<h1>字符串函数 - memchr</h1>
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
<p>原型:extern void *memchr(void *buf, char ch, unsigned count);</p>
|
||||
|
||||
<p>用法:#include <string.h></p>
|
||||
|
||||
<p>功能:从buf所指内存区域的前count个字节查找字符ch。</p>
|
||||
|
||||
<p>说明:当第一次遇到字符ch时停止查找。如果成功,返回指向字符ch的指针;否则返回NULL。</p>
|
||||
|
||||
举例:<pre>
|
||||
|
||||
// memchr.c
|
||||
|
||||
#include <syslib.h>
|
||||
#include <string.h>
|
||||
|
||||
main()
|
||||
{
|
||||
char *s="Hello, Programmers!";
|
||||
char *p;
|
||||
|
||||
clrscr();
|
||||
|
||||
p=memchr(s,'P',strlen(s));
|
||||
if(p)
|
||||
printf("%s",p);
|
||||
else
|
||||
printf("Not Found!");
|
||||
|
||||
getchar();
|
||||
return 0;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
</pre>相关函数:<a href="memccpy.html">memccpy</a>,<a href="memmove.html">memmove</a>,<a href="strcpy.html">strcpy</a>
|
||||
|
||||
46
docs/c/memcmp.html
Normal file
46
docs/c/memcmp.html
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,46 @@
|
||||
<h1>字符串函数 - memcmp</h1>
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
<p>原型:extern int memcmp(void *buf1, void *buf2, unsigned int count);</p>
|
||||
|
||||
<p>用法:#include <string.h></p>
|
||||
|
||||
<p>功能:比较内存区域buf1和buf2的前count个字节。</p>
|
||||
|
||||
<p>说明:</p>
|
||||
<pre>
|
||||
当buf1<buf2时,返回值<0
|
||||
当buf1=buf2时,返回值=0
|
||||
当buf1>buf2时,返回值>0
|
||||
</pre>
|
||||
举例:<pre>
|
||||
|
||||
// memcmp.c
|
||||
|
||||
#include <syslib.h>
|
||||
#include <string.h>
|
||||
|
||||
main()
|
||||
{
|
||||
char *s1="Hello, Programmers!";
|
||||
char *s2="Hello, programmers!";
|
||||
int r;
|
||||
|
||||
clrscr();
|
||||
|
||||
r=memcmp(s1,s2,strlen(s1));
|
||||
if(!r)
|
||||
printf("s1 and s2 are identical");
|
||||
else
|
||||
if(r<0)
|
||||
printf("s1 less than s2");
|
||||
else
|
||||
printf("s1 greater than s2");
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
getchar();
|
||||
return 0;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
</pre>相关函数:<a href="memicmp.html">memicmp</a>,<a href="strcmp.html">strcmp</a>
|
||||
|
||||
35
docs/c/memcpy.html
Normal file
35
docs/c/memcpy.html
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,35 @@
|
||||
<h1>字符串函数 - memcpy</h1>
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
<p>原型:extern void *memcpy(void *dest, void *src, unsigned int count);</p>
|
||||
|
||||
<p>用法:#include <string.h></p>
|
||||
|
||||
<p>功能:由src所指内存区域复制count个字节到dest所指内存区域。</p>
|
||||
|
||||
<p>说明:src和dest所指内存区域不能重叠,函数返回指向dest的指针。</p>
|
||||
|
||||
举例:<pre>
|
||||
|
||||
// memcpy.c
|
||||
|
||||
#include <syslib.h>
|
||||
#include <string.h>
|
||||
|
||||
main()
|
||||
{
|
||||
char *s="Golden Global View";
|
||||
char d[20];
|
||||
|
||||
clrscr();
|
||||
|
||||
memcpy(d,s,strlen(s));
|
||||
d[strlen(s)]=0;
|
||||
printf("%s",d);
|
||||
|
||||
getchar();
|
||||
return 0;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
</pre>相关函数:<a href="memccpy.html">memccpy</a>,<a href="memmove.html">memmove</a>,<a href="strcpy.html">strcpy</a>
|
||||
|
||||
47
docs/c/memicmp.html
Normal file
47
docs/c/memicmp.html
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,47 @@
|
||||
<h1>字符串函数 - memicmp</h1>
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
<p>原型:extern int memicmp(void *buf1, void *buf2, unsigned int count);</p>
|
||||
|
||||
<p>用法:#include <string.h></p>
|
||||
|
||||
<p>功能:比较内存区域buf1和buf2的前count个字节但不区分字母的大小写。</p>
|
||||
|
||||
<p>说明:memicmp同memcmp的唯一区别是memicmp不区分大小写字母。</p>
|
||||
<pre>
|
||||
当buf1<buf2时,返回值<0
|
||||
当buf1=buf2时,返回值=0
|
||||
当buf1>buf2时,返回值>0
|
||||
</pre>
|
||||
|
||||
举例:<pre>
|
||||
|
||||
// memicmp.c
|
||||
|
||||
#include <syslib.h>
|
||||
#include <string.h>
|
||||
|
||||
main()
|
||||
{
|
||||
char *s1="Hello, Programmers!";
|
||||
char *s2="Hello, programmers!";
|
||||
int r;
|
||||
|
||||
clrscr();
|
||||
|
||||
r=memicmp(s1,s2,strlen(s1));
|
||||
if(!r)
|
||||
printf("s1 and s2 are identical");
|
||||
else
|
||||
if(r<0)
|
||||
printf("s1 less than s2");
|
||||
else
|
||||
printf("s1 greater than s2");
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
getchar();
|
||||
return 0;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
</pre>相关函数:<a href="memcmp.html">memcmp</a>,<a href="stricmp.html">stricmp</a>
|
||||
|
||||
35
docs/c/memmove.html
Normal file
35
docs/c/memmove.html
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,35 @@
|
||||
<h1>字符串函数 - memmove</h1>
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
<p>原型:extern void *memmove(void *dest, const void *src, unsigned int count);</p>
|
||||
|
||||
<p>用法:#include <string.h></p>
|
||||
|
||||
<p>功能:由src所指内存区域复制count个字节到dest所指内存区域。</p>
|
||||
|
||||
<p>说明:src和dest所指内存区域可以重叠,但复制后src内容会被更改。函数返回指向dest的指针。</p>
|
||||
|
||||
举例:<pre>
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
// memmove.c
|
||||
|
||||
#include <syslib.h>
|
||||
#include <string.h>
|
||||
|
||||
main()
|
||||
{
|
||||
char *s="Golden Global View";
|
||||
|
||||
clrscr();
|
||||
|
||||
memmove(s,s+7,strlen(s)-7);
|
||||
s[strlen(s)-7]=0;
|
||||
printf("%s",s);
|
||||
|
||||
getchar();
|
||||
return 0;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
</pre>相关函数:<a href="memccpy.html">memccpy</a>,<a href="memcpy.html">memcpy</a>,<a href="strcpy.html">strcpy</a>
|
||||
|
||||
34
docs/c/memset.html
Normal file
34
docs/c/memset.html
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,34 @@
|
||||
<h1>字符串函数 - memset</h1>
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
<p>原型:extern void *memset(void *buffer, int c, int count);</p>
|
||||
|
||||
<p>用法:#include <string.h></p>
|
||||
|
||||
<p>功能:把buffer所指内存区域的前count个字节设置成字符c。</p>
|
||||
|
||||
<p>说明:返回指向buffer的指针。</p>
|
||||
|
||||
举例:<pre>
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
// memset.c
|
||||
|
||||
#include <syslib.h>
|
||||
#include <string.h>
|
||||
|
||||
main()
|
||||
{
|
||||
char *s="Golden Global View";
|
||||
|
||||
clrscr();
|
||||
|
||||
memset(s,'G',6);
|
||||
printf("%s",s);
|
||||
|
||||
getchar();
|
||||
return 0;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
</pre>相关函数:<a href="bzero.html">bzero</a>,<a href="setmem.html">setmem</a>,<a href="strset.html">strset</a>
|
||||
|
||||
34
docs/c/modf.html
Normal file
34
docs/c/modf.html
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,34 @@
|
||||
<h1>数学函数 - modf</h1>
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
<p>原型:extern float modf(float num, float *i);</p>
|
||||
|
||||
<p>用法:#include <math.h></p>
|
||||
|
||||
<p>功能:将浮点数num分解成整数部分和小数部分。</p>
|
||||
|
||||
<p>说明:返回小数部分,将整数部分存入*i所指内存中。</p>
|
||||
|
||||
举例:<pre>
|
||||
|
||||
// modf.c
|
||||
|
||||
#include <syslib.h>
|
||||
#include <math.h>
|
||||
|
||||
main()
|
||||
{
|
||||
float x, i;
|
||||
|
||||
clrscr(); // clear screen
|
||||
textmode(0x00); // 6 lines per LCD screen
|
||||
|
||||
x=modf(-74.12,&i);
|
||||
printf("-74.12=%.0f+(%.2f)",i,x);
|
||||
|
||||
getchar();
|
||||
return 0;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
</pre>相关函数:<a href="frexp.html">frexp</a>,<a href="ldexp.html">ldexp</a>
|
||||
|
||||
41
docs/c/move.html
Normal file
41
docs/c/move.html
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,41 @@
|
||||
<h1>标准库函数 - move</h1>
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
<p>原型:extern void gotoxy(int x, int y);</p>
|
||||
|
||||
<p>用法:#include <system.h></p>
|
||||
|
||||
<p>功能:将光标移动到指定位置</p>
|
||||
|
||||
<p>说明:gotoxy(x,y)将光标移动到指定行y和列x。</p>
|
||||
gotoxy(0,0)将光标移动到屏幕左上角。
|
||||
move(row,col)是到gotoxy的宏,将光标移动到指定行row和列col
|
||||
move(1,1)将光标移动到屏幕左上角。
|
||||
举例:<pre>
|
||||
|
||||
// gotoxy.c
|
||||
|
||||
#include <system.h>
|
||||
|
||||
main()
|
||||
{
|
||||
int i;
|
||||
char *scrbuf=(char *)0x280;
|
||||
|
||||
/* write to ScreenBuf, faster than printf or putchar */
|
||||
for(i=0;i<85;i++) scrbuf[i]='+';
|
||||
UpdateLCD(0x00);
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
gotoxy(2,2); // row 3, col 3
|
||||
|
||||
getchar();
|
||||
|
||||
move(2,2); // row 2, col 2
|
||||
|
||||
getchar();
|
||||
return 0;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
</pre>相关函数:无
|
||||
|
||||
35
docs/c/movmem.html
Normal file
35
docs/c/movmem.html
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,35 @@
|
||||
<h1>字符串函数 - movmem</h1>
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
<p>原型:extern void movmem(void *src, void *dest, unsigned int count);</p>
|
||||
|
||||
<p>用法:#include <string.h></p>
|
||||
|
||||
<p>功能:由src所指内存区域复制count个字节到dest所指内存区域。</p>
|
||||
|
||||
<p>说明:src和dest所指内存区域可以重叠,但复制后src内容会被更改。函数返回指向dest的指针。</p>
|
||||
|
||||
举例:<pre>
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
// movmem.c
|
||||
|
||||
#include <syslib.h>
|
||||
#include <string.h>
|
||||
|
||||
main()
|
||||
{
|
||||
char *s="Golden Global View";
|
||||
|
||||
clrscr();
|
||||
|
||||
movmem(s,s+7,strlen(s)-7);
|
||||
s[strlen(s)-7]=0;
|
||||
printf("%s",s);
|
||||
|
||||
getchar();
|
||||
return 0;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
</pre>相关函数:<a href="memmove.html">memmove</a>
|
||||
|
||||
44
docs/c/noidle.html
Normal file
44
docs/c/noidle.html
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,44 @@
|
||||
<h1>标准库函数 - noidle</h1>
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
<p>原型:extern void noidle(void);</p>
|
||||
|
||||
<p>用法:#include <system.h></p>
|
||||
|
||||
<p>功能:调用系统例程</p>
|
||||
|
||||
<p>说明:文曲星是单任务系统,为防止应用程序占用过多的系统时间而影响系统程序的执行</p>
|
||||
<pre>
|
||||
|
||||
同时也为了防止个别程序崩溃而造成系统无法启动,文曲星内核在中断到来时会检
|
||||
测应用程序所执行的时间,如果在4秒内系统程序没有得到运行,则中断程序将强迫
|
||||
文曲星进入睡眠状态,即所谓的死机。
|
||||
因此,当程序运算时间过长(一般为循环过程)时,请调用noidle来防止系统关机。
|
||||
</pre>
|
||||
|
||||
举例:<pre>
|
||||
|
||||
// noidle.c
|
||||
|
||||
#include <system.h>
|
||||
|
||||
main()
|
||||
{
|
||||
int i,j;
|
||||
clrscr();
|
||||
printf("Waiting...\n");
|
||||
|
||||
for(i=0;i<10;i++)
|
||||
for(j=0;j<32767;j++)
|
||||
{
|
||||
noidle();
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
printf("System Shutdown?");
|
||||
|
||||
getchar();
|
||||
return 0;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
</pre>相关函数:无
|
||||
|
||||
43
docs/c/outtextxy.html
Normal file
43
docs/c/outtextxy.html
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,43 @@
|
||||
<h1>标准库函数 - outtextxy</h1>
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
<p>原型:extern void TextOut(int x, int y, char *str, int mode);</p>
|
||||
|
||||
<p>用法:#include <system.h></p>
|
||||
|
||||
<p>功能:在屏幕上指定位置输出字符串</p>
|
||||
|
||||
<p>说明:outtextxy为指向TextOut的宏,用法相同。</p>
|
||||
<pre>
|
||||
|
||||
str所指向字符串可以为中文或英文。中文显示成16x16点阵,英文显示成8x16点阵。
|
||||
mode决定往屏幕上写的方式,其值含义如下:
|
||||
0:背景透明,点阵中为0的点不显示。
|
||||
1:正常方式,即点阵中为0的点擦除,为1的点显示。
|
||||
2:反显方式,即点阵中为1的点擦除,为0的点显示。
|
||||
3:异或方式,即点阵中点的值和屏幕当前位置的值作异或后取值,为0则擦除,为1显示。
|
||||
</pre>
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
举例:<pre>
|
||||
|
||||
// TextOut.c
|
||||
|
||||
#include <system.h>
|
||||
|
||||
main()
|
||||
{
|
||||
clrscr();
|
||||
|
||||
TextOut(0,0,"文曲星",1);
|
||||
TextOut(10,10,"文曲星",0);
|
||||
|
||||
TextOut(20,20,"您好",2);
|
||||
TextOut(30,30,"GGV-金远见",3);
|
||||
|
||||
getchar();
|
||||
return 0;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
</pre>相关函数:无
|
||||
|
||||
31
docs/c/pow.html
Normal file
31
docs/c/pow.html
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,31 @@
|
||||
<h1>数学函数 - pow</h1>
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
<p>原型:extern float pow(float x, float y);</p>
|
||||
|
||||
<p>用法:#include <math.h></p>
|
||||
|
||||
<p>功能:计算x的y次幂。</p>
|
||||
|
||||
<p>说明:x应大于零,返回幂指数的结果。</p>
|
||||
|
||||
举例:<pre>
|
||||
|
||||
// pow.c
|
||||
|
||||
#include <syslib.h>
|
||||
#include <math.h>
|
||||
|
||||
main()
|
||||
{
|
||||
clrscr(); // clear screen
|
||||
textmode(0x00); // 6 lines per LCD screen
|
||||
|
||||
printf("4^5=%f",pow(4.,5.));
|
||||
|
||||
getchar();
|
||||
return 0;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
</pre>相关函数:<a href="pow10.html">pow10</a>
|
||||
|
||||
32
docs/c/pow10.html
Normal file
32
docs/c/pow10.html
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,32 @@
|
||||
<h1>数学函数 - pow10</h1>
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
<p>原型:extern float pow10(float x);</p>
|
||||
|
||||
<p>用法:#include <math.h></p>
|
||||
|
||||
<p>功能:计算10的x次幂。</p>
|
||||
|
||||
<p>说明:相当于pow(10.0,x)。</p>
|
||||
|
||||
举例:<pre>
|
||||
|
||||
// pow10.c
|
||||
|
||||
#include <syslib.h>
|
||||
#include <math.h>
|
||||
|
||||
main()
|
||||
{
|
||||
clrscr(); // clear screen
|
||||
textmode(0x00); // 6 lines per LCD screen
|
||||
|
||||
printf("10^3.2=%f\n",pow10(3.2));
|
||||
printf("10^3.2=%f",pow(10,3.2));
|
||||
|
||||
getchar();
|
||||
return 0;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
</pre>相关函数:<a href="pow.html">pow</a>
|
||||
|
||||
84
docs/c/printf.html
Normal file
84
docs/c/printf.html
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,84 @@
|
||||
<h1>输入输出 - printf</h1>
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
<p>原型:extern void printf(const char *format,...);</p>
|
||||
|
||||
<p>用法:#include <stdio.h></p>
|
||||
|
||||
<p>功能:格式化字符串输出</p>
|
||||
|
||||
<p>说明:format指定输出格式,后面跟要输出的变量</p>
|
||||
<pre>
|
||||
目前printf支持以下格式:
|
||||
%c 单个字符
|
||||
%d 十进制整数
|
||||
%f 十进制浮点数
|
||||
%o 八进制数
|
||||
%s 字符串
|
||||
%u 无符号十进制数
|
||||
%x 十六进制数
|
||||
%% 输出百分号%
|
||||
一个格式说明可以带有几个修饰符,用来指定显示宽度,小数尾书及左对齐等:
|
||||
- 左对齐
|
||||
+ 在一个带符号数前加"+"或"-"号
|
||||
0 域宽用前导零来填充,而不是用空白符
|
||||
域宽是一个整数,设置了打印一个格式化字符串的最小域。精度使用小数点后加数字表示的,
|
||||
给出每个转换说明符所要输出的字符个数。
|
||||
<font color=red>注意</font>:带修饰符的显示可能不正常
|
||||
</pre>
|
||||
|
||||
举例:<pre>
|
||||
|
||||
// printf.c
|
||||
|
||||
#include <stdio.h>
|
||||
#include <system.h>
|
||||
|
||||
main()
|
||||
{
|
||||
int i;
|
||||
char *str="GGV";
|
||||
|
||||
clrscr();
|
||||
|
||||
textmode(0x00);
|
||||
printf("Printf Demo-%%c");
|
||||
printf("--------------");
|
||||
printf("%c-%c-%c-%c\n",'D','e','m','o');
|
||||
printf("%2c-%2c-%2c-%2c\n",'D','e','m','o');
|
||||
printf("%02c-%02c-%02c-%02c\n",'D','e','m','o');
|
||||
printf("%-2c-%-2c-%-2c-%-2c\n",'D','e','m','o');
|
||||
|
||||
getchar();
|
||||
clrscr();
|
||||
textmode(0x00); // not nessary
|
||||
i=7412;
|
||||
printf("Printf Demo-%%d");
|
||||
printf("--------------");
|
||||
printf("%d\n",i);
|
||||
printf("%14d",i);
|
||||
printf("%+10d\n",i); // output format not correct(bug)
|
||||
printf("%-10d\n",i);
|
||||
|
||||
getchar();
|
||||
clrscr();
|
||||
printf("Printf - d,o,x");
|
||||
printf("--------------");
|
||||
printf("%d\n",i);
|
||||
printf("%o\n",i); // %o and %x not implemented
|
||||
printf("%x\n",i);
|
||||
|
||||
getchar();
|
||||
clrscr();
|
||||
printf("Printf Demo-%%s");
|
||||
printf("--------------");
|
||||
printf(" %s\n","Demo End");
|
||||
printf(" %s\n","Thanx");
|
||||
printf(" %s\n %s","Golden","Global View");
|
||||
|
||||
getchar();
|
||||
return 0;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
</pre>相关函数:无
|
||||
|
||||
42
docs/c/putchar.html
Normal file
42
docs/c/putchar.html
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,42 @@
|
||||
<h1>输入输出 - putchar</h1>
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
<p>原型:extern void putchar(char c);</p>
|
||||
|
||||
<p>用法:#include <stdio.h></p>
|
||||
|
||||
<p>功能:在屏幕上显示字符c</p>
|
||||
|
||||
<p>说明:字符输出在屏幕的当前位置。</p>
|
||||
可用move或gotoxy改变光标位置。
|
||||
|
||||
举例:<pre>
|
||||
|
||||
// putchar.c
|
||||
|
||||
#include <stdio.h>
|
||||
#include <system.h>
|
||||
|
||||
#define CPR 14
|
||||
|
||||
main()
|
||||
{
|
||||
int i,j,k;
|
||||
|
||||
clrscr();
|
||||
|
||||
textmode(0x00);
|
||||
for(i=1;i<6;i++)
|
||||
{
|
||||
k=i>3?(6-i):i;
|
||||
move(i,CPR/2-k);
|
||||
for(j=1;j<k*2;j++) putchar('*');
|
||||
}
|
||||
gotoxy(10,10); // Hide Cursor
|
||||
|
||||
getchar();
|
||||
return 0;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
</pre>相关函数:无
|
||||
|
||||
43
docs/c/putpixel.html
Normal file
43
docs/c/putpixel.html
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,43 @@
|
||||
<h1>标准库函数 - putpixel</h1>
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
<p>原型:extern void putpixel(int x, int y, int mode);</p>
|
||||
|
||||
<p>用法:#include <system.h></p>
|
||||
|
||||
<p>功能:在屏幕的指定位置上画点</p>
|
||||
|
||||
<p>说明:(x,y)为屏幕上点的坐标,mode值含义如下:</p>
|
||||
mode=0:清除(x,y)处的点
|
||||
1:在(x,y)处画点
|
||||
2:将(x,y)处的点的状态取反
|
||||
|
||||
举例:<pre>
|
||||
|
||||
// pixel.c
|
||||
|
||||
#include <system.h>
|
||||
|
||||
main()
|
||||
{
|
||||
int i,j;
|
||||
|
||||
clrscr();
|
||||
printf("V");
|
||||
gotoxy(10,10); // Hide cursor
|
||||
|
||||
for(i=0;i<8;i++)
|
||||
for(j=0;j<16;j++)
|
||||
{
|
||||
if(getpixel(i,j))
|
||||
putpixel(10+i,10+j,1);
|
||||
else
|
||||
putpixel(10+i,10+j,0);
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
getchar();
|
||||
return 0;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
</pre>相关函数:<a href="getpixel.html">getpixel</a>
|
||||
|
||||
45
docs/c/pyfc.html
Normal file
45
docs/c/pyfc.html
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,45 @@
|
||||
<h1>标准库函数 - pyfc</h1>
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
<p>原型:extern char *pyfc(char *str);</p>
|
||||
|
||||
<p>用法:#include <system.h></p>
|
||||
|
||||
<p>功能:给定一个汉字str,查询对应的拼音。</p>
|
||||
|
||||
<p>说明:返回一个指向对应拼音字符串。多音字的几个读音之间用空格分隔。
|
||||
拼音保存在系统缓冲区中。如想保留请将其复制到程序的变量中。 </p>
|
||||
|
||||
举例:<pre>
|
||||
|
||||
// pyfc.c
|
||||
|
||||
#include <system.h>
|
||||
#include <string.h>
|
||||
|
||||
main()
|
||||
{
|
||||
char *s1,*s2,*s3;
|
||||
clrscr();
|
||||
|
||||
s1=strdup(pyfc("文"));
|
||||
s2=strdup(pyfc("曲"));
|
||||
s3=strdup(pyfc("星"));
|
||||
|
||||
printf(" 文 曲 星\n");
|
||||
printf("%s%s%s",s1,s2,s3); // Not right?
|
||||
|
||||
getchar();
|
||||
while(*s2++!=' '); // uh...'qu' has 2 tones
|
||||
|
||||
clrscr();
|
||||
printf(" 文 曲 星\n");
|
||||
printf("%s%s%s",s1,s2,s3); // Not right?
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
getchar();
|
||||
return 0;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
</pre>相关函数:无
|
||||
|
||||
47
docs/c/realloc.html
Normal file
47
docs/c/realloc.html
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,47 @@
|
||||
<h1>动态内存 - realloc</h1>
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
<p>原型:extern void *realloc(void *mem_address, unsigned int newsize);</p>
|
||||
|
||||
<p>用法:#include <alloc.h></p>
|
||||
|
||||
<p>功能:改变mem_address所指内存区域的大小为newsize长度。</p>
|
||||
|
||||
<p>说明:如果重新分配成功则返回指向被分配内存的指针,否则返回空指针NULL。</p>
|
||||
当内存不再使用时,应使用free()函数将内存块释放。
|
||||
|
||||
举例:<pre>
|
||||
|
||||
// realloc.c
|
||||
|
||||
#include <syslib.h>
|
||||
#include <alloc.h>
|
||||
|
||||
main()
|
||||
{
|
||||
char *p;
|
||||
|
||||
clrscr(); // clear screen
|
||||
|
||||
p=(char *)malloc(100);
|
||||
if(p)
|
||||
printf("Memory Allocated at: %x",p);
|
||||
else
|
||||
printf("Not Enough Memory!\n");
|
||||
|
||||
getchar();
|
||||
|
||||
p=(char *)realloc(p,256);
|
||||
if(p)
|
||||
printf("Memory Reallocated at: %x",p);
|
||||
else
|
||||
printf("Not Enough Memory!\n");
|
||||
|
||||
free(p);
|
||||
|
||||
getchar();
|
||||
return 0;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
</pre>相关函数:<a href="calloc.html">calloc</a>,<a href="free.html">free</a>,<a href="malloc.html">malloc</a>
|
||||
|
||||
46
docs/c/rectangle.html
Normal file
46
docs/c/rectangle.html
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,46 @@
|
||||
<h1>标准库函数 - rectangle</h1>
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
<p>原型:extern void rectangle(int left, int top, int right, int bottom, int mode);</p>
|
||||
|
||||
<p>用法:#include <system.h></p>
|
||||
|
||||
<p>功能:在屏幕上画一矩形。</p>
|
||||
|
||||
<p>说明:(left,top)指定左上角坐标,(right,bottom)指定右下角坐标。</p>
|
||||
<pre>
|
||||
mode决定画图方式,其值含义如下:
|
||||
0:清除方式
|
||||
1:正常方式
|
||||
2:反相方式
|
||||
</pre>
|
||||
|
||||
举例:<pre>
|
||||
|
||||
// rectangle.c
|
||||
|
||||
#include <system.h>
|
||||
|
||||
main()
|
||||
{
|
||||
int c;
|
||||
|
||||
clrscr();
|
||||
gotoxy(10,10); // Hide cursor(moved out of screen)
|
||||
|
||||
rectangle(1,0,111,47,1);
|
||||
getchar();
|
||||
|
||||
block(10,5,100,40,1);
|
||||
rectangle(20,10,90,30,0); // invisible for clear mode if screen if blank
|
||||
getchar();
|
||||
|
||||
rectangle(40,2,80,42,2);
|
||||
getchar();
|
||||
|
||||
getchar();
|
||||
return 0;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
</pre>相关函数:<a href="block.html">block</a>
|
||||
|
||||
34
docs/c/setmem.html
Normal file
34
docs/c/setmem.html
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,34 @@
|
||||
<h1>字符串函数 - setmem</h1>
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
<p>原型:extern void setmem(void *buf, unsigned int count, char ch);</p>
|
||||
|
||||
<p>用法:#include <string.h></p>
|
||||
|
||||
<p>功能:把buf所指内存区域前count个字节设置成字符ch。</p>
|
||||
|
||||
<p>说明:返回指向buf的指针。</p>
|
||||
|
||||
举例:<pre>
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
// setmem.c
|
||||
|
||||
#include <syslib.h>
|
||||
#include <string.h>
|
||||
|
||||
main()
|
||||
{
|
||||
char *s="Golden Global View";
|
||||
|
||||
clrscr();
|
||||
|
||||
setmem(s,6,'G');
|
||||
printf("%s",s);
|
||||
|
||||
getchar();
|
||||
return 0;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
</pre>相关函数:<a href="bzero.html">bzero</a>,<a href="memset.html">memset</a>,<a href="strset.html">strset</a>
|
||||
|
||||
33
docs/c/sin.html
Normal file
33
docs/c/sin.html
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,33 @@
|
||||
<h1>数学函数 - sin</h1>
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
<p>原型:extern float sin(float x);</p>
|
||||
|
||||
<p>用法:#include <math.h></p>
|
||||
|
||||
<p>功能:计算x(弧度表示)的正弦值。</p>
|
||||
|
||||
<p>说明:x的值域为[-1.0,1.0]。</p>
|
||||
|
||||
举例:<pre>
|
||||
|
||||
// sin.c
|
||||
|
||||
#include <syslib.h>
|
||||
#include <math.h>
|
||||
|
||||
main()
|
||||
{
|
||||
float x;
|
||||
clrscr(); // clear screen
|
||||
textmode(0x00); // 6 lines per LCD screen
|
||||
|
||||
x=M_PI/2; // M_PI=PI=3.14159265..., defined in math.h
|
||||
printf("sin(PI/2)=%f",sin(x));
|
||||
|
||||
getchar();
|
||||
return 0;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
</pre>相关函数:<a href="asin.html">asin</a>,<a href="acos.html">acos</a>,<a href="atan.html">atan</a>,<a href="atan2.html">atan2</a>,<a href="cos.html">cos</a>,<a href="tan.html">tan</a>
|
||||
|
||||
35
docs/c/sinh.html
Normal file
35
docs/c/sinh.html
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,35 @@
|
||||
<h1>数学函数 - sinh</h1>
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
<p>原型:extern float sinh(float x);</p>
|
||||
|
||||
<p>用法:#include <math.h></p>
|
||||
|
||||
<p>功能:计算x(弧度表示)的双曲正弦值。</p>
|
||||
|
||||
<p>说明:sinh(x)=(e^x-e^(-x))/2。</p>
|
||||
|
||||
举例:<pre>
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
// sinh.c
|
||||
|
||||
#include <syslib.h>
|
||||
#include <math.h>
|
||||
|
||||
main()
|
||||
{
|
||||
float x;
|
||||
|
||||
clrscr(); // clear screen
|
||||
textmode(0x00); // 6 lines per LCD screen
|
||||
|
||||
x=PI/4.;
|
||||
printf("sinh(%.4f)=%.4f\n",x,sinh(x));
|
||||
|
||||
getchar();
|
||||
return 0;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
</pre>相关函数:<a href="cosh.html">cosh</a>,<a href="tanh.html">tanh</a>
|
||||
|
||||
35
docs/c/sleep.html
Normal file
35
docs/c/sleep.html
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,35 @@
|
||||
<h1>标准库函数 - sleep</h1>
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
<p>原型:extern void sleep(unsigned int sec);</p>
|
||||
|
||||
<p>用法:#include <system.h></p>
|
||||
|
||||
<p>功能:短暂延时</p>
|
||||
|
||||
<p>说明:延时sec秒</p>
|
||||
|
||||
举例:<pre>
|
||||
|
||||
// sleep.c
|
||||
|
||||
#include <system.h>
|
||||
|
||||
main()
|
||||
{
|
||||
int c;
|
||||
|
||||
clrscr();
|
||||
printf("\nHello, world!");
|
||||
|
||||
sleep(1);
|
||||
|
||||
clrscr();
|
||||
printf("\nHi, guys");
|
||||
|
||||
getchar();
|
||||
return 0;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
</pre>相关函数:<a href="delay.html">delay</a>
|
||||
|
||||
3
docs/c/sqrt.html
Normal file
3
docs/c/sqrt.html
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,3 @@
|
||||
<h1>数学函数 - sqrt</h1>
|
||||
<h1><EFBFBD><EFBFBD>ѧ<EFBFBD><EFBFBD><EFBFBD><EFBFBD> - sqrt</h1>
|
||||
<h1><EFBFBD><EFBFBD>ѧ<EFBFBD><EFBFBD><EFBFBD><EFBFBD> - sqrt</h1>
|
||||
36
docs/c/stpcpy.html
Normal file
36
docs/c/stpcpy.html
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,36 @@
|
||||
<h1>字符串函数 - stpcpy</h1>
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
<p>原型:extern char *stpcpy(char *dest,char *src);</p>
|
||||
|
||||
<p>用法:#include <string.h></p>
|
||||
|
||||
<p>功能:把src所指由NULL结束的字符串复制到dest所指的数组中。</p>
|
||||
|
||||
<p>说明:src和dest所指内存区域不可以重叠且dest必须有足够的空间来容纳src的字符串。</p>
|
||||
返回指向dest结尾处字符(NULL)的指针。
|
||||
|
||||
举例:<pre>
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
// stpcpy.c
|
||||
|
||||
#include <syslib.h>
|
||||
#include <string.h>
|
||||
|
||||
main()
|
||||
{
|
||||
char *s="Golden Global View";
|
||||
char d[20];
|
||||
|
||||
clrscr();
|
||||
|
||||
stpcpy(d,s);
|
||||
printf("%s",d);
|
||||
|
||||
getchar();
|
||||
return 0;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
</pre>相关函数:<a href="strcpy.html">strcpy</a>
|
||||
|
||||
36
docs/c/strcat.html
Normal file
36
docs/c/strcat.html
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,36 @@
|
||||
<h1>字符串函数 - strcat</h1>
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
<p>原型:extern char *strcat(char *dest,char *src);</p>
|
||||
|
||||
<p>用法:#include <string.h></p>
|
||||
|
||||
<p>功能:把src所指字符串添加到dest结尾处(覆盖dest结尾处的'\0')并添加'\0'。</p>
|
||||
|
||||
<p>说明:src和dest所指内存区域不可以重叠且dest必须有足够的空间来容纳src的字符串。</p>
|
||||
返回指向dest的指针。
|
||||
|
||||
举例:<pre>
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
// strcat.c
|
||||
|
||||
#include <syslib.h>
|
||||
#include <string.h>
|
||||
|
||||
main()
|
||||
{
|
||||
char d[20]="Golden Global";
|
||||
char *s=" View";
|
||||
|
||||
clrscr();
|
||||
|
||||
strcat(d,s);
|
||||
printf("%s",d);
|
||||
|
||||
getchar();
|
||||
return 0;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
</pre>相关函数:<a href="strncat.html">strncat</a>
|
||||
|
||||
38
docs/c/strchr.html
Normal file
38
docs/c/strchr.html
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,38 @@
|
||||
<h1>字符串函数 - strchr</h1>
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
<p>原型:extern char *strchr(char *s,char c);</p>
|
||||
|
||||
<p>用法:#include <string.h></p>
|
||||
|
||||
<p>功能:查找字符串s中首次出现字符c的位置</p>
|
||||
|
||||
<p>说明:返回首次出现c的位置的指针,如果s中不存在c则返回NULL。</p>
|
||||
|
||||
举例:<pre>
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
// strchr.c
|
||||
|
||||
#include <syslib.h>
|
||||
#include <string.h>
|
||||
|
||||
main()
|
||||
{
|
||||
char *s="Golden Global View";
|
||||
char *p;
|
||||
|
||||
clrscr();
|
||||
|
||||
strchr(s,'V');
|
||||
if(p)
|
||||
printf("%s",p);
|
||||
else
|
||||
printf("Not Found!");
|
||||
|
||||
getchar();
|
||||
return 0;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
</pre>相关函数:<a href="memchr.html">memchr</a>
|
||||
|
||||
45
docs/c/strcmp.html
Normal file
45
docs/c/strcmp.html
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,45 @@
|
||||
<h1>字符串函数 - strcmp</h1>
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
<p>原型:extern int strcmp(char *s1,char * s2);</p>
|
||||
|
||||
<p>用法:#include <string.h></p>
|
||||
|
||||
<p>功能:比较字符串s1和s2。</p>
|
||||
|
||||
<p>说明:</p>
|
||||
当s1<s2时,返回值<0
|
||||
当s1=s2时,返回值=0
|
||||
当s1>s2时,返回值>0
|
||||
|
||||
举例:<pre>
|
||||
|
||||
// strcmp.c
|
||||
|
||||
#include <syslib.h>
|
||||
#include <string.h>
|
||||
|
||||
main()
|
||||
{
|
||||
char *s1="Hello, Programmers!";
|
||||
char *s2="Hello, programmers!";
|
||||
int r;
|
||||
|
||||
clrscr();
|
||||
|
||||
r=strcmp(s1,s2);
|
||||
if(!r)
|
||||
printf("s1 and s2 are identical");
|
||||
else
|
||||
if(r<0)
|
||||
printf("s1 less than s2");
|
||||
else
|
||||
printf("s1 greater than s2");
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
getchar();
|
||||
return 0;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
</pre>相关函数:<a href="bcmp.html">bcmp</a>,<a href="memcmp.html">memcmp</a>,<a href="stricmp.html">stricmp</a>,<a href="strncmp.html">strncmp</a>
|
||||
|
||||
45
docs/c/strcmpi.html
Normal file
45
docs/c/strcmpi.html
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,45 @@
|
||||
<h1>字符串函数 - strcmpi</h1>
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
<p>原型:extern int stricmp(char *s1,char * s2);</p>
|
||||
|
||||
<p>用法:#include <string.h></p>
|
||||
|
||||
<p>功能:比较字符串s1和s2,但不区分字母的大小写。</p>
|
||||
|
||||
<p>说明:strcmpi是到stricmp的宏定义,实际未提供此函数。</p>
|
||||
当s1<s2时,返回值<0
|
||||
当s1=s2时,返回值=0
|
||||
当s1>s2时,返回值>0
|
||||
|
||||
举例:<pre>
|
||||
|
||||
// stricmp.c
|
||||
|
||||
#include <syslib.h>
|
||||
#include <string.h>
|
||||
|
||||
main()
|
||||
{
|
||||
char *s1="Hello, Programmers!";
|
||||
char *s2="Hello, programmers!";
|
||||
int r;
|
||||
|
||||
clrscr();
|
||||
|
||||
r=stricmp(s1,s2);
|
||||
if(!r)
|
||||
printf("s1 and s2 are identical");
|
||||
else
|
||||
if(r<0)
|
||||
printf("s1 less than s2");
|
||||
else
|
||||
printf("s1 greater than s2");
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
getchar();
|
||||
return 0;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
</pre>相关函数:<a href="bcmp.html">bcmp</a>,<a href="strcmp.html">strcmp</a>,<a href="stricmp.html">stricmp</a>
|
||||
|
||||
32
docs/c/strcpy.html
Normal file
32
docs/c/strcpy.html
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,32 @@
|
||||
<h1>字符串函数 - strcpy</h1>
|
||||
|
||||
<p>原型:extern char *strcpy(char *dest,char *src);</p>
|
||||
<p>用法:#include <string.h></p>
|
||||
<p>功能:把src所指由NULL结束的字符串复制到dest所指的数组中。</p>
|
||||
<p>说明:src和dest所指内存区域不可以重叠且dest必须有足够的空间来容纳src的字符串。
|
||||
返回指向dest的指针。</p>
|
||||
|
||||
举例:
|
||||
|
||||
<pre>
|
||||
// strcpy.c
|
||||
|
||||
#include <syslib.h>
|
||||
#include <string.h>
|
||||
|
||||
main()
|
||||
{
|
||||
char *s="Golden Global View";
|
||||
char d[20];
|
||||
|
||||
clrscr();
|
||||
|
||||
strcpy(d,s);
|
||||
printf("%s",d);
|
||||
|
||||
getchar();
|
||||
return 0;
|
||||
}
|
||||
</pre>
|
||||
相关函数:<a href="memccpy.html">memccpy</a>,<a href="memcpy.html">memcpy</a>,<a href="stpcpy.html">stpcpy</a>,<a href="strdup.html">strdup</a>
|
||||
|
||||
36
docs/c/strcspn.html
Normal file
36
docs/c/strcspn.html
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,36 @@
|
||||
<h1>字符串函数 - strcspn</h1>
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
<p>原型:extern int strcspn(char *s1,char *s2);</p>
|
||||
|
||||
<p>用法:#include <string.h></p>
|
||||
|
||||
<p>功能:在字符串s1中搜寻s2中所出现的字符。</p>
|
||||
|
||||
<p>说明:返回第一个出现的字符在s1中的下标值,亦即在s1中出现而s2中没有出现的子串的长度。</p>
|
||||
|
||||
举例:<pre>
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
// strcspn.c
|
||||
|
||||
#include <syslib.h>
|
||||
#include <string.h>
|
||||
|
||||
main()
|
||||
{
|
||||
char *s="Golden Global View";
|
||||
char *r="new";
|
||||
int n;
|
||||
|
||||
clrscr();
|
||||
|
||||
n=strcspn(s,r);
|
||||
printf("The first char both in s1 and s2 is: %c",s[n]);
|
||||
|
||||
getchar();
|
||||
return 0;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
</pre>相关函数:<a href="strpbrk.html">strpbrk</a>
|
||||
|
||||
35
docs/c/strdup.html
Normal file
35
docs/c/strdup.html
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,35 @@
|
||||
<h1>字符串函数 - strdup</h1>
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
<p>原型:extern char *strdup(char *s);</p>
|
||||
|
||||
<p>用法:#include <string.h></p>
|
||||
|
||||
<p>功能:复制字符串s</p>
|
||||
|
||||
<p>说明:返回指向被复制的字符串的指针,所需空间由malloc()分配且可以由free()释放。</p>
|
||||
|
||||
举例:<pre>
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
// strdup.c
|
||||
|
||||
#include <syslib.h>
|
||||
#include <string.h>
|
||||
|
||||
main()
|
||||
{
|
||||
char *s="Golden Global View";
|
||||
char *d;
|
||||
|
||||
clrscr();
|
||||
|
||||
d=strdup(s);
|
||||
printf("%s",d);
|
||||
|
||||
getchar();
|
||||
return 0;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
</pre>相关函数:<a href="memccpy.html">memccpy</a>,<a href="memcpy.html">memcpy</a>,<a href="strcpy.html">strcpy</a>
|
||||
|
||||
45
docs/c/stricmp.html
Normal file
45
docs/c/stricmp.html
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,45 @@
|
||||
<h1>字符串函数 - stricmp</h1>
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
<p>原型:extern int stricmp(char *s1,char * s2);</p>
|
||||
|
||||
<p>用法:#include <string.h></p>
|
||||
|
||||
<p>功能:比较字符串s1和s2,但不区分字母的大小写。</p>
|
||||
|
||||
<p>说明:strcmpi是到stricmp的宏定义,实际未提供此函数。</p>
|
||||
当s1<s2时,返回值<0
|
||||
当s1=s2时,返回值=0
|
||||
当s1>s2时,返回值>0
|
||||
|
||||
举例:<pre>
|
||||
|
||||
// stricmp.c
|
||||
|
||||
#include <syslib.h>
|
||||
#include <string.h>
|
||||
|
||||
main()
|
||||
{
|
||||
char *s1="Hello, Programmers!";
|
||||
char *s2="Hello, programmers!";
|
||||
int r;
|
||||
|
||||
clrscr();
|
||||
|
||||
r=stricmp(s1,s2);
|
||||
if(!r)
|
||||
printf("s1 and s2 are identical");
|
||||
else
|
||||
if(r<0)
|
||||
printf("s1 less than s2");
|
||||
else
|
||||
printf("s1 greater than s2");
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
getchar();
|
||||
return 0;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
</pre>相关函数:<a href="bcmp.html">bcmp</a>,<a href="strcmp.html">strcmp</a>,<a href="stricmp.html">stricmp</a>
|
||||
|
||||
33
docs/c/strlen.html
Normal file
33
docs/c/strlen.html
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,33 @@
|
||||
<h1>字符串函数 - strlen</h1>
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
<p>原型:extern int strlen(char *s);</p>
|
||||
|
||||
<p>用法:#include <string.h></p>
|
||||
|
||||
<p>功能:计算字符串s的长度</p>
|
||||
|
||||
<p>说明:返回s的长度,不包括结束符NULL。</p>
|
||||
|
||||
举例:<pre>
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
// strlen.c
|
||||
|
||||
#include <syslib.h>
|
||||
#include <string.h>
|
||||
|
||||
main()
|
||||
{
|
||||
char *s="Golden Global View";
|
||||
|
||||
clrscr();
|
||||
|
||||
printf("%s has %d chars",s,strlen(s));
|
||||
|
||||
getchar();
|
||||
return 0;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
</pre>相关函数:无
|
||||
|
||||
33
docs/c/strlwr.html
Normal file
33
docs/c/strlwr.html
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,33 @@
|
||||
<h1>字符串函数 - strlwr</h1>
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
<p>原型:extern char *strlwr(char *s);</p>
|
||||
|
||||
<p>用法:#include <string.h></p>
|
||||
|
||||
<p>功能:将字符串s转换为小写形式</p>
|
||||
|
||||
<p>说明:只转换s中出现的大写字母,不改变其它字符。返回指向s的指针。</p>
|
||||
|
||||
举例:<pre>
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
// strlwr.c
|
||||
|
||||
#include <syslib.h>
|
||||
#include <string.h>
|
||||
|
||||
main()
|
||||
{
|
||||
char *s="Copywrite 1999-2000 GGV Technologies";
|
||||
|
||||
clrscr();
|
||||
|
||||
printf("%s",strlwr(s));
|
||||
|
||||
getchar();
|
||||
return 0;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
</pre>相关函数:<a href="strupr.html">strupr</a>
|
||||
|
||||
Some files were not shown because too many files have changed in this diff Show More
Loading…
x
Reference in New Issue
Block a user